
Gannets are seabirds comprising the genus Morus in the family Sulidae, closely related to boobies, commonly named 'gugas' in Scotland.

The Los Angeles Basin is a sedimentary basin located in Southern California, in a region known as the Peninsular Ranges. The basin is also connected to an anomalous group of east-west trending chains of mountains collectively known as the Transverse Ranges. The present basin is a coastal lowland area, whose floor is marked by elongate low ridges and groups of hills that is located on the edge of the Pacific Plate. The Los Angeles Basin, along with the Santa Barbara Channel, the Ventura Basin, the San Fernando Valley, and the San Gabriel Basin, lies within the greater Southern California region. The majority of the jurisdictional land area of the city of Los Angeles physically lies within this basin.

A bone bed is any geological stratum or deposit that contains bones of whatever kind. Inevitably, such deposits are sedimentary in nature. Not a formal term, it tends to be used more to describe especially dense collections such as Lagerstätte. It is also applied to brecciated and stalagmitic deposits on the floor of caves, which frequently contain osseous remains.
Henry Weed Fowler was an American zoologist born in Holmesburg, Pennsylvania.

The lingcod or ling cod, also known as the buffalo cod or cultus cod, is a fish of the greenling family Hexagrammidae. It is the only extant member of the genus Ophiodon. A slightly larger, extinct species, Ophiodon ozymandias, is known from fossils from the Late Miocene of Southern California.

Siliceous ooze is a type of biogenic pelagic sediment located on the deep ocean floor. Siliceous oozes are the least common of the deep sea sediments, and make up approximately 15% of the ocean floor. Oozes are defined as sediments which contain at least 30% skeletal remains of pelagic microorganisms. Siliceous oozes are largely composed of the silica based skeletons of microscopic marine organisms such as diatoms and radiolarians. Other components of siliceous oozes near continental margins may include terrestrially derived silica particles and sponge spicules. Siliceous oozes are composed of skeletons made from opal silica SiO2·nH2O, as opposed to calcareous oozes, which are made from skeletons of calcium carbonate (CaCO3·nH2O) organisms (i.e. coccolithophores). Silica (Si) is a bioessential element and is efficiently recycled in the marine environment through the silica cycle. Distance from land masses, water depth and ocean fertility are all factors that affect the opal silica content in seawater and the presence of siliceous oozes.

The Monterey Formation is an extensive Miocene oil-rich geological sedimentary formation in California, with outcrops of the formation in parts of the California Coast Ranges, Peninsular Ranges, and on some of California's off-shore islands. The type locality is near the city of Monterey, California. The Monterey Formation is the major source-rock for 37 to 38 billion barrels of oil in conventional traps such as sandstones. This is most of California's known oil resources. The Monterey has been extensively investigated and mapped for petroleum potential, and is of major importance for understanding the complex geological history of California. Its rocks are mostly highly siliceous strata that vary greatly in composition, stratigraphy, and tectono-stratigraphic history.

The Coyote Mountains are a small mountain range in San Diego and Imperial Counties in southern California. The Coyotes form a narrow ESE trending 2 mi (3.2 km) wide range with a length of about 12 mi (19 km). The southeast end turns and forms a 2 mi (3.2 km) north trending "hook". The highest point is Carrizo Mountain on the northeast end with an elevation of 2,408 feet (734 m). Mine Peak at the northwest end of the range has an elevation of 1,850 ft (560 m). Coyote Wash along I-8 along the southeast margin of the range is 100 to 300 feet in elevation. Plaster City lies in the Yuha Desert about 5.5 mi (8.9 km) east of the east end of the range.
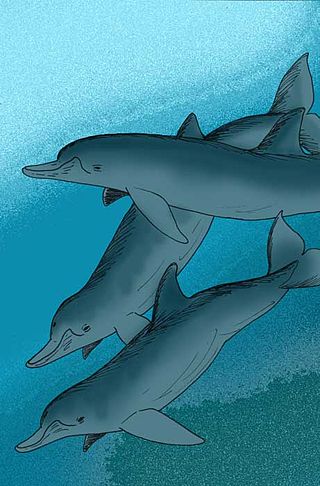
Australodelphis mirus is an extinct Pliocene dolphin. A. mirus is known from fossils found in the Sørsdal Formation, Mule Peninsula, Vestfold Hills, East Antarctica. The genus has been described as an example of convergent evolution with beaked whales.

Alisea is an extinct genus of prehistoric marine clupeiform fish that lived in what is now California during the Upper Miocene subepoch. Although generally considered a relative of the herrings in the family Clupeidae, an affinity to shads has also been suggested due to its large size and well-developed abdominal scutes. Its name derives from alise, an alternate spelling for the Hindi name of the related ilish fish.

Bolbocara is an extinct genus of rattail that lived during the Upper Miocene subepoch of Southern California. It contains a single species, B. gyrinus. It may be related to the extant genus Bathygadus.

Chalcidichthys is an extinct genus of prehistoric manefish. It contains a single species, C. malacapterygius, that lived during the Upper Miocene of Southern California. It is known from the Modelo Formation in Los Angeles County, and specimens were found during construction of a tunnel on Sepulveda Boulevard. It is assumed to have preyed on siphonophores, like its living relatives.

Absalomichthys velifer is an extinct, prehistoric manefish that lived during the Upper Miocene of what is now Southern California in the United States. Its dorsal fin was huge in comparison with living species. It is known from the Modelo Formation of Los Angeles County.
Bathylagus is a genus of deep-sea smelts, some species of which are noted for having stylophthalmine larvae.

The Sisquoc Formation is a sedimentary geologic unit widespread in Southern California, both on the coast and in mountains near the coast. Overlying the Monterey Formation, it is of upper Miocene and lower Pliocene age. The formation consists of claystone, mudstone, siltstone, shale, diatomite, and conglomerates, with considerable regional variation, and was deposited in a moderately deep marine environment at a depth of approximately 500–5,000 feet (150–1,520 m). Since some of its diatomites, along with those of the underlying Monterey Formation, are of unusual purity and extent, they can be mined as diatomaceous earth. France-based Imerys operates a mine in the Sisquoc and Monterey Formations in the hills south of Lompoc, California, the largest such operation in the world.

Rhabdosargus holubi, the Cape stumpnose, is a species of fish in the seabream family, Sparidae. It is native to southern Africa, where it can be found mainly along the eastern coast of South Africa.
The Modelo Formation is a Miocene geologic formation in the Simi Hills and western Santa Susana Mountains of southern California, including under parts of Los Angeles.
Norrisanima miocaena is an extinct species of Balaenopteroidea from the late Miocene of California. It was originally considered a species of Megaptera, but is now considered a stem-balaenopteroid.

Dioplotherium is an extinct genus of mammal known from Neogene deposits in the Southeastern United States.
Eoseira is an extinct genus of diatoms belonging to the family Aulacoseiraceae and containing the single species Eoseira wilsonii. The species is dated to the Early Eocene Ypresian stage and has only been found at the type locality in east central British Columbia.














