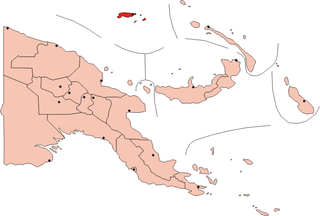
The Admiralty Islands are an archipelago group of 18 islands in the Bismarck Archipelago, to the north of New Guinea in the South Pacific Ocean. These are also sometimes called the Manus Islands, after the largest island.

The black flying fox or black fruit bat is a bat in the family Pteropodidae. It is among the largest bats in the world, but is considerably smaller than the largest species in its genus, Pteropus. The black flying fox is native to Australia, Papua New Guinea, and Indonesia. It is not a threatened species.
The angulate pipistrelle, also known as the New Guinea pipistrelle, is a species of vesper bat found in Papua New Guinea and the Solomon Islands.

The red-fronted lorikeet, also known as the red-spotted lorikeet or red-rumped lorikeet is a species of parrot in the family Psittaculidae. It is found in northern New Guinea and the island of Biak. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical moist montane forests.
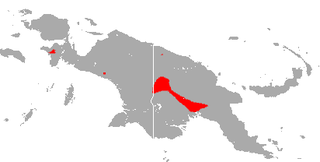
Wollaston's roundleaf bat is a species of bat in the family Hipposideridae. It is found in West Papua, Indonesia and Papua New Guinea. It was named after the explorer Sandy Wollaston.

The common tube-nosed fruit bat is a species of megabat in the family Pteropodidae. It is found at islands north of Australia, and in Indonesia, Papua New Guinea, the Philippines and the Solomon Islands.

The Banks flying fox is a species of megabat in the family Pteropodidae. It is endemic to Vanuatu. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical dry forests and subtropical or tropical swamps. These small fruit bats are about 15 cm. long with grey and brown on its head and back with a yellow-orange neck and yellow-gray bellies. Its diet consists of coconut flowers and Vaveli trees fruit since its home is tropical.

The small flying fox, island flying fox or variable flying fox is a species of flying fox in the family Pteropodidae. It is found in Australia, Cambodia, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Maldives, Myanmar, Papua New Guinea, the Philippines, the Solomon Islands, Thailand, and Vietnam.
The lesser flying fox or Sanborn's flying fox is a species of flying fox in the family Pteropodidae. It is found in Papua New Guinea and the Solomon Islands. The species is poorly known, but is believed to inhabit coastal lowlands, including tropical rainforest. Although the species has been found plantations, the habitat of the species is fragmented by increasing agriculture and logging.

The great flying fox, also known as the greater flying fox or Bismarck flying fox, is a species of megabat in the genus Pteropus, found throughout lowland areas of New Guinea and in the Bismarck Archipelago. Conflicting evidence suggests that its closest relative is either the spectacled flying fox or, jointly, the Pelew and insular flying foxes. Two subspecies are recognized. At up to 1.6 kg (3.5 lb) in weight, it is among the heaviest bats in the world and the largest bat in Melanesia. It is a gregarious animal which roosts with hundreds or thousands of individuals. In part due to its wide variation in color, it has many taxonomic synonyms, including Pteropus degener, Pteropus papuanus, and Pteropus sepikensis. It may forage during the day or night in search of fruit, including figs or fruits from the family Sapotaceae. It is considered a least-concern species by the IUCN, though its numbers have been negatively impacted by what appeared to be a disease, as well as by hunting for bushmeat that occurs across its range.

The Geelvink Bay flying fox or Geelvink Bay fruit bat is a species of flying fox in the family Pteropodidae. It is endemic to the islands of Yapen, Numfor, and Rani, which lie north of New Guinea in Indonesia's Papua Province. The name comes from Geelvink Bay, now Cenderawasih Bay.

The insular flying fox or Pacific flying fox is a species of flying fox in the family Pteropodidae. It is geographically widespread, the most widespread flying fox in the Pacific: it is found in American Samoa, the Cook Islands, Fiji, New Caledonia, Niue, Papua New Guinea, Samoa, the Solomon Islands, Tonga, and Vanuatu.

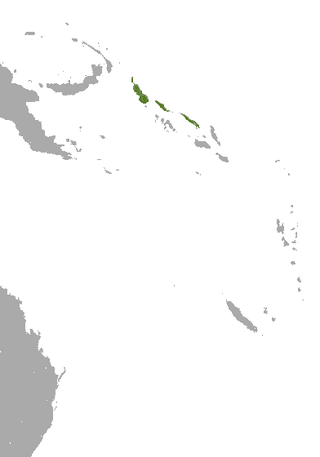
The Vanikoro flying fox, also known locally as the basapine, is a species of bat in the family Pteropodidae. It has only been found in the Vanikoro island group located in the southern Solomon Islands. The species as a whole was originally known from just a few specimens collected sometime before 1930 but following surveys conducted on the island in the early 1990s did not detect this species again causing the Vanikoro flying fox to be listed as extinct. However, the species was rediscovered by a survey conducted in late 2014 which indicated a population in the high hundreds or low thousands and reported all observations.

The Bougainville monkey-faced bat or Bougainville flying monkey is a megabat endemic to Bougainville Island of Papua New Guinea and Choiseul Island of the Solomon Islands in Melanesia. It inhabits mature forests in upland areas, within the Autonomous Region of Bougainville and Bougouriba Province.

The Bismarck masked flying fox is a species of flying fox in the family Pteropodidae found in Papua New Guinea and named after the Bismarck Archipelago. It was once considered a subspecies of Pteropus temminckii before being reassessed in 2001. This species has two subspecies, P. c. capistratus and P. c. ennisae. The IUCN classified it as Near Threatened in 2009, noting that the rate of decline is almost high enough to reclassify the species as Vulnerable.

Andersen's flying fox is a species of flying fox in the family Pteropodidae found in south Burma and west Thailand. Although it is hunted for both food and as a pest, it is not known if this has a significant impact on the species. It has been seen roosting in tall, well-established trees in urban areas and will fly several kilometres to eat wild and cultivated fruits. The species was named after Knud Christian Andersen. It was last recorded in Thailand in 1970 and, presumably, there is still a small viable population in Myanmar.

The Rennell flying fox is a species of flying fox found in the Solomon Islands. It is an endangered species risking extinction.

The big-eared flying fox is a species of bat in the family Pteropodidae, larger bats who subsist largely on fruits. The species is distributed across a range in Indonesia, Papua New Guinea and islands nearing the Cape York peninsula at the northeast of Australia, at elevations less than 500 metres and often in coastal mangroves.

Andersen's naked-backed fruit bat or Andersen's bare-backed fruit bat is a large cave-dwelling species of megabat in the family Pteropodidae. It is endemic to the Bismarck Archipelago including the Admiralty Islands in Papua New Guinea.




















