
Ixodiphagus hookeri, the tick wasp, is an encyrtid wasp which lays its eggs into ticks. It seems to use a symbiotic bacteria, Wolbachia pipientis, to weaken the tick's immune system.

The marsh rice rat is a semiaquatic North American rodent in the family Cricetidae. It usually occurs in wetland habitats, such as swamps and salt marshes. It is found mostly in the eastern and southern United States, from New Jersey and Kansas south to Florida and northeasternmost Tamaulipas, Mexico; its range previously extended further west and north, where it may have been a commensal in corn-cultivating communities. Weighing about 40 to 80 g, the marsh rice rat is a medium-sized rodent that resembles the common black and brown rat. The upperparts are generally gray-brown, but are reddish in many Florida populations. The feet show several specializations for life in the water. The skull is large and flattened, and is short at the front.

Amblyomma is a genus of hard ticks. Some are disease vectors, for example the Rocky Mountain spotted fever in Brazil or ehrlichiosis in the United States.

Rickettsia parkeri is a gram-negative intracellular bacterium. The organism is found in the Western Hemisphere and is transmitted via the bite of hard ticks of the genus Amblyomma. R. parkeri causes mild spotted fever disease in humans, whose most common signs and symptoms are fever, an eschar at the site of tick attachment, rash, headache, and muscle aches. Doxycycline is the most common drug used to reduce the symptoms associated with disease.
Maritrema heardi is a parasitic fluke that infects the marsh rice rat in a salt marsh at Cedar Key, Florida. It was first listed as Maritrema sp. II in 1988, then described as the only species of a new genus, Floridatrema heardi, in 1994, and eventually reassigned in 2003 to Maritrema as Maritrema heardi. Its intermediate host is the fiddler crab Uca pugilator and it lives in the intestine of the marsh rice rat, its definitive host. Together with two other species of Maritrema, it is very common in affected marsh rice rats; it infects 19% of studied rats at Cedar Key. According to Tkach and colleagues, M. heardi is probably primarily a parasite of birds that has secondarily infected the marsh rice rat. Floridatrema was distinguished from Maritrema on the basis of its possession of loops of the uterus that extend forward to the place where the intestine is forked or even to the pharynx. Genetically, M. heardi may be closest to the morphologically similar M. neomi, which infects Neomys water shrews in the Carpathians.
Ctenophthalmus pseudagyrtes is a species of fleas in the family Hystrichopsyllidae. It is widespread in North America, east of the Rocky Mountains, and is found mainly on small mammals. In Missouri, it has been recorded on the Virginia opossum, northern short-tailed shrew, eastern mole, raccoon, eastern chipmunk, Florida woodrat, prairie vole, woodland vole, white-footed mouse, including nests, marsh rice rat, hispid cotton rat, house mouse, and brown rat. Hosts recorded in Tennessee include the Virginia opossum, northern short-tailed shrew, eastern mole, eastern chipmunk, southern red-backed vole, rock vole, woodland vole, white-footed mouse, golden mouse, hispid cotton rat, marsh rice rat, and house mouse.
Stenoponia americana is a species of large flea in the family Hystrichopsyllidae. It is widespread in North America east of the Great Plains and is found mainly on rodents, notably deermice (Peromyscus) and voles (Microtus). In Missouri, it has been recorded on the fox squirrel, brush mouse, cotton mouse, prairie vole, woodland vole, and white-footed mouse. Hosts recorded in Tennessee include the northern short-tailed shrew, woodland vole, white-footed mouse, hispid cotton rat, marsh rice rat, and house mouse. In South Carolina, recorded hosts include the cotton mouse, hispid cotton rat, and marsh rice rat.
Polygenis gwyni is a flea that commonly infects the hispid cotton rat in the southern United States; it is also frequently found on other species ecologically associated with the cotton rat. Hosts recorded in South Carolina include the cotton rat as well as the Florida woodrat, cotton mouse, marsh rice rat, and brown rat.
Euschoengastia peromysci is a mite in the genus Euschoengastia of the family Trombiculidae. Recorded hosts include the cotton mouse and marsh rice rat in Georgia; the northern short-tailed shrew, northern red-backed vole, northern flying squirrel, rock vole, white-footed mouse, and deermouse in Tennessee; and northern red-backed vole, southern bog lemming, masked shrew, and eastern red squirrel in North Carolina, among others.
Euschoengastia setosa is a mite in the genus Euschoengastia of the family Trombiculidae that mostly parasitizes small rodents and lagomorphs. Recorded hosts include marsh rice rat in Georgia; the deermouse in Tennessee; and the eastern red squirrel in North Carolina, among others.
Eutrombicula batatas is a species of chigger.

Haemogamasus is a genus of mites in the family Haemogamasidae. In North America, they mostly infect rodents, in addition to other small mammals such as shrews, talpids, and Virginia opossums.
Ixodes affinis is a species of tick in the genus Ixodes. Some reported hosts are:
Ixodes brunneus is a species of tick in the genus Ixodes. It is normally a parasite of birds, but has also been recorded on the marsh rice rat.
Ixodes cookei is a species of tick in the genus Ixodes. It is normally a parasite of carnivorans, such as raccoons, foxes, and weasels, but has also been recorded on the groundhog and the marsh rice rat. In the northeastern United States, it is a vector of Powassan virus.
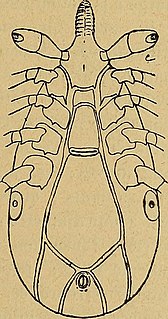
Ixodes minor is a species of tick in the genus Ixodes. Some reported hosts are:
Ixodes texanus is a species of ticks in the genus Ixodes. It mainly infects raccoons, but has also been recorded on the marsh rice rat in Georgia.
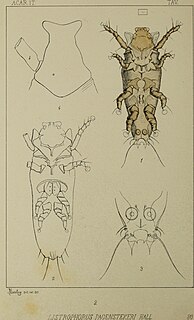
Listrophoridae is a family of mites in the suborder Psoroptidia of the order Sarcoptiformes. The family contains small, long mites specialized for grasping the hairs of mammals. North American genera include:
Prolistrophorus bakeri is a parasitic mite in the genus Prolistrophorus. Together with the Argentine P. hirstianus, it forms the subgenus Beprolistrophorus. P. bakeri has been found on the hispid cotton rat, marsh rice rat, and cotton mouse in Georgia, South Carolina, Texas, and Florida and on Oryzomys couesi in Colima. It was formerly placed in the genus Listrophorus.







