
Allantoin is a chemical compound with formula C4H6N4O3. It is also called 5-ureidohydantoin or glyoxyldiureide. It is a diureide of glyoxylic acid. Allantoin is a major metabolic intermediate in most organisms including animals, plants and bacteria. It is produced from uric acid, which itself is a degradation product of nucleic acids, by action of urate oxidase (uricase). Allantoin also occurs as a natural mineral compound (IMA symbol Aan).

The enzyme urate oxidase (UO), uricase or factor-independent urate hydroxylase, absent in humans, catalyzes the oxidation of uric acid to 5-hydroxyisourate:
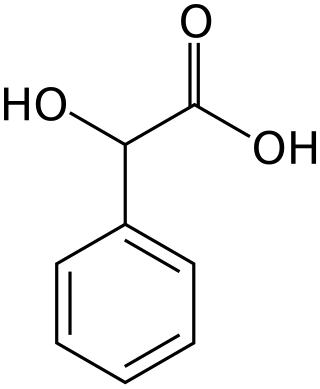
Mandelic acid is an aromatic alpha hydroxy acid with the molecular formula C6H5CH(OH)CO2H. It is a white crystalline solid that is soluble in water and polar organic solvents. It is a useful precursor to various drugs. The molecule is chiral. The racemic mixture is known as paramandelic acid.
Mandelate racemase is a bacterial enzyme which catalyzes the interconversion of the enantiomers of mandelate via an enol intermediate. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

The enzyme phenylalanine racemase is the enzyme that acts on amino acids and derivatives. It activates both the L & D stereo isomers of phenylalanine to form L-phenylalanyl adenylate and D-phenylalanyl adenylate, which are bound to the enzyme. These bound compounds are then transferred to the thiol group of the enzyme followed by conversion of its configuration, the D-isomer being the more favorable configuration of the two, with a 7 to 3 ratio between the two isomers. The racemisation reaction of phenylalanine is coupled with the highly favorable hydrolysis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to adenosine monophosphate (AMP) and pyrophosphate (PP), thermodynamically allowing it to proceed. This reaction is then drawn forward by further hydrolyzing PP to inorganic phosphate (Pi), via Le Chatelier's principle.

Methylmalonyl CoA epimerase is an enzyme involved in fatty acid catabolism that is encoded in human by the "MCEE" gene located on chromosome 2. It is routinely and incorrectly labeled as "methylmalonyl-CoA racemase". It is not a racemase because the CoA moiety has 5 other stereocenters.
Serine racemase is the first racemase enzyme in human biology to be identified. This enzyme converts L-serine to its enantiomer form, D-serine. D-serine acts as a neuronal signaling molecule by activating NMDA receptors in the brain.
In enzymology, an acetoin racemase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, an alanine racemase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

α-Methylacyl-CoA racemase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AMACR gene. AMACR catalyzes the following chemical reaction:
In enzymology, an amino-acid racemase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, glutamate racemase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a maleate isomerase, or maleate cis-tran isomerase, is a member of the Asp/Glu racemase superfamily discovered in bacteria. It is responsible for catalyzing cis-trans isomerization of the C2-C3 double bond in maleate to produce fumarate, which is a critical intermediate in citric acid cycle. The presence of an exogenous mercaptan is required for catalysis to happen.
In enzymology, a proline racemase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a tartrate epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphodiester α-N-acetylglucosaminidase (EC 3.1.4.45) catalyzes the reaction
Allantoicase is an enzyme (EC 3.5.3.4) that in humans is encoded by the ALLC gene. Allantoicase catalyzes the chemical reaction
In molecular biology 2-oxo-4-hydroxy-4-carboxy-5-ureidoimidazoline decarboxylase EC 4.1.1.n1 is an enzyme involved in purine catabolism. It catalyses the decarboxylation of 2-oxo-4-hydroxy-4-carboxy-5-ureidoimidazoline (OHCU) into S(+)-allantoin. It is the third step of the conversion of uric acid to allantoin. Step one is catalysed by urate oxidase and step two is catalysed by hydroxyisourate hydrolase.
Hydantoin racemase is an enzyme with systematic name D-5-monosubstituted-hydantoin racemase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction











