
Canada has a vast geography that occupies much of the continent of North America, sharing a land border with the contiguous United States to the south and the U.S. state of Alaska to the northwest. Canada stretches from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west; to the north lies the Arctic Ocean. Greenland is to the northeast with a shared border on Hans Island. To the southeast Canada shares a maritime boundary with France's overseas collectivity of Saint Pierre and Miquelon, the last vestige of New France. By total area, Canada is the second-largest country in the world, after Russia. By land area alone, however, Canada ranks fourth, the difference being due to it having the world's largest proportion of fresh water lakes. Of Canada's thirteen provinces and territories, only two are landlocked while the other eleven all directly border one of three oceans.

The Continental Divide of the Americas is the principal, and largely mountainous, hydrological divide of the Americas. The Continental Divide extends from the Bering Strait to the Strait of Magellan, and separates the watersheds that drain into the Pacific Ocean from those river systems that drain into the Atlantic and Arctic Ocean, including those that drain into the Gulf of Mexico, the Caribbean Sea, and Hudson Bay.

The Pacific Coast Ranges are the series of mountain ranges that stretch along the West Coast of North America from Alaska south to Northern and Central Mexico. Although they are commonly thought to be the westernmost mountain range of the continental United States and Canada, the geologically distinct Insular Mountains of Vancouver Island lie farther west.

The Canadian Rockies or Canadian Rocky Mountains, comprising both the Alberta Rockies and the British Columbian Rockies, is the Canadian segment of the North American Rocky Mountains. It is the easternmost part of the Canadian Cordillera, which is the northern segment of the North American Cordillera, the expansive system of interconnected mountain ranges between the Interior Plains and the Pacific Coast that runs northwest–southeast from central Alaska to the Isthmus of Tehuantepec in Mexico.
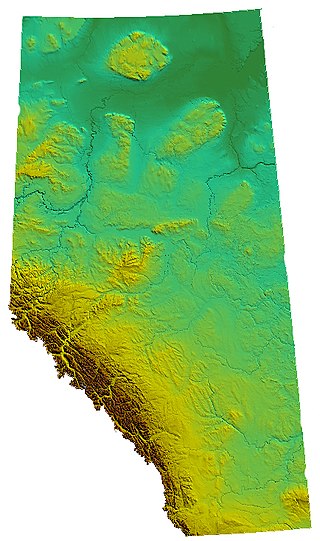
Alberta is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. Located in Western Canada, the province has an area of 661,190 km2 (255,290 sq mi) and is bounded to the south by the United States state of Montana along 49° north for 298 km (185 mi); to the east at 110° west by the province of Saskatchewan for 1,223 km (760 mi); and at 60° north the Northwest Territories for 644 km (400 mi). The southern half of the province borders British Columbia along the Continental Divide of the Americas on the peaks of the Rocky Mountains, while the northern half borders British Columbia along the 120th meridian west. Along with Saskatchewan it is one of only two landlocked provinces or territories.
The Missouri Coteau, or Missouri Plateau, is a large plateau that stretches along the eastern side of the valley of the Missouri River in central North Dakota and north-central South Dakota in the United States. In the Canadian provinces of Saskatchewan and Alberta this physiographic region is classified as the Uplands Missouri Coteau, which is a part of the Great Plains Province or Alberta Plateau Region, which extends across the southwest corner of the province of Saskatchewan as well as the southeast corner of the province of Alberta. Historically, in Canada the area was known as the Palliser's Triangle and regarded as an extension of the Great American Desert and unsuitable for agriculture and thus designated by Canadian geographer and explorer John Palliser. The terrain of the Missouri Coteau features low hummocky, undulating, rolling hills, potholes, and grasslands. Apart from being a geographical area, the Missouri Coteau also has a cultural connection to the people of the area, the Métis people of South Dakota, along with other Indigenous groups. The history of this plateau is large, and the Missouri Coteau has a significance to these people.
The Highland Rim is a geographic term for the area in Tennessee, North Alabama, and Kentucky which surrounds the Central Basin. Geologically, the Central Basin is a dome. The Highland Rim is a cuesta surrounding the basin, and the border where the difference in elevation is sharply pronounced is an escarpment.
The Pacific Cordillera, also known as the Western Cordillera or simply The Cordillera, is a top-level physiographic region of Canada, referring mainly to the extensive cordillera system in Western and Northwestern Canada that constitutes the northern part of the North American Cordillera. The mountain ranges in this region were covered during the Pleistocene by the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, the extent of which gives perspective on the geographic extent of this region. The cordillera extends from the Alaska's Brooks and Alaska Ranges, southeast through most of the Yukon and British Columbia as well as the southwestern fringe of Northwest Territories and Alberta, to stretch its margin beyond the Canada–United States border with five extensive lobes reaching into the mountain valleys of Montana and Washington.

