
Jellyfish, also known as sea jellies, are the medusa-phase of certain gelatinous members of the subphylum Medusozoa, which is a major part of the phylum Cnidaria.

Box jellyfish are cnidarian invertebrates distinguished by their box-like body. Some species of box jellyfish produce potent venom delivered by contact with their tentacles. Stings from some species, including Chironex fleckeri, Carukia barnesi, Malo kingi, and a few others, are extremely painful and often fatal to humans.

Hydrozoa is a taxonomic class of individually very small, predatory animals, some solitary and some colonial, most of which inhabit saline water. The colonies of the colonial species can be large, and in some cases the specialized individual animals cannot survive outside the colony. A few genera within this class live in freshwater habitats. Hydrozoans are related to jellyfish and corals and belong to the phylum Cnidaria.

In zoology, a tentacle is a flexible, mobile, and elongated organ present in some species of animals, most of them invertebrates. In animal anatomy, tentacles usually occur in one or more pairs. Anatomically, the tentacles of animals work mainly like muscular hydrostats. Most forms of tentacles are used for grasping and feeding. Many are sensory organs, variously receptive to touch, vision, or to the smell or taste of particular foods or threats. Examples of such tentacles are the eyestalks of various kinds of snails. Some kinds of tentacles have both sensory and manipulatory functions.

The lion's mane jellyfish, also known as the giant jellyfish, arctic red jellyfish, or the hair jelly, is one of the largest known species of jellyfish. Its range is confined to cold, boreal waters of the Arctic, northern Atlantic, and northern Pacific Oceans. It is common in the English Channel, Irish Sea, North Sea, and in western Scandinavian waters south to Kattegat and Øresund. It may also drift into the southwestern part of the Baltic Sea. Similar jellyfish – which may be the same species – are known to inhabit seas near Australia and New Zealand. The largest recorded specimen was measured off the coast of Massachusetts in 1865 and had a bell with a diameter of 210 centimetres and tentacles around 36.6 m (120 ft) long. Lion's mane jellyfish have been observed below 42°N latitude for some time in the larger bays of the East Coast of the United States.

Aequorea victoria, also sometimes called the crystal jelly, is a bioluminescent hydrozoan jellyfish, or hydromedusa, that is found off the west coast of North America.

Pelagia noctiluca is a jellyfish in the family Pelagiidae and the only currently recognized species in the genus Pelagia. It is typically known in English as the mauve stinger, but other common names are purple-striped jelly, purple stinger, purple people eater, purple jellyfish, luminous jellyfish and night-light jellyfish. In Greek, pelagia means "(she) of the sea", from pelagos "sea, open sea"; in Latin noctiluca is the combining form of nox, "night"", and lux, "light"; thus, Pelagia noctiluca can be described as a marine organism with the ability to glow in the dark (bioluminescence). It is found worldwide in tropical and warm temperate seas, although it is suspected that records outside the North Atlantic region, which includes the Mediterranean and Gulf of Mexico, represent closely related but currently unrecognized species.
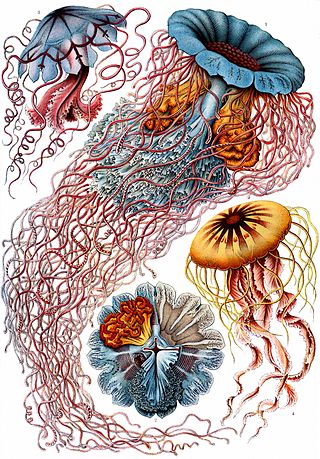
Discomedusae is a subclass of jellyfish in the class Scyphozoa. It is the sister taxon of Coronamedusae. Discomedusae contains about 155 named species and there are likely to be many more as yet undescribed. Jellyfish in this subclass are much more likely to have swarming events or form blooms than those in Coronamedusae. Discomedusae consists of two orders, Rhizostomeae and Semaeostomeae.

Turritopsis dohrnii, also known as the immortal jellyfish, is a species of small, biologically immortal jellyfish found worldwide in temperate to tropic waters. It is one of the few known cases of animals capable of reverting completely to a sexually immature, colonial stage after having reached sexual maturity as a solitary individual. Others include the jellyfish Laodicea undulata and species of the genus Aurelia.

