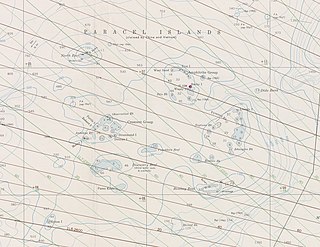
The Paracel Islands, also known as the Xisha Islands and the Hoàng Sa Archipelago, are a disputed archipelago in the South China Sea currently under de facto administration by the People's Republic of China.

The Sulu Sea is a body of water in the southwestern area of the Philippines, separated from the South China Sea in the northwest by Palawan and from the Celebes Sea in the southeast by the Sulu Archipelago. Borneo is found to the southwest and Visayas to the northeast.

Farallón de Pájaros, also known as Uracus or Urracas, is a small (2.3 km2) uninhabited volcanic island, the northernmost island and also farthest west in the Northern Mariana Islands chain.

Necker Island is a small island in the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands. It is located at 23°34′30″N164°42′01″W in the Pacific Ocean, 430 miles northwest of Honolulu, Hawaii, 155 miles northwest of Nihoa, and 8 miles north of the Tropic of Cancer. It is part of the state of Hawaii in the United States. It contains important prehistoric archaeological sites of the Hawaiian culture and is part of the Hawaiian Islands National Wildlife Refuge within the Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument.

The Pearl and Hermes Atoll, also known as Pearl and Hermes Reef, is part of the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands, a group of small islands and atolls that form the farthest northwest portion of the Hawaiian island chain. The atoll consists of a variable number of flat and sandy islets, typically between five and seven. More were noted in historical sources but have since been lost to erosion and rising sea levels.
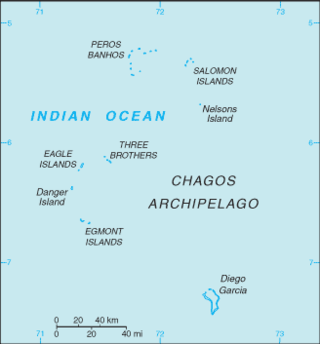
The British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT) is an archipelago of 55 islands in the Indian Ocean, located south of India. It is situated approximately halfway between Africa and Indonesia. The islands form a semicircular group with an open sea towards the east. The largest, Diego Garcia, is located at the southern extreme end. It measures 60 square kilometres (23 sq mi) and accounts for almost three-quarters of the total land area of the territory. Diego Garcia is the only inhabited island and is home to the joint UK-US naval support facility. Other islands within the archipelago include Danger Island, Three Brothers Islands, Nelson Island, and Peros Banhos, as well as the island groups of the Egmont Islands, Eagle Islands, and the Salomon Islands.

The Great Chagos Bank, in the Chagos Archipelago, about 500 km (310 mi) south of Maldives, is the largest atoll structure in the world, with a total area of 12,642 km2 (4,881 sq mi). The atoll is administered by the United Kingdom through the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT).

Maug consists of a group of three small uninhabited islands. This island group is part of the Northern Islands Municipality of the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands, itself part of the Marianas archipelago in the Oceanian sub-region of Micronesia.

Sarigan or Sariguan is an uninhabited volcanic island in the Pacific Ocean. It is part of the Northern Mariana Islands, a U.S. territory. Sarigan is located 37 kilometers (20 nmi) northeast of Anatahan island, 67 km (36 nmi) south of Guguan and 150 km (81 nmi) north of Saipan, the largest island in the Northern Marianas. The island has been sparsely populated, but in modern times has been uninhabited due to volcanic activity. It is a currently a nature preserve.

Pana Tinani is an island in the Louisiade Archipelago in Milne Bay Province, Papua New Guinea.

Pocklington Reef is a coral reef and a mostly submerged atoll in the far southeast of Papua New Guinea.

The Deboyne Islands are an atoll, composed of a group of reefs and islands in the north of the Louisiade Archipelago, Papua New Guinea.

Nigehörn is an uninhabited artificial island in the North Sea belonging to the German city of Hamburg.

The Duchateau Islands are an island group in the Coral Sea, belonging to Papua New Guinea. They lie to the east of Panarairai Island in the Louisiade Archipelago.
The Calvados Chain are a group of islands in the Solomon Sea, belonging to Papua New Guinea within the Louisiade Archipelago.

The Jomard Islands are an uninhabited island group in the Coral Sea, belonging to Papua New Guinea, It lies to the east of Montemont Islands in the Louisiade Archipelago.
The Laseinie Islands are an archipelago in the Solomon Sea. Politically they belong to Bwanabwana Rural LLG of Samarai-Murua District of Milne Bay Province, in the southeastern region of Papua New Guinea. They are located southeast of the D'Entrecasteaux Islands. They are part of the Louisiade Archipelago.

Makada is an island in the Duke of York Islands archipelago in Papua New Guinea. It is located in the east of the country, in the East New Britain Province, about 800 km to the east of the Port Moresby.
On the morning of March 13, 1888, an explosion took place on Ritter Island, a small volcanic island in the Bismarck and Solomon Seas, between New Britain and Umboi Island. The explosion resulted in the collapse of most of the island and generated a tsunami with runups of up to 15 meters (49 ft) that caused damage more than 700 kilometers (430 mi) away and killed anywhere between 500 and 3,000 on neighboring islands, including scientists and explorers. This event is the largest volcanic island sector collapse in recent history.
















