
Operation Chronicle was the Allied invasion of Woodlark and Kiriwina Islands, in the South West Pacific, during World War II. The operation was a subordinate action that formed part of the wider Operation Cartwheel, the advance towards Rabaul. An early planning name for this operation was Operation Coronet. Preliminary actions commenced on 23–24 June 1943 when small reconnaissance parties were landed on both islands. The main operation was executed without opposition on 30 June 1943. Around 16,800 personnel took part, divided into two forces. The United States Army provided the majority of ground troops, which were supported by a United States Marine Corps defense battalion as well as U.S. and Australian aircraft and naval vessels.

The New Britain campaign was a World War II campaign fought between Allied and Imperial Japanese forces. The campaign was initiated by the Allies in late 1943 as part of a major offensive which aimed to neutralise the important Japanese base at Rabaul, the capital of New Britain, and was conducted in two phases between December 1943 and the end of the war in August 1945.

The Battle of the Treasury Islands was a Second World War battle that took place between 27 October and 12 November 1943 on the Treasury Islands group, part of the Solomon Islands. The battle formed part of the wider Pacific War and involved New Zealand and US forces fighting against Japanese troops. The majority of the ground forces were provided by the New Zealand 3rd Division.

The Battle of the Green Islands or Operation Squarepeg was fought from 15 to 20 February 1944, between Imperial Japan and Allied forces from the New Zealand 3rd Division and the United States. Undertaken after landings to secure lodgments on New Britain and Bougainville, the main focus of the operation was the capture of Nissan Island, which was secured by New Zealand forces after only a short ground campaign. At only very limited cost in terms of casualties, the Allied operation resulted in the capture of several small atolls in the island chain, which were subsequently used to support air and naval operations focused on reducing the main Japanese base on Rabaul.

The Battle of Cape Gloucester was fought in the Pacific theater of World War II between Japanese and Allied forces on the island of New Britain, Territory of New Guinea, between 26 December 1943 and 16 January 1944. Codenamed Operation Backhander, the US landing formed part of the wider Operation Cartwheel, the main Allied strategy in the South West Pacific Area and Pacific Ocean Areas during 1943–1944. It was the second landing the US 1st Marine Division had conducted during the war thus far, after Guadalcanal. The objective of the operation was to capture the two Japanese airfields near Cape Gloucester that were defended by elements of the Japanese 17th Division.

The Battle of Vella Lavella was fought from 15 August – 6 October 1943 between the Empire of Japan and the Allied forces from New Zealand and the United States at the end of the New Georgia campaign. Vella Lavella, an island located in the Solomon Islands, had been occupied by Japanese forces early during the war in the Pacific. Following the Battle of Munda Point, the Allies recaptured the island in late 1943, following a decision to bypass a large concentration of Japanese troops on the island of Kolombangara.

The Battle of Arawe was fought between Allied and Japanese forces during the New Britain campaign of World War II. The battle formed part of the Allied Operation Cartwheel and had the objective of serving as a diversion before a larger landing at Cape Gloucester in late December 1943. The Japanese military was expecting an Allied offensive in western New Britain and was reinforcing the region at the time of the Allied landing in the Arawe area on 15 December 1943. The Allies secured Arawe after about a month of intermittent fighting with the outnumbered Japanese force.

The Admiralty Islands campaign was a series of battles in the New Guinea campaign of World War II in which the United States Army's 1st Cavalry Division took the Japanese-held Admiralty Islands.

When World War II broke out the United States Naval Construction Battalions (Seabees) did not exist. The logistics of a two theater war were daunting to conceive. Rear Admiral Moreell completely understood the issues. What needed to be done was build staging bases to take the war to the enemy, across both oceans, and create the construction force to do the work. Naval Construction Battalions were first conceived at Bureau of Yards and Docks (BuDocks) in the 1930s. The onset of hostilities clarified to Radm. Moreell the need for developing advance bases to project American power. The solution: tap the vast pool of skilled labor in the U.S. Put it in uniform to build anything, anywhere under any conditions and get the Marine Corps to train it. The first volunteers came skilled. To obtain these tradesmen, military age was waived to age 50. It was later found that several past 60 had managed to get in. Men were given advanced rank/pay based upon experience making the Seabees the highest paid group in the U.S. military. The first 60 battalions had an average age of 37.

The Landings at Cape Torokina, also known as Operation Cherryblossom, took place at the beginning of the Bougainville campaign in World War II. The amphibious landings were carried out by elements of the United States Marine Corps in November 1943 on Bougainville Island in the South Pacific, as part of Allied efforts to advance towards the main Japanese base around Rabaul under Operation Cartwheel. Coming in the wake of Allied successes at Guadalcanal and in the central Solomons, the landings were intended to secure a beachhead with the purpose of establishing several bases from which to project air and naval power closer towards Rabaul, in an effort to neutralize the large Japanese force that had been established there.

