
Kluane National Park and Reserve are two protected areas in the southwest corner of the territory of Yukon. The National Park Reserve was set aside in 1972 to become a national park, pending settlement of First Nations land claims. It covered an area of 22,013 square kilometres. When agreement was reached with the Champagne and Aishihik First Nations over an eastern portion of the Reserve, that part—about 5,900 square kilometres —became a national park in 1993, and is a unit of the national park system administered co-operatively with Parks Canada. The larger western section remains a Reserve, awaiting a final land claim settlement with the Kluane First Nation. The park borders British Columbia to the south, while the Reserve borders both British Columbia to the south, and the United States (Alaska) to the south and west.

Alsek River is a wilderness river flowing from Yukon into Northern British Columbia and into Alaska. It enters the Gulf of Alaska at Dry Bay.

An ice field is a mass of interconnected valley glaciers on a mountain mass with protruding rock ridges or summits. They are often found in the colder climates and higher altitudes of the world where there is sufficient precipitation for them to form. The higher peaks of the underlying mountain rock that protrude through the icefields are known as nunataks. Ice fields are larger than alpine glaciers, but smaller than ice caps and ice sheets. The topography of ice fields is determined by the shape of the surrounding landforms, while ice caps have their own forms overriding underlying shapes.
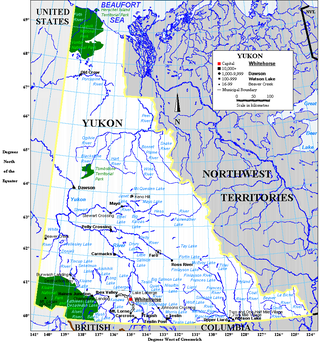
Yukon is in the northwestern corner of Canada and is bordered by Alaska, British Columbia and the Northwest Territories. The sparsely populated territory abounds with natural scenery, snowmelt lakes and perennial white-capped mountains, including many of Canada's highest mountains. The territory's climate is Arctic in territory north of Old Crow, subarctic in the region, between Whitehorse and Old Crow, and humid continental climate south of Whitehorse and in areas close to the British Columbia border. Most of the territory is boreal forest with tundra being the main vegetation zone only in the extreme north and at high elevations.

Tatshenshini-Alsek Park or Tatshenshini-Alsek Provincial Wilderness Park is a provincial park in British Columbia, Canada. The park is 9,580 km2 (3,700 sq mi) in size. It was established in 1993 after an intensive campaign by Canadian and American conservation organizations to halt mining exploration and development in the area, and protect the area for its strong natural heritage and biodiversity values.

The Boundary Ranges, also known in the singular and as the Alaska Boundary Range, are the largest and most northerly subrange of the Coast Mountains. They begin at the Nass River, near the southern end of the Alaska Panhandle in the Canadian province of British Columbia and run to the Kelsall River, near the Chilkoot Pass, beyond which are the Alsek Ranges of the Saint Elias Mountains, and northwards into the Yukon Territory flanking the west side of the Yukon River drainage as far as Champagne Pass, north of which being the Yukon Ranges. To their east are the Skeena Mountains and Stikine Plateau of the Interior Mountains complex that lies northwest of the Interior Plateau; the immediately adjoining subregion of the Stikine Plateau is the Tahltan Highland. To their northeast is the Tagish Highland, which is a subregion of the Yukon Plateau. Both highlands are considered in some descriptions as included in the Coast Mountains. The Alexander Archipelago lies offshore and is entirely within Alaska.

The Fairweather Range is the unofficial name for a mountain range located in the U.S. state of Alaska and the Canadian province of British Columbia. It is the southernmost range of the Saint Elias Mountains. The northernmost section of the range is situated in Tatshenshini-Alsek Provincial Park while the southernmost section resides in Glacier Bay National Park, in the Hoonah-Angoon Census Area. In between it goes through the southeastern corner of Yakutat Borough. Peaks of this range include Mount Fairweather and Mount Quincy Adams 4,150 m (13,615 ft).

The Tatshenshini River is a river in the Canadian boreal forest, in the southwestern Yukon and the northwestern corner of British Columbia. It originates in British Columbia, near Haines Highway. It flows north into Yukon, then it turns west and south before it returns into British Columbia, where it flows through the Tatshenshini-Alsek Provincial Wilderness Park. There it joins the Alsek River, which then flows into the Pacific Ocean in Alaska, United States. It is popular for wilderness rafting trips.

The Alsek Ranges are the southeasternmost subdivision of the Saint Elias Mountains of the Pacific Cordillera. They span the region between the Alsek River, Glacier Bay and the Kelsall River. Their western boundary is the Grand Pacific Glacier, beyond which is the Fairweather Range, another subdivision of the St. Elias Mountains. To their east is the northernmost section of the Boundary Ranges, the northernmost subdivision of the Coast Mountains and which are also known as the Alaska Boundary Range, and which run south to the Nass River and form, as their name indicates, the spine of the boundary between the American state of Alaska and the Canadian province of British Columbia.

