Related Research Articles
Ad hominem, short for argumentum ad hominem, refers to several types of arguments, some but not all of which are fallacious. Typically this term refers to a rhetorical strategy where the speaker attacks the character, motive, or some other attribute of the person making an argument rather than attacking the substance of the argument itself. The most common form of ad hominem is "A makes a claim x, B asserts that A holds a property that is unwelcome, and hence B concludes that argument x is wrong".

A false dilemma, also referred to as false dichotomy, is an informal fallacy based on a premise that erroneously limits what options are available. The source of the fallacy lies not in an invalid form of inference but in a false premise. This premise has the form of a disjunctive claim: it asserts that one among a number of alternatives must be true. This disjunction is problematic because it oversimplifies the choice by excluding viable alternatives. For example, a false dilemma is committed when it is claimed that, "Stacey spoke out against capitalism; therefore, she must be a communist". One of the options excluded is that Stacey may be neither communist nor capitalist. False dilemmas often have the form of treating two contraries, which may both be false, as contradictories, of which one is necessarily true. Various inferential schemes are associated with false dilemmas, for example, the constructive dilemma, the destructive dilemma or the disjunctive syllogism. False dilemmas are usually discussed in terms of deductive arguments. But they can also occur as defeasible arguments. Our liability to commit false dilemmas may be due to the tendency to simplify reality by ordering it through either-or-statements, which is to some extent already built into our language. This may also be connected to the tendency to insist on clear distinction while denying the vagueness of many common expressions.
A loaded question is a form of complex question that contains a controversial assumption.

A slippery slope argument (SSA), in logic, critical thinking, political rhetoric, and caselaw, is an argument in which a party asserts that a relatively small first step leads to a chain of related events culminating in some significant effect. The core of the slippery slope argument is that a specific decision under debate is likely to result in unintended consequences. The strength of such an argument depends on whether the small step really is likely to lead to the effect. This is quantified in terms of what is known as the warrant. This type of argument is sometimes used as a form of fearmongering in which the probable consequences of a given action are exaggerated in an attempt to scare the audience, although, differentiation is necessary, since, in other cases, it might be demonstrable that the small step will likely lead to an effect.

A straw man is a form of argument and an informal fallacy of having the impression of refuting an argument, whereas the real subject of the argument was not addressed or refuted, but instead replaced with a false one. One who engages in this fallacy is said to be "attacking a straw man".
A fallacy is the use of invalid or otherwise faulty reasoning, or "wrong moves" in the construction of an argument. A fallacious argument may be deceptive by appearing to be better than it really is. Some fallacies are committed intentionally to manipulate or persuade by deception, while others are committed unintentionally due to carelessness or ignorance. The soundness of legal arguments depends on the context in which the arguments are made.
Special pleading is an informal fallacy wherein one cites something as an exception to a general or universal principle, without justifying the special exception. It is the application of a double standard.
The genetic fallacy is a fallacy of irrelevance that is based solely on someone's or something's history, origin, or source rather than its current meaning or context. This overlooks any difference to be found in the present situation, typically transferring the positive or negative esteem from the earlier context. In other words, a claim is ignored in favor of attacking or championing its source.

