Tre Taverne was a place on the ancient Appian Way, about 50 km from Rome, designed for the reception of travellers, as the name indicates.

Lanuvium, modern Lanuvio, is an ancient city of Latium vetus, some 32 kilometres (20 mi) southeast of Rome, a little southwest of the Via Appia.

Segni is an Italian town and comune located in Lazio. The city is situated on a hilltop in the Lepini Mountains and overlooks the valley of the Sacco River.

Ardea is an ancient town and comune (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Rome Capital, 35 kilometres south of Rome and about 4 kilometres from today's Mediterranean coast.
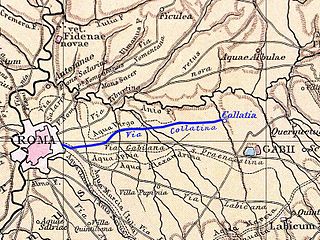
Collatia was an ancient town of central Italy, c. 15 km northeast of Rome by the Via Collatina.

Crustumerium was an ancient town of Latium, on the edge of the Sabine territory, near the headwaters of the Allia, not far from the Tiber.
The Via Laurentina is the name borne by an ancient and a modern road of Italy, both leading southwards from Rome.

The Circus of Maxentius is an ancient structure in Rome, Italy, part of a complex of buildings erected by emperor Maxentius on the Via Appia between AD 306 and 312. It is situated between the second and third miles of the Via Appia, between the basilica and catacombs of San Sebastiano and the imposing late republican tomb of Caecilia Metella, which dominates the hill that rises immediately to the east of the complex. It is part of the Appian Way Regional Park.

Vicovaro is a comune (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Rome in the Italian region Lazio, located about 45 kilometres (28 mi) northeast of Rome.

Isola Sacra is situated in the Lazio region of Italy south of Rome, near the Tyrrhenian Sea. It is part of the town of Fiumicino.
Ad Turres was an ancient city of Etruria. Ad Turres stood on the Via Aurelia, 10 miles from Lorium and 12 miles from Pyrgi. The location of Ad Turres is not precisely known; the editors of the Barrington Atlas of the Greek and Roman World tentatively place it near Palidoro, comune of Rome, Province of Rome, Lazio, Italy. The site is included on the Peutinger Table.

The Lancia Ardea is a small family car produced by Italian car manufacturer Lancia between 1939 and 1953. Its unusually short bonnet reportedly contained the smallest V4 engine ever commercialized in a small family car.

Via Asinaria was an ancient Roman road that started from Porta Asinaria in the Aurelian walls (Rome). It was somehow connected with the Via Latina, as it is reported that Belisarius, during its advance on Rome, left the Via Latina to enter the city from Porta Asinaria; the latter was considered one of the main accesses for those coming from the south, as in ancient times the 17th-century Porta San Giovanni didn't exist.
Careiae was an ancient town of Etruria, on the Via Clodia, the first station beyond Veii. The town is mentioned by Frontinus and appears in the Tabula Peutingeriana. Its site is at the abandoned village of Galera, approximately 25 km from Rome.

Fregenae was a maritime town of ancient Etruria, situated between Alsium and the mouth of the Tiber. The modern Fregene is an Italian hamlet (frazione) of Fiumicino, in the Metropolitan City of Rome Capital, Lazio. As of 2012 its population was of 6,445.

Saxa Rubra was a village and station on the Roman Flaminian Way, 9 miles (14 km) from Rome, Italy.

Casal Rotondo is the largest tomb on the Appian Way, to the southeast of Rome, Italy. A small farmhouse has been constructed on the top.

Via Cristoforo Colombo is a street in Rome (Italy) that links the historic centre to Ostia. Along most of its route, the street has three lanes for each direction of movement. With its 27 kilometres (17 mi) length it is the longest Italian road among those included within the borders of a single municipality and, in several stretches, the largest in Italy.

Musarna is an Etruscan settlement located approximately 10 km west of Viterbo, Italy. The site was discovered in 1849 and has been the site of excavations carried out by the École française de Rome since 1983.















