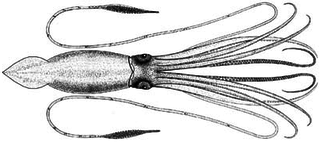
The giant squid is a species of deep-ocean dwelling squid in the family Architeuthidae. It can grow to a tremendous size, offering an example of abyssal gigantism: recent estimates put the maximum size at around 12–13 m (39–43 ft) for females and 10 m (33 ft) for males, from the posterior fins to the tip of the two long tentacles. The mantle of the giant squid is about 2 m long, and the length of the squid excluding its tentacles rarely exceeds 5 m (16 ft). Claims of specimens measuring 20 m (66 ft) or more have not been scientifically documented.

The cetacean family Monodontidae comprises two living whale species, the narwhal and the beluga whale and at least four extinct species, known from the fossil record. Beluga and Narwhal are native to coastal regions and pack ice around the Arctic Ocean. Both species are relatively small whales, between three and five metres in length, with a forehead melon, and a short or absent snout. They do not have a true dorsal fin, but do have a narrow ridge running along the back, which is much more pronounced in the narwhal. They are highly vocal animals, communicating with a wide range of sounds. Like other whales, they also use echolocation to navigate. Belugas can be found in the far north of the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans; the distribution of narwhals is restricted to the Arctic and Atlantic Oceans.

Moray eels, or Muraenidae, are a family of eels whose members are found worldwide. There are approximately 200 species in 15 genera which are almost exclusively marine, but several species are regularly seen in brackish water, and a few are found in fresh water.

Sand sharks, also known as sand tiger sharks, gray nurse sharks or ragged tooth sharks, are mackerel sharks of the family Odontaspididae. They are found worldwide in temperate and tropical waters. The three species are in two genera.

In biogeography, a cosmopolitan distribution is the range of a taxon that extends across all of the world, in appropriate habitats; most cosmopolitan species are known to be highly adaptable to a range of climatic and environmental conditions, though this is not always so. Killer whales (orcas) are among the most well-known cosmopolitan species on the planet, as they maintain several different resident and transient (migratory) populations in every major oceanic body on Earth, from the Arctic Circle to Antarctica and every coastal and open-water region in-between. Such a taxon is said to have a cosmopolitan distribution, or exhibit cosmopolitanism, as a species; another example, the rock dove, in addition to having been bred domestically for centuries, now occurs in most urban areas across the world.
Aphyonidae is a family of eel-like fishes in the order Ophidiiformes. They are found in tropical and subtropical waters throughout the world. They are deep-sea fishes, living between 2,000 metres (6,600 ft) and 6,000 metres (20,000 ft) depth.

Asteliaceae is a family of flowering plants, placed in the order Asparagales of the monocots.

The longnose pygmy shark is a rare species of squaliform shark in the family Dalatiidae and the only member its genus. It is known only from a handful of specimens collected from the cold oceanic waters of the Southern Hemisphere, between the surface and a depth of 502 m (1,647 ft). Reaching 37 cm (15 in) in length, this diminutive shark is characterized by a slender, dark brown body with a very long, bulbous snout. In addition, it has two spineless dorsal fins of nearly equal size, with the origin of the first lying over the pectoral fin bases. The longnose pygmy shark does not appear substantially threatened by fisheries, and has been assessed as Least Concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
A blind fish is a fish without functional eyes. Most blind fish species are found in dark habitats such as the deep ocean, deep river channels and underground.
Malacoglanis gelatinosus is a species of catfish of the family Trichomycteridae, and the only species of the genus Malacoglanis. This fish grows to about 2.0 centimetres (.79 in) SL. and is native to the Caquetá River basin of Colombia. Stauroglanis is the sister group to a monophyletic group formed by Malacoglanis and Sarcoglanis.
The Sarcoglanidinae are a subfamily of catfishes of the family Trichomycteridae. It includes six genera: Ammoglanis, Malacoglanis, Microcambeva, Sarcoglanis, Stauroglanis, and Stenolicmus.
Psednos is a genus of snailfishes found in all the world's oceans.
Aphyonus is a genus of blind cusk eels from the family Aphyonidae. It contains four species. A sampling of specimens of Aphyonus showed that the type species of Aphyonus, A. gelatinosus, was not closely related to the other known species in the genus, and a new genus Paraphyonus was named for these, including two newly identified species. The result of this classification is that Aphyonus would be a monotypic genus.
Paraphyonus is a genus of blind cusk eels found in the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans. This genus was created for species formerly classified under Aphyonus when sampling of specimens showed that the type species of Aphyonus, A. gelatinosus, was not closely related to the other known species in the genus, including the newly identified species P. iselini and P. merretti. This work also brought Barathronus solomonensis into the new genus. The result of this classification is that Aphyonus would be a monotypic genus.

Patiria chilensis is a species of starfish in the family Asterinidae. It is found in the southeastern Pacific Ocean along the coasts of South America. It is a broadly pentagonal, cushion-like starfish with five short arms.

Luidia magellanica is a species of starfish in the family Luidiidae. It is found in the southeastern Pacific Ocean on the coast of South America.

Meyenaster is a genus of starfish in the family Asteriidae. It is a monotypic genus and the only species is Meyenaster gelatinosus which was first described by the Prussian botanist and zoologist Franz Julius Ferdinand Meyen in 1834. It is found in the southeastern Pacific Ocean on the coasts of South America.

Heliaster helianthus, the sun star, is a species of Asteroidea (starfish) in the family Heliasteridae. It is found in shallow water rocky habitats and in the kelp forests off the Pacific coast of Ecuador, Peru and Chile.

Tetrapygus is a genus of sea urchins in the family Arbaciidae. It is a monotypic genus and the only species is Tetrapygus niger which was first described by the Chilean naturalist Juan Ignacio Molina in 1782. It is found in the southeastern Pacific Ocean on the coasts of South America.
Psednos gelatinosus, the gelatinous dwarf snailfish, is a species of snailfish found in the north-eastern Atlantic Ocean off the coast of south-eastern Greenland.