Media manipulation is a series of related techniques in which partisans create an image or argument that favours their particular interests. Such tactics may include the use of logical fallacies, manipulation, outright deception (disinformation), rhetorical and propaganda techniques, and often involve the suppression of information or points of view by crowding them out, by inducing other people or groups of people to stop listening to certain arguments, or by simply diverting attention elsewhere. In Propaganda: The Formation of Men's Attitudes, Jacques Ellul writes that public opinion can only express itself through channels which are provided by the mass media of communication – without which there could be no propaganda. It is used within public relations, propaganda, marketing, etc. While the objective for each context is quite different, the broad techniques are often similar.
A faulty generalization is an informal fallacy wherein a conclusion is drawn about all or many instances of a phenomenon on the basis of one or a few instances of that phenomenon. It is similar to a proof by example in mathematics. It is an example of jumping to conclusions. For example, one may generalize about all people or all members of a group, based on what one knows about just one or a few people:
Argument from fallacy is the formal fallacy of analyzing an argument and inferring that, since it contains a fallacy, its conclusion must be false. It is also called argument to logic, the fallacy fallacy, the fallacist's fallacy, and the bad reasons fallacy.
Informal fallacies are a type of incorrect argument in natural language. The source of the error is not just due to the form of the argument, as is the case for formal fallacies, but can also be due to their content and context. Fallacies, despite being incorrect, usually appear to be correct and thereby can seduce people into accepting and using them. These misleading appearances are often connected to various aspects of natural language, such as ambiguous or vague expressions, or the assumption of implicit premises instead of making them explicit.
In philosophy, a formal fallacy, deductive fallacy, logical fallacy or non sequitur is a pattern of reasoning rendered invalid by a flaw in its logical structure that can neatly be expressed in a standard logic system, for example propositional logic. It is defined as a deductive argument that is invalid. The argument itself could have true premises, but still have a false conclusion. Thus, a formal fallacy is a fallacy where deduction goes wrong, and is no longer a logical process. This may not affect the truth of the conclusion, since validity and truth are separate in formal logic.
Appeal to the stone, also known as argumentum ad lapidem, is a logical fallacy that dismisses an argument as untrue or absurd. The dismissal is made by stating or reiterating that the argument is absurd, without providing further argumentation. This theory is closely tied to proof by assertion due to the lack of evidence behind the statement and its attempt to persuade without providing any evidence.
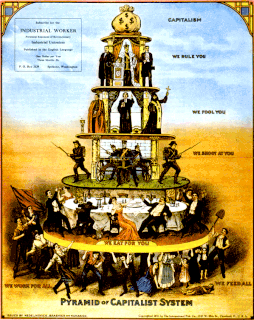
A number of propaganda techniques based on social psychological research are used to generate propaganda. Many of these same techniques can be classified as logical fallacies, since propagandists use arguments that, while sometimes convincing, are not necessarily valid.
Flag-waving is a fallacious argument or propaganda technique used to justify an action based on the undue connection to nationalism or patriotism or benefit for an idea, group or country. It is a variant of argumentum ad populum. This fallacy appeals to emotion instead to logic of the audience aiming to manipulate them to win an argument. All ad populum fallacies are based on the presumption that the recipients already have certain beliefs, biases, and prejudices about the issue.
In argumentation theory, an argumentum ad populum is a fallacious argument which is based on affirming that something is real because the majority thinks so. Other names for the fallacy include common belief fallacy or appeal to (common) belief, appeal to the majority, appeal to the masses, appeal to popularity, argument from consensus, authority of the many, bandwagon fallacy, consensus gentium, democratic fallacy, mob appeal, and truth by association.
An argument from authority, also called an appeal to authority, or argumentum ad verecundiam, is a form of argument in which the opinion of an authority on a topic is used as evidence to support an argument. Some consider that it is used in a cogent form if all sides of a discussion agree on the reliability of the authority in the given context, and others consider it to always be a fallacy to cite the views of an authority on the discussed topic as a means of supporting an argument.
Coming from the Greek origin, κολακεία, which means flattery, the word "kolakeia" means to flatter someone as a means to take advantage of or gain something from them through speech. Kolakeia's concept is to overload someone with compliments so the speaker can slip in another idea that the listener may not agree upon. It may also include a subtle compliment where the listener does not know it happened but it affects their way of thinking. The use of the kolakeia is often looked down upon because it is not a true concept of speech. The use of this type of communication, allows people to question the speaker's motives.
References
- ↑ "Fallacy: Appeal to Flattery". The Nizkor Project. Archived from the original on 6 August 2012. Retrieved 10 December 2010.
- ↑ Sprouse, Scott (2017). The Reasoning Skills Workbook. p. 48. ISBN 9781387214617 . Retrieved 19 January 2017.
- 1 2 3 Bennett, Bo (2012). Logically Fallacious: The Ultimate Collection of Over 300 Logical Fallacies. p. 61. ISBN 9781456607371 . Retrieved 19 January 2018.
- ↑ Gary Curtis. "Emotional Appeal". Fallacy Files. Retrieved 19 January 2018.