
Adria is a town and comune in the province of Rovigo in the Veneto region of northern Italy, situated between the mouths of the rivers Adige and Po. The remains of the Etruscan city of Atria or Hatria are to be found below the modern city, three to four metres below the current level. Adria and Spina were the Etruscan ports and depots for Felsina. Adria may have given its name during an early period to the Adriatic Sea, to which it was connected by channels.

Mediolanum, the ancient city where Milan now stands, was originally an Insubrian city, but afterwards became an important Roman city in northern Italy. The city was settled by the Insubres around 600 BC, conquered by the Romans in 222 BC, and developed into a key centre of Western Christianity and capital of the Western Roman Empire. It declined under the ravages of the Gothic War, its capture by the Lombards in 569, and their decision to make Ticinum the capital of their Kingdom of Italy.

The province of Chieti is a province in the Abruzzo region of Italy. Its provincial capital is the city Chieti, which has a population of 50,770 inhabitants. The province has a total population of 387,649 inhabitants as of 2017 and spans an area of 2,599.58 square kilometres (1,003.70 sq mi). It is divided into 104 comuni (comune) and the provincial president is Mario Pupillo.

Cerveteri is a town and comune of northern Lazio in the region of the Metropolitan City of Rome. Known by the ancient Romans as Caere, and previously by the Etruscans as Caisra or Cisra, and as Agylla by the Greeks, its modern name derives from Caere Vetus used in the 13th century to distinguish it from Caere Novum.

Monteleone di Spoleto, is a town and comune of Italy, in the province of Perugia in southeast Umbria at 978 meters (3209 ft) above sea-level overhanging the upper valley of the Corno River. It is one of the more remote towns in Umbria, on a mountain road from Norcia and Cascia to Leonessa and Rieti in the Lazio.
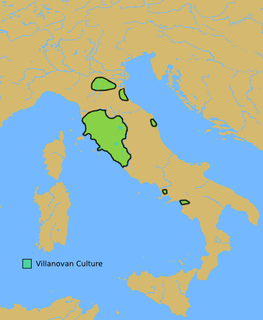
The Villanovan culture, regarded as the oldest phase of Etruscan civilization, was the earliest Iron Age culture of Central Italy and Northern Italy. It directly followed the Bronze Age Proto-Villanovan culture which branched off from the Urnfield culture of Central Europe. This gave way in the 7th century BC to an increasingly orientalizing culture influenced by Greek traders and colonists who settled in South Italy.

Asciano is a comune and hill town in the province of Siena in the Italian region Tuscany. It is located at the centre of the Crete senesi between the river Ombrone and the torrent Copra, some 30 kilometres (19 mi) southeast of the town of Siena by rail.

The National Roman Museum is a museum, with several branches in separate buildings throughout the city of Rome, Italy. It shows exhibits from the pre- and early history of Rome, with a focus on archaeological findings from the period of Ancient Rome.

Etruscan art was produced by the Etruscan civilization in central Italy between the 10th and 1st centuries BC. From around 750 BC it was heavily influenced by Greek art, which was imported by the Etruscans, but always retained distinct characteristics. Particularly strong in this tradition were figurative sculpture in terracotta, wall-painting and metalworking especially in bronze. Jewellery and engraved gems of high quality were produced.

San Maurizio al Monastero Maggiore is a church in Milan, northern Italy. It was originally attached to the most important female convent of the Benedictines in the city, Monastero Maggiore, which is now in use as the Civic Archaeological Museum. The church today is used every Sunday from October to June to celebrate in the Byzantine Rite, in Greek according to the Italo-Albanian tradition. It is also used as concert hall.

The National Archaeological Museum of Florence is an archaeological museum in Florence, Italy. It is located at 1 piazza Santissima Annunziata, in the Palazzo della Crocetta.

The Museo Nazionale della Magna Grecia, Museo Archeologico Nazionale di Reggio Calabria or Palazzo Piacentini is a museum in Reggio Calabria, southern Italy, housing an archaeological collection from sites in Magna Graecia.
The city Milan, Italy, has had three different systems of defending walls. The oldest, Roman walls were developed in two stages, the first in the Republican and the second in the Imperial era. The second wall system was realized in the Middle Ages, after the destruction of the city by Frederick I Barbarossa. Finally, the latest wall system was built by the Spanish rulers. While very little remains of these walls, their structure is clearly reflected in the urbanistic layout of the city. In particular, modern Milan has two roughly circular rings of streets, namely the "Cerchia dei Navigli" and the "Cerchia dei Bastioni", which essentially correspond to the Medieval and Spanish walls, respectively. Note that a third ring of roads just beyond the Inner Ring Road, called the External Ring Road, does not owe itself to any old city walls; but was part of the 1884 Beruto Plan for the city of Milan, created and named after a municipal engineer and public servant to the local city government.

The Museo Egizio is a museum sited in the Sforza Castle of Milan, Italy. The Sforzesco Castle is one of the most famous monuments in Milan and is home to several museums including the Egyptian Section of the Milan Archaeological Museum, the Museum of Ancient Art, the Pinacoteca and the Museum of Musical Instruments.

The Tarquinia National Museum is an archaeological museum dedicated to the Etruscan civilization in Tarquinia, Italy. Its collection consists primarily of the artifacts which were excavated from the Necropolis of Monterozzi to the east of the city. It is housed in the Palazzo Vitelleschi.
The Museo Archeologico Regionale Paolo Orsi of Syracuse, Sicily is one of the principal archaeological museums of Europe.

The National Archaeological Museum of the Marche Region is an archaeological museum in the port of Ancona, Marche, Italy. It is located in the Palazzo Ferretti, and 13,195 people visited the collections in 2015.

The National Archaeological Museum of Altino is an Archaeology museum located in Altino, in the municipality of Quarto d'Altino, in the Metropolitan City of Venice, Italy, next to archaeological site of Altinum.






























