Lucius Tarquinius Superbus was the legendary seventh and final king of Rome, reigning 25 years until the popular uprising that led to the establishment of the Roman Republic. He is commonly known as Tarquin the Proud, from his cognomen Superbus.
The year 509 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. In the Roman Republic it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Brutus and Collatinus. The denomination 509 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Lucius Junius Brutus was the semi-legendary founder of the Roman Republic, and traditionally one of its first consuls in 509 BC. He was reputedly responsible for the expulsion of his uncle the Roman king Tarquinius Superbus after the suicide of Lucretia, which led to the overthrow of the Roman monarchy. He was involved in the abdication of fellow consul Tarquinius Collatinus, and executed two of his sons for plotting the restoration of the Tarquins.

Segni is an Italian town and comune located in Lazio. The city is situated on a hilltop in the Lepini Mountains and overlooks the valley of the Sacco River.

The Rape of Lucrece (1594) is a narrative poem by William Shakespeare about the legendary Roman noblewoman Lucretia. In his previous narrative poem, Venus and Adonis (1593), Shakespeare had included a dedicatory letter to his patron, the Earl of Southampton, in which he promised to compose a "graver labour". Accordingly, The Rape of Lucrece has a serious tone throughout.

Lucius Junius Moderatus Columella was a prominent Roman writer on agriculture in the Roman Empire.
Lucius is a masculine given name which began use as Lucius, abbreviated L., one of the small group of common Latin forenames found in the culture of ancient Rome. Lucius probably derives from Latin word lux, meaning "light", related to the Latin verb lucere and cognate to the name Lucas. Another proposed etymology is derivation from Etruscan Lauchum meaning "king", which was more directly transferred into Latin as Lucumo.

Tarquinia, formerly Corneto, is an old city in the province of Viterbo, Lazio, Central Italy, known chiefly for its ancient Etruscan tombs in the widespread necropoleis, or cemeteries. Tarquinia was designated as a UNESCO World Heritage site, acknowledging its exceptional contribution to our understanding of Etruscan civilization.

Publius Valerius Poplicola or Publicola was one of four Roman aristocrats who led the overthrow of the monarchy, and became a Roman consul, the colleague of Lucius Junius Brutus in 509 BC, traditionally considered the first year of the Roman Republic.

The Rutuli or Rutulians were an ancient people in Italy. The Rutuli were located in a territory whose capital was the ancient town of Ardea, located about 35 km southeast of Rome.

The gens Tarquinia was a plebeian family at ancient Rome, usually associated with Lucius Tarquinius Priscus and Lucius Tarquinius Superbus, the fifth and seventh Kings of Rome. Most of the Tarquinii who appear in history are connected in some way with this dynasty, but a few appear during the later Republic, and others from inscriptions, some dating as late as the fourth century AD.
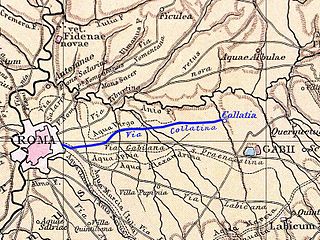
Collatia was an ancient town of central Italy, c. 15 km northeast of Rome by the Via Collatina.
Demaratus, frequently called Demaratus of Corinth, was the father of Lucius Tarquinius Priscus, the fifth King of Rome, the grandfather or great-grandfather of Lucius Tarquinius Superbus, the seventh and last Roman king, and an ancestor of Lucius Junius Brutus and Lucius Tarquinius Collatinus, the first consuls of the Roman Republic.

Sextus Tarquinius was one of the sons of the last king of Rome, Lucius Tarquinius Superbus. In the original account of the Tarquin dynasty presented by Fabius Pictor, he is the second son, between Titus and Arruns. However, according to Livy and Dionysius of Halicarnassus, he was either the third or first son, respectively. According to Roman tradition, his rape of Lucretia was the precipitating event in the overthrow of the monarchy and the establishment of the Roman Republic.

Carsoli is a town and comune in the province of L'Aquila, Abruzzo. The ancient Roman city lies 4 kilometres (2.5 mi) southwest of the modern town.

Lucius Tarquinius Ar. f. Ar. n. Collatinus was one of the first two consuls of the Roman Republic in 509 BC, together with Lucius Junius Brutus. The two men had led the revolution which overthrew the Roman monarchy. He was forced to resign his office and go into exile as a result of the hatred he had helped engender in the people against the former ruling house.
The Battle of Silva Arsia was a battle in 509 BC between the republican forces of ancient Rome and Etruscan forces of Tarquinii and Veii led by the deposed Roman king Lucius Tarquinius Superbus. It resulted in victory to the nascent Roman Republic.

Spurius Lucretius Tricipitinus is a semi-legendary figure in early Roman history. He was the first Suffect Consul of Rome and was also the father of Lucretia, whose rape by Sextus Tarquinius, followed by her suicide, resulted in the dethronement of King Lucius Tarquinius Superbus, therefore directly precipitating the founding of the Roman Republic. It is believed that Lucretius and his accomplishments are at least partly mythical and most ancient references to him were penned by Livy and Plutarch.

In Rome's early semi-legendary history, Tarquinia was the daughter of Lucius Tarquinius Priscus, the fifth king of Rome,. Her father, Lucius Tarquinius Priscus, gave her in marriage to Servius Tullius, the sixth king of Rome. She was the mother of Lucius Junius Brutus, who overthrew the monarchy and became one of Rome's first consuls in 509 BC. She had another son, who was put to death by Superbus after he took the Roman rule from Servius.
The overthrow of the Roman monarchy was an event in ancient Rome that took place between the 6th and 5th centuries BC where a political revolution replaced the then-existing Roman monarchy under Lucius Tarquinius Superbus with a republic. The details of the event were largely forgotten by the Romans a few centuries later; later Roman historians presented a narrative of the events, traditionally dated to c. 509 BC, but it is largely believed to be fictitious by modern scholars.