The Tagish Highland is an upland area on the inland side of the northernmost Boundary Ranges of the Coast Mountains, spanning far northwestern British Columbia from Atlin Lake to the area of the pass at Champagne, Yukon between the Alsek and Yukon Rivers. In some classification systems, and in local terminology, the Tagish Highland is considered to be part of the Boundary Ranges, as is the neighbouring Tahltan Highland to its south. As classified by the Canadian Mountain Encyclopedia per S. Holland, the Tagish Highland is part of the system unofficially described as the Interior Mountains.

Mount Quincy Adams is a mountain located on the border between United States and Canada. It is named after John Quincy Adams (1767–1848), the sixth president of the United States.

Kluane / Wrangell–St. Elias / Glacier Bay / Tatshenshini-Alsek is an international park system located in Canada and the United States, at the border of Yukon, Alaska and British Columbia.

This article comprises three sortable tables of major mountain peaks of Canada.

The Boreal Cordillera Ecozone, as defined by the Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC), is a Canadian terrestrial ecozone occupying most of the northern third of British Columbia and southern half of Yukon. Within it is found Kluane National Park and Reserve, and a small portion of the southern range of Nahanni National Park Reserve. Most of the area's population is based in the city of Whitehorse, and it contains most of Yukon's population. The portion in British Columbia is barely populated.

Giant current ripples (GCRs), also known as giant gravel bars or giant gravel dunes, are a form of subaqueous dune. They are active channel topographic forms up to 20 m high, which occur within near-thalweg areas of the main outflow routes created by glacial lake outburst floods. Giant current ripple marks are large scale analogues of small current ripples formed by sand in streams. Giant current ripple marks are important features associated with scablands. As a landscape component, they are found in several areas that were previously in the vicinity of large glacial lakes.

Mount Barnard, also named Boundary Peak 160, is a mountain in Alaska and British Columbia, located on the Canada–United States border, and part of the Alsek Ranges of the Saint Elias Mountains. In 1923 Boundary Peak 160 was named Mount Barnard in honour of Edward Chester Barnard, a U.S. Boundary Commissioner from 1915 to 1921 and chief topographer of the United States and Canada Boundary Survey from 1903 to 1915. The first ascent of Mount Barnard was made on August 24, 1966, from the head of Tarr Inlet by D. Kenyon King, Peter H. Robinson and David P. Johnston. The details on file with Peak Service at Bartlett Cove, Glacier Bay National Monument, Gustavus, Alaska.

Kaskawulsh Mountain is a 2,969-metre (9,741-foot) mountain summit of the Saint Elias Mountains in Kluane National Park of Yukon, Canada. Surrounded by ice on all sides, the mountain is situated in the notch where the main arm of the Kaskawulsh Glacier merges with its south arm. The Stairway Glacier lies to the west, and the Atrypa Glacier to the south. The mountain cannot be seen from any roads, but can be seen by plane, or by hiking to the summit of Observation Mountain which is located at the head of the Slims River valley. The nearest higher peak is GJ43, 3.8 km (2.4 mi) to the west.

Mount Archibald is a prominent 2,588-metre (8,491-foot) mountain summit located in the Kluane Ranges of the Saint Elias Mountains in Yukon, Canada. The mountain is situated 21 km (13 mi) west of Haines Junction, 5.9 km (4 mi) south of Mount Decoeli, and 27 km (17 mi) east-southeast of Mount Cairnes, which is the nearest higher peak. Set on the boundary line of Kluane National Park, Archibald can be seen from the Alaska Highway, weather permitting. The mountain was named after Edgar Archibald (1885-1968), a Canadian agricultural scientist. The mountain's name was officially adopted August 12, 1980, by the Geographical Names Board of Canada. On a clear day, the summit offers views deep into Kluane National Park of giants such as Mt. Logan, Mt. Vancouver, and Mt. Kennedy.

Mount Martha Black, elevation 2,512-metre (8,241-foot), is the highest point in the Auriol Range of the Saint Elias Mountains in Yukon, Canada. The multi-summit massif is situated 11 km (7 mi) southwest of Haines Junction, 16 km (10 mi) northwest of Mount Worthington, and 18.6 km (12 mi) southeast of Mount Archibald, which is the nearest higher peak. Set within Kluane National Park, Mount Martha Black can be seen from the Alaska Highway, weather permitting. The mountain was named after Martha Black (1866-1957), the second woman elected to the House of Commons of Canada. The mountain's name was officially adopted August 12, 1980, by the Geographical Names Board of Canada.

Ulu Mountain is a mountain in Yukon, Canada.





