Chrysaora hysoscella, the compass jellyfish, is a common species of jellyfish that inhabits coastal waters in temperate regions of the northeastern Atlantic Ocean, including the North Sea and Mediterranean Sea. In the past it was also recorded in the southeastern Atlantic, including South Africa, but this was caused by confusion with close relatives; C. africana, C. fulgida and an undescribed species tentatively referred to as "C. agulhensis".

Narcomedusae is an order of hydrozoans in the subclass Trachylinae. Members of this order do not normally have a polyp stage. The medusa has a dome-shaped bell with thin sides. The tentacles are attached above the lobed margin of the bell with usually a gastric pouch above each. There are no bulbs on the tentacles and no radial canals. Narcomedusans are mostly inhabitants of the open sea and deep waters. They can be found in the Mediterranean in large numbers.

Cydippida is an order of comb jellies. They are distinguished from other comb jellies by their spherical or oval bodies, and the fact their tentacles are branched, and can be retracted into pouches on either side of the pharynx. The order is not monophyletic, that is, more than one common ancestor is believed to exist.

Bathykorus bouilloni is a species of hydrozoan first described in 2010. It is a deep-sea species found in the Arctic Ocean, and appears to be common at depths below 1,000 m (3,300 ft). It is the only species in the monotypic genus Bathykorus. The genus name comes from the Greek bathy meaning "deep" and korus meaning "helmet", referring to the depth at which this species is found and to the shape of the bell. Its helmet-like appearance bears a resemblance to the helmet of Darth Vader, giving it the nickname Darth Vader jellyfish. The specific name is in honour of Dr. Jean Bouillon, (1926–2009), a marine zoologist.
Vallentinia gabriellae, the hitch-hiking jellyfish, is a species of small, inconspicuous hydrozoan in the family Olindiidae. It is endemic to a few isolated parts of the western Atlantic Ocean. It is elusive in the wild but sometimes makes its appearance unexpectedly in seawater cultures of other organisms in the laboratory.

Olindias is a genus of hydrozoans in the family Olindiidae.
Maeotias is a genus of hydrozoans in the family Olindiidae. It is a monotypic genus with only a single species, Maeotias marginata, commonly known as the Black Sea jellyfish or brackish water hydromedusa and often referred to as Maeotias inexpectata in the literature. It was first described from the Don and Kuban estuaries of the Sea of Azov, and also occurs in the Black Sea, all of which are areas of low salinity. It has been recorded in several other estuarine locations around the world and is regarded as an invasive species.

Carybdea marsupialis is a venomous species of box jellyfish, in the small family Carybdeidae within the class Cubozoa.

Cyanea nozakii or Cyanea nozaki (misspelling), commonly known as the ghost jellyfish, is a species of jellyfish found in the northern Pacific Ocean near the coasts of China and Japan. Along with other species of large jellyfish, it is showing a greater tendency to appear in large numbers and cause blooms.

The thimble jellyfish is a species of cnidarian found in the warm West Atlantic Ocean, including the Caribbean. It is a tiny jellyfish with a straight-sided, flat-topped bell. This jellyfish is the most common cause of seabather's eruption, a reaction caused by the injection of juvenile jellyfish nematocysts into human skin.
Euplokamis is a genus of ctenophores, or comb jellies, belonging to the monotypic family Euplokamididae. It shares the common name sea gooseberry with species of the genus Pleurobrachia. Despite living for hundreds of millions of years in marine environments, there is minimal research regarding Euplokamis, because they are uncommon. Research on the evolution of the basic body structures of diploblastic metazoans revealed that there are four major phyla, including the Ctenophores. Although the morphology of Euplokamis often resembles the medusa stage of Cnidarians, their eight rows of combs are one distinguishing feature that led to the official classification of Ctenophores. After being originally described by Chun (1879), the family Euplokamididae was expanded by Mills (1987) due to the discovery of a new species, Euplokamis dunlapae. Further research indicated that Euplokamis should be identified from Mertensiidae due to the rows of combs and some compression. They may also be distinguished from the genus Pleurobrachia due to their more elongated shape. Additionally, various adaptations of Euplokamis have been observed such as the use of tentacles for movement/feeding, a complex nervous system, and bioluminescent capabilities. Other characteristics including a defined mesoderm, lack of stinging cells, developmental differences, and symmetry supported the reclassification of these organisms.

















