
Biology – The natural science that studies life. Areas of focus include structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy.

Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms that drift in water but are unable to actively propel themselves against currents. The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankters. In the ocean, they provide a crucial source of food to many small and large aquatic organisms, such as bivalves, fish, and baleen whales.
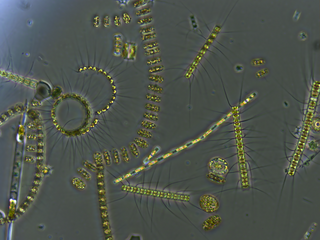
Zooplankton are the animal component of the planktonic community, having to consume other organisms to thrive. Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents. Consequently, they drift or are carried along by currents in the ocean, or by currents in seas, lakes or rivers.

The Oligohymenophorea are a large class of ciliates. There is typically a ventral groove containing the mouth and distinct oral cilia, separate from those of the body. These include a paroral membrane to the right of the mouth and membranelles, usually three in number, to its left. The cytopharynx is inconspicuous and never forms the complex cyrtos found in similar classes. Body cilia generally arise from monokinetids, with dikinetids occurring in limited distribution over part of the body.

Paramecium is a genus of eukaryotic, unicellular ciliates, widespread in freshwater, brackish, and marine environments. Paramecia are often abundant in stagnant basins and ponds. Because some species are readily cultivated and easily induced to conjugate and divide, they have been widely used in classrooms and laboratories to study biological processes. Paramecium species are commonly studied as model organisms of the ciliate group and have been characterized as the "white rats" of the phylum Ciliophora.

A unicellular organism, also known as a single-celled organism, is an organism that consists of a single cell, unlike a multicellular organism that consists of multiple cells. Organisms fall into two general categories: prokaryotic organisms and eukaryotic organisms. Most prokaryotes are unicellular and are classified into bacteria and archaea. Many eukaryotes are multicellular, but some are unicellular such as protozoa, unicellular algae, and unicellular fungi. Unicellular organisms are thought to be the oldest form of life, with early protocells possibly emerging 3.5–4.1 billion years ago.

In biology, a biological life cycle is a series of stages of the life of an organism, that begins as a zygote, often in an egg, and concludes as an adult that reproduces, producing an offspring in the form of a new zygote which then itself goes through the same series of stages, the process repeating in a cyclic fashion.
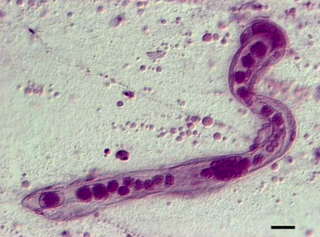
Dicyemida, also known as Rhombozoa, is a phylum of tiny parasites that live in the renal appendages of cephalopods.

Symbion pandora is a jug-shaped microscopic aquatic animal that dwells on the mouth-parts of Norway lobsters. The animals are less than ½ mm wide, with sac-like bodies, and three distinctly different forms in different parts of their three-stage life cycle.

The family Argulidae, whose members are commonly known as carp lice or fish lice, are parasitic crustaceans in the class Ichthyostraca. It is the only family in the monotypic subclass Branchiura and the order Arguloida, although a second family, Dipteropeltidae, has been proposed. Although they are thought to be primitive forms, they have no fossil record.
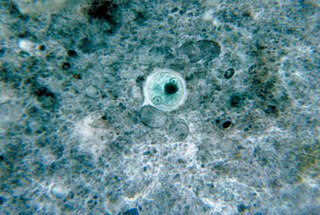
A microbial cyst is a resting or dormant stage of a microorganism, that can be thought of as a state of suspended animation in which the metabolic processes of the cell are slowed and the cell ceases all activities like feeding and locomotion. Many groups of single-celled, microscopic organisms, or microbes, possess the ability to enter this dormant state.

Protozoa are a polyphyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic debris. Historically, protozoans were regarded as "one-celled animals".
Hematodinium is a genus of dinoflagellates. Species in this genus, such as Hematodinium perezi, the type species, are internal parasites of the hemolymph of crustaceans such as the Atlantic blue crab and Norway lobster. Species in the genus are economically damaging to commercial crab fisheries, including causing bitter crab disease in the large Tanner or snow crab fisheries of the Bering Sea.

Marine microorganisms are defined by their habitat as microorganisms living in a marine environment, that is, in the saltwater of a sea or ocean or the brackish water of a coastal estuary. A microorganism is any microscopic living organism or virus, which is invisibly small to the unaided human eye without magnification. Microorganisms are very diverse. They can be single-celled or multicellular and include bacteria, archaea, viruses, and most protozoa, as well as some fungi, algae, and animals, such as rotifers and copepods. Many macroscopic animals and plants have microscopic juvenile stages. Some microbiologists also classify viruses as microorganisms, but others consider these as non-living.
Hyalophysa chattoni is an apostome ciliate of the order Apostomatida. The polymorphic symbiont is carried as an encysted phoront on the exoskeleton of few arthropods belonging to the subphylum Crustacea and undergoes metamorphosis during the host's premolt followed by various other life-cycle stages.

Colliniidae is a family of ciliates of the order Apostomatida.

The Foettingeriidae are a family of apostome ciliates of the order Apostomatida. Like other apostomes, they are symbiotic with Crustacea, and live in microbial cysts on their host's exoskeleton for most of their life. They excyst, or leave their cysts, when their hosts molt their exoskeleton in order to feed on the exuvial fluids trapped in their host's molted exoskeleton.

Collinia is a genus of parasitoid ciliates of the Colliniidae family.

Cothurnia is a genus of freshwater and marine peritrichs in the family Vaginicolidae. It is characterised by living in a transparent tubular lorica. During the feeding or vegetative phase of its life cycle, Cothurnia attaches to submerged surfaces through a short stalk — mostly on the surfaces of fishes, crustaceans and aquatic plants. It is commonly studied for its epibiotic relationship with the host that it is attached to.

Marine protists are defined by their habitat as protists that live in marine environments, that is, in the saltwater of seas or oceans or the brackish water of coastal estuaries. Life originated as marine single-celled prokaryotes and later evolved into more complex eukaryotes. Eukaryotes are the more developed life forms known as plants, animals, fungi and protists. Protists are the eukaryotes that cannot be classified as plants, fungi or animals. They are mostly single-celled and microscopic. The term protist came into use historically as a term of convenience for eukaryotes that cannot be strictly classified as plants, animals or fungi. They are not a part of modern cladistics because they are paraphyletic.
















