
Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is a country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and its offshore islands in Melanesia. It shares its only land border with Indonesia to the west and its other close neighbors are Australia to the south and the Solomon Islands to the east. Its capital, located on its southern coast, is Port Moresby. The country is the world's third largest island country, with an area of 462,840 km2 (178,700 sq mi).

Melanesia is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from New Guinea in the west to the Fiji Islands in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea.

Bougainville, officially the Autonomous Region of Bougainville, is an autonomous region in Papua New Guinea. The largest island is Bougainville Island, while the region also includes Buka Island and a number of outlying islands and atolls. The current capital is Buka, situated on Buka Island.

Bougainville Island is the main island of the Autonomous Region of Bougainville, which is part of Papua New Guinea. Its land area is 9,300 km2 (3,600 sq mi). The population of the whole province, including nearby islets such as the Carterets, is approximately 300,000. The highest point is Mount Balbi, on the main island, at 2,715 m (8,907 ft).
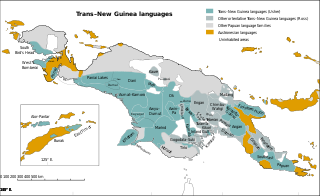
Trans–New Guinea (TNG) is an extensive family of Papuan languages spoken on the island of New Guinea and neighboring islands, a region corresponding to the country Papua New Guinea as well as parts of Indonesia.

The Papuan languages are the non-Austronesian languages spoken on the western Pacific island of New Guinea, as well as neighbouring islands in Indonesia, Solomon Islands, and East Timor. It is a strictly geographical grouping, and does not imply a genetic relationship.

Western New Guinea, also known as Papua, Indonesian New Guinea, and Indonesian Papua, is the western half of the island of New Guinea, formerly Dutch and granted to Indonesia in 1962. Given the island is alternatively named Papua, the region is also called West Papua.

The approximately 450 Oceanic languages are a branch of the Austronesian languages. The area occupied by speakers of these languages includes Polynesia, as well as much of Melanesia and Micronesia. Though covering a vast area, Oceanic languages are spoken by only two million people. The largest individual Oceanic languages are Eastern Fijian with over 600,000 speakers, and Samoan with an estimated 400,000 speakers. The Gilbertese (Kiribati), Tongan, Tahitian, Māori and Tolai languages each have over 100,000 speakers. The common ancestor which is reconstructed for this group of languages is called Proto-Oceanic.
The Kol language is a language spoken in eastern New Britain island, Papua New Guinea. There are about 4000 speakers in Pomio District of East New Britain Province, mostly on the southern side of New Britain island.

The Yawa languages, also known as Yapen languages, are a small family of two closely related Papuan languages, Yawa and Saweru, which are often considered to be divergent dialects of a single language. They are spoken on central Yapen Island and nearby islets, in Cenderawasih Bay, Indonesian Papua, which they share with the Austronesian Yapen languages.

The Central Solomon languages are the four Papuan languages spoken in the state of Solomon Islands.

Papua New Guinea, a sovereign state in Oceania, is the most linguistically diverse country in the world. According to Ethnologue, there are 840 living languages spoken in the country. In 2006, Papua New Guinea Prime Minister Sir Michael Somare stated that "Papua New Guinea has 832 living languages ."

New Guinea is the world's second-largest island, with an area of 785,753 km2 (303,381 sq mi). Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the 150-kilometre wide Torres Strait, though both landmasses lie on the same continental shelf, and were united during episodes of low sea level in the Pleistocene glaciations as the combined landmass of Sahul. Numerous smaller islands are located to the west and east. The island's name was given by Spanish explorer Yñigo Ortiz de Retez during his maritime expedition of 1545 due to the resemblance of the indigenous peoples of the island to those in the African region of Guinea.
The Seimat language is one of three Western Admiralty Islands languages, the other two being Wuvulu-Aua and the extinct Kaniet. The language is spoken by approximately 1000 people on the Ninigo and the Anchorite Islands in western Manus Province of Papua New Guinea. It has subject–verb–object (SVO) word order.

The Tiang language, also known as Djaul, is a language spoken in Papua New Guinea.
Yakamul, also known as Kap or Ali, is an Austronesian language spoken in East Aitape Rural LLG, Sandaun Province, Papua New Guinea. It is spoken in the village of Yakamul on the north coast and on the islands of Ali, Angel, and Seleo islands.

The Papuan Peninsula, also known as the Bird's Tail Peninsula, is a large peninsula in Papua New Guinea, southeast of the city of Lae, that makes up the southeastern portion of the island of New Guinea. The peninsula is the easternmost extent of the New Guinea Highlands and consists largely of the Owen Stanley Range, with peaks such as Mount Victoria and Mount Suckling. On the south coast is Port Moresby, the capital and largest city of Papua New Guinea.
Gumawana is an Austronesian language spoken by people living on the Amphlett Islands of the Milne Bay Province of Papua New Guinea.
Tumleo is an Austronesian language of coastal Sandaun Province, Papua New Guinea, on Tumleo Island and the Aitape coast in East Aitape Rural LLG.
Mwatebu is an Austronesian language spoken in a single village in the D'Entrecasteaux Islands of Papua New Guinea. It is spoken in the single village of Mwatebu in Duau Rural LLG, Milne Bay Province.
















