
The hourglass dolphin is a small dolphin in the family Delphinidae that inhabits offshore Antarctic and sub-Antarctic waters. It is commonly seen from ships crossing the Drake Passage but has a circumpolar distribution.
Percy Alexander Hulley is a South African zoologist and ichthyologist. He is a research associate at the South African Museum and has described many species of fish including the taillight shark.

Notothenioidei is one of 19 suborders of the order Perciformes. The group is found mainly in Antarctic and Subantarctic waters, with some species ranging north to southern Australia and southern South America. Notothenioids constitute approximately 90% of the fish biomass in the continental shelf waters surrounding Antarctica.

The northern pika is a species of pika found across mountainous regions of northern Asia, from the Ural Mountains to northern Japan and south through Mongolia, Manchuria and northern Korea. An adult northern pika has a body length of 12.5–18.5 centimeters (4.9–7.3 in), and a tail of 0.5–1.2 centimeters (0.20–0.47 in). The pika sheds its fur twice annually, bearing a reddish-brown coat in the summer and grayish-brown coat in winter. It feeds on various plant material and makes "hay piles" for winter use.

Raja, also known as raia, is a genus of skates in the family Rajidae containing 16 species. Formerly a wastebasket genus, many species historically categorized here have been moved to other genera in the family, such as Amblyraja, Beringraja, Dipturus, Leucoraja and Rostroraja. Raja are flat-bodied, cartilaginous fish with a rhombic shapes due to their large pectoral fins extending from or near from the snouts to the bases of their tails. Their sharp snouts are produced by a cranial projection of rostral cartilage. The mouth and gills are located on the underside of the body. They may be either solid-coloured or patterned, and most skates have spiny or thorn-like structures on the upper surface, while some species contain weak electrical organs within their tails. Mating typically occurs in the spring and the female lays numerous eggs per clutch which are encapsulated in leathery cases, commonly known as "mermaid’s purses". Species vary in size, ranging from about 40 to 140 cm (1.3–4.6 ft) in length. These bottom-dwellers are active during both day and night, and typically feed on molluscs, crustaceans and fish. Raja skates are found in the East Atlantic, also in the Mediterranean, and western Indian Ocean, ranging from relatively shallow water to a depth of 800 m (2,600 ft). Skates and related species have fossil records dating from the Upper Cretaceous period, thus this well-adapted species is quite ancient.

The barndoor skate is a species of marine cartilaginous fish in the skate family Rajidae of the order Rajiformes. It is native to the northwestern Atlantic Ocean, and is found from the Grand Banks of Newfoundland and the southern side of the Gulf of St. Lawrence south to North Carolina. The fish is one of the largest skates found in the North Atlantic Ocean, reaching lengths up to 1.5 m (5 ft). It is carnivorous, feeding on invertebrates and other fish found near the sea floor.
The thickbody skate is a species of fish in the family Rajidae found off the coasts of Argentina, Chile, and Uruguay. Its natural habitat is open seas.

The broad skate is a poorly known species of skate in the family Rajidae. It occurs at depths of 846 to 2,324 metres, and has been observed via remotely operated underwater vehicle by the Monterey Bay Aquarium Research Institute as deep as 3,167 metres (10,390 ft), making it one of the deepest-occurring skates known. It is sporadically distributed in the Pacific Ocean, from the Gulf of Panama to British Columbia and the Bering Sea, to the Tohoku Slope off northern Honshu and the Okhotsk Slope off Hokkaido. The species name, badia, comes from the Latin batius meaning "brown", referring to its color.

The thorny skate is a species of fish in the family Rajidae. This bottom-living skate lives in the North and south-eastern Atlantic Ocean in depths ranging from 20 to 1,000 m (66–3,281 ft) and water temperatures from −1 to 14 °C (30–57 °F).
The bigmouth skate is a species of fish in the family Rajidae. It lives near the bottom in deep waters in Southeast Atlantic in depths below 1,000 m (3,280 ft). Its maximum size is 77 cm (30 in). It has a hard, roughly triangular snout and smooth body with star-based thorns around its eyes, tail, and elsewhere. Its top side is dark gray and underside has white spots. As the name suggests, it has a large mouth.
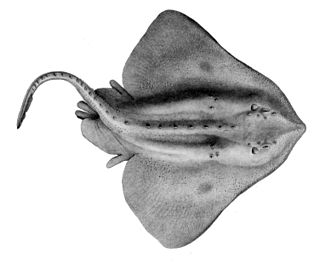
The Arctic skate is a species of fish in the family Rajidae. It lives near the seabed between 140 and 2,500 m deep in the Arctic Ocean and waters around Canada and northern and north-western Europe, in the northern Pacific Ocean, and in waters surrounding Antarctica and New Zealand.
The southern thorny skate is a species of fish in the family Rajidae. It lives off the coast of Argentina and Uruguay, and around the Falkland Islands in depths ranging from 51 to 642 m. Its maximum size is 69 cm. It lays oblong egg capsules with horn-like projections at the corners which are laid in sandy or muddy flats. The eggs measure 86.4 mm in length and 56.2 mm in width.
Jensen's skate, also known as the shortail skate, is a poorly known species of fish discovered in 2004 during a study of bottom ichthyofauna aboard the Norwegian RV G.O. Sars, where four species were identified, including A. jenseni.

Aega psora is a species of isopod crustacean that parasitises a number of fish species in the North Atlantic. It is a serious ectoparasite of larger species of fish, particularly when they are injured.
Eudactylina corrugata is a species of parasitic copepod found on the little skate and the thorny skate that is only known from St. Andrews, New Brunswick and Woods Hole, Massachusetts.
Amblyraja reversa, commonly known as the reversed skate, is a deepwater skate known from a single specimen. Based on the single specimen, its range is predicted to include at least the Western Indian Ocean, specifically the Baluchistan coast in the Arabian Sea.
Amblyraja taaf, commonly known as the whiteleg skate or thorny skate, is a little-known skate found at depths ranging from 150 to 600 m. It has been located off Crozet and Kerguelen Islands. Other specimens have been found off the coast of South Africa and Madagascar, but may be unrepresentative of the skate's native regions. Because of the limited knowledge of its biology and extent of capture in fisheries, this species is assessed as data deficient.

EVA1C is a transmembrane protein in humans that is encoded by the EVA1C gene on Chromosome 21. The EVA1C protein is thought to be involved in herapin binding activity. In addition, the gene is thought to be associated with diseases such as X-Linked Intellectual Disability-Short Stature-Overweight Syndrome.