The North American Cordillera, sometimes also called the Western Cordillera of North America, the Western Cordillera, or the Pacific Cordillera, is the North American portion of the American Cordillera, the mountain chain system along the Pacific coast of the Americas. The North American Cordillera covers an extensive area of mountain ranges, intermontane basins, and plateaus in Western and Northwestern Canada, Western United States, and Mexico, including much of the territory west of the Great Plains.

Westlock County is a municipal district in central Alberta, Canada that is north of Edmonton. The county was formerly known as the Municipal District of Westlock No. 92, and was created in 1943 from the merger of five smaller municipal districts.

The Okanagan Highland is an elevated hilly plateau area in British Columbia, Canada, and the U.S. state of Washington. Rounded mountains with elevations up to 8,000 ft (2,400 m) above sea level and deep, narrow valleys are characteristic of the region.

The Spectrum Range, formerly gazetted as the Spectrum Mountains and the Rainbow Mountains, is a small mountain range in Cassiar Land District of northwestern British Columbia, Canada. Located at the southern end of the Tahltan Highland, it borders the Skeena Mountains in the east and the Boundary Ranges of the Coast Mountains in the west. The Spectrum Range is surrounded by the Arctic Lake Plateau in the southwest and the Kitsu Plateau in the northwest, both of which contain volcanic features such as cinder cones. It lies at the southern end of the Mount Edziza volcanic complex which includes the two neighbouring plateaus as well as Mount Edziza and the Big Raven Plateau to the north. The mountain range is drained on all sides by streams within the Stikine River watershed and, unlike Mount Edziza to the north, contains relatively small separate glaciers. Mount Edziza Provincial Park is the main protected area surrounding the Spectrum Range.

Northern Alberta is a geographic region located in the Canadian province of Alberta.

Nahta Cone is a small cinder cone in Cassiar Land District of northwestern British Columbia, Canada. It has an elevation of 1,670 metres and lies near the northern edge of the Arctic Lake Plateau, a glacially scored plateau of the Tahltan Highland which in turn extends along the western side of the Stikine Plateau. The cone is about 70 kilometres south-southeast of the community of Telegraph Creek and lies in the southwestern corner of Mount Edziza Provincial Park, one of the largest provincial parks in British Columbia.

The Mount Edziza volcanic complex is a group of volcanoes and associated lava flows in northwestern British Columbia, Canada. Located on the Tahltan Highland, it is 40 kilometres southeast of Telegraph Creek and 85 kilometres southwest of Dease Lake. The complex encompasses a broad, steep-sided lava plateau that extends over 1,000 square kilometres. Its highest summit is 2,786 metres in elevation, making the MEVC the highest of four large complexes in an extensive north–south trending volcanic region. It is obscured by an ice cap characterized by several outlet glaciers that stretch out to lower altitudes.

The Peace River Formation is a stratigraphical unit of middle Albian age in the Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin.

The Mess Creek Escarpment is a long, discontinuous cliff along Mess Creek in Cassiar Land District of northwestern British Columbia, Canada. It forms the east-central side of Mess Creek valley and consists of two segments separated about 5 kilometres by Walkout Creek valley. The northern segment extends about 8 kilometres southeast along the southwestern side of the Big Raven Plateau while the southern segment extends generally south along the northwestern, western and southwestern edges of the Kitsu Plateau for about 10 kilometres. With an elevation of more than 1,700 metres, the Mess Creek Escarpment rises more than 910 metres above the floor of Mess Creek valley. The escarpment lies within the boundaries of Mount Edziza Provincial Park.

The Fraser Lowland is a landform and physiographic region in the Pacific Northwest of North America, shared between the Canadian province of British Columbia and the U.S. state of Washington. The region includes much of the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia, and the coastal plains of Washington's Whatcom County. As a physiographic region, the Fraser Lowland is part of the Georgia Depression, which in turn is part of the Coastal Trough.
Hubert Lake Wildland Provincial Park is a wildland provincial park in central Alberta, Canada. The park was established on 4 October 2000 and has an area of 9,665.46 hectares. The park is included in the Upper Athabasca Region Land Use Framework.

