The Landing on Emirau was the last of the series of operations that made up Operation Cartwheel, General Douglas MacArthur's strategy for the encirclement of the major Japanese base at Rabaul. A force of nearly 4,000 United States Marines landed on the island of Emirau on 20 March 1944. The island was not occupied by the Japanese and there was no fighting. It was developed into an airbase which formed the final link in the chain of bases surrounding Rabaul. The isolation of Rabaul permitted MacArthur to turn his attention westward and commence his drive along the north coast of New Guinea toward the Philippines.

The Landing at Jacquinot Bay was an Allied amphibious operation undertaken on 4 November 1944 during the New Britain Campaign of World War II. The landing was conducted as part of a change in responsibility for Allied operations on New Britain. The Australian 5th Division, under Major General Alan Ramsay, took over from the US 40th Infantry Division, which was needed for operations in the Philippines. The purpose of the operation was to establish a logistics base at Jacquinot Bay on the south coast of New Britain to support the 5th Division's planned operations near the major Japanese garrison at Rabaul.
Emirau Airport is an airfield in Emirau Island, Papua New Guinea.

The 147th Regiment (Regional Training Institute) is a training regiment of the Ohio Army National Guard. Previously known as the 147th Infantry Regiment and the 6th Ohio Infantry, it has served in several American wars as a combat infantry unit, but now maintains the Ohio Regional Training Institute (RTI) in Columbus, Ohio. Its regimental motto is Cargoneek Guyoxim, which is a Chippewa language phrase meaning "Always Ready." The lineage of the regiment is carried by the 174th Air Defense Artillery Regiment.

Peleliu Naval Base was a major United States Navy sea and airbase base on Peleliu island, one of sixteen states of Palau. The United States Marine Corps took the island in the Battle of Peleliu during World War II. Battle of Peleliu was a costly conflict that started September 15, 1944, and ended November 27, 1944. On September 30, 1944, Peleliu is declared occupied. The taking of Peleliu and Morotai gave the sea and air protection needed for the later invasion of the Philippines. US Navy Seabee built a number of facilities at Peleliu Naval Base.

Naval Base Brisbane was a major United States Navy base built in the early part of World War II at Brisbane, Queensland, Australia. At first, operated as a base for patrol aircraft and convoy escort aircraft to protect the last leg of the Pacific War to the Southwest Pacific. As the US Navy expanded in the island hopping campaign, Naval Base Brisbane expanded to include a submarine base, repair depot, seaplane base and other facilities. US Navy operations started on April 14, 1942, and ended after the war in 1945.

Naval Base Banika Island was a United States Navy base built during World War II on Mbanika Island in the Russell Islands, part of the Solomon Islands. A larger supply depot was built to support the ships fighting in the Pacific War. Also built were a repair base for landing craft, PT boats, and other boats. Banika Island offered excellent fleet anchorage. Banika Island was taken during the Solomon Islands campaign. Also at the base was built the Renard Sound Seaplane Base.
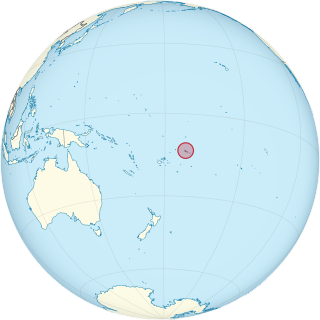
Naval Base Upolu was a naval base built by the United States Navy in 1942 to support the World War II effort. The base was located on Upolu Island, Samoa in the Western Pacific Ocean, part of the Samoan Islands's Naval Base Samoa. After the surprise attack on Naval Station Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941, the US Navy was in need of setting up more advance bases in the Pacific Ocean. At Naval Base Upolu the Navy built a sea port, an airbase and a seaplane base.

Naval Base Funafuti was a naval base built by the United States Navy in 1942 to support the World War II effort. The base was located on the Island of Funafuti of the Ellice Islands in the Western Pacific Ocean. The island is now Tuvalu, an island country in the Polynesian. After the surprise attack on Naval Station Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941, the US Navy was in need of setting up more advance bases in the Pacific Ocean. At Naval Base Funafuti the Navy built a sea port, a small hospital, PT boat base, a seaplane base and an airbase. The United States Marine Corps landed on Funafuti on 2 October 1942 and on Nanumea and Nukufetau in August 1943. The Japanese had already occupied Tarawa and other islands in what is now Kiribati, but were delayed by the losses at the Battle of the Coral Sea.

Naval Base Majuro was a major United States Navy base built on Majuro Atoll, in the Marshall Islands to support the World War II efforts in the Pacific War. The base was built after the Battle of Majuro-Kwajalein ended 3 February 1944. Majuro was found to be unoccupied and abandoned when the United States Army arrived. The US Navy built airfields, a seaport, and other facilities on the captured islands. The base was part of the vast Naval Base Marshall Islands.




















