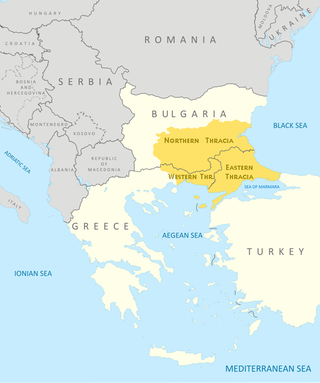
Thrace is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe. Bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Sea to the east, it comprises present-day southeastern Bulgaria, northeastern Greece, and the European part of Turkey, roughly the Roman Province of Thrace. Lands also inhabited by ancient Thracians extended in the north to modern-day Northern Bulgaria and Romania and to the west into Macedonia.

Sozopol is an ancient seaside town located 35 km south of Burgas on the southern Bulgarian Black Sea Coast. Today it is one of the major seaside resorts in the country, known for the Apollonia art and film festival that is named after one of the town's ancient names.

Burgas, sometimes transliterated as Bourgas, is the second largest city on the Bulgarian Black Sea Coast in the region of Northern Thrace and the fourth-largest city in Bulgaria after Sofia, Plovdiv, and Varna, with a population of 203,000 inhabitants, while 277,922 live in its urban area. It is the capital of Burgas Province and an important industrial, transport, cultural and tourist centre.

Pomorie, historically known as Anchialos, is a town and seaside resort in southeastern Bulgaria, located on a narrow rocky peninsula in Burgas Bay on the southern Bulgarian Black Sea Coast.

Western Thrace or West Thrace, also known as Greek Thrace or Aegean Thrace, is a geographic and historical region of Greece, between the Nestos and Evros rivers in the northeast of the country; East Thrace, which lies east of the river Evros, forms the European part of Turkey, and the area to the north, in Bulgaria, is known as Northern Thrace.

The Nestos, Mesta is a river in Bulgaria and Greece. It rises in the Rila Mountains and flows into the Aegean Sea near the island of Thasos. It plunges down towering canyons toward the Aegean Sea through mostly metamorphic formations. At the end, the main stream spreads over the coastal plain of Chrysoupolis and expands as a deltaic system with freshwater lakes and ponds forming the Nestos delta. The length of the river is 230 km (140 mi), of which 126 km (78 mi) flow through Bulgaria and the rest in Greece. Its drainage area is 5,184 km2 (2,002 sq mi), of which 66% in Bulgaria. It forms some gorges in Rila and Pirin. The longest gorge between Pirin to the west and the Rhodope Mountains to the east is the 25-km long Momina Klisura in Bulgaria.

Kaliakra is a cape in the Southern Dobruja region of the northern Bulgarian Black Sea Coast, which ends with a long and narrow headland 12 kilometres (7 mi) east of Kavarna, 60 kilometres (37 mi) northeast of Varna and 65 kilometres (40 mi) southwest of Mangalia. The coast is steep with vertical cliffs reaching 70 metres (230 ft) down to the sea. Kaliakra is a nature reserve, where dolphins and cormorants can be observed. It sits on the Via Pontica, a major bird migration route from Africa into Eastern and Northern Europe. Many rare and migrant birds can be seen here in spring and autumn and, like much of this coastline, is home to several rare breeding birds. The rest of the reserve also has unusual breeding birds; saker falcon, lesser grey shrike and a host of others.

The Despotate of Dobruja or Principality of Karvuna was a 14th-century quasi-independent Bulgarian polity in the region of modern Dobruja, that split off from the Second Bulgarian Empire under the influence of the Byzantine Empire. The Despotate of Dobruja existed from 1356 to 1411.

Shabla is a town and seaside resort in northeastern Bulgaria, administrative centre of the Shabla Municipality part of Dobrich Province. Shabla municipality includes the following villages: Bojanovo, Chernomortsi, Durankulak, Ezerets, Gorichane, Gorun, Granichar, Krapets, Prolez, Smin, Staevtsi, Tvarditsa, Tyulenovo, Vaklino and Zahari Stoyanovo. As of December 2009, the town itself had a population of 3,586 inhabitants. It is situated on the Bulgarian Black Sea Coast in the vicinity of the salt-water Lake Shabla and Bulgaria's easternmost point, Cape Shabla.

St. Thomas Island or Zmiyski ostrov, is a Bulgarian island in the Black Sea.

Devnya is a town in Varna Province, Northeastern Bulgaria, located about 25 km away to the west from the city of Varna and The Black Sea Coast. It is the administrative centre of the homonymous Devnya Municipality. As of December 2009, the town has a population of 8,383 inhabitants.

East Thrace or Eastern Thrace, also known as Turkish Thrace or European Turkey, is the part of Turkey that is geographically a part of Southeast Europe. It accounts for 3.03% of Turkey's land area and 15% of its population. The largest city is Istanbul, which straddles the Bosporus between Europe and Asia. East Thrace is of historic importance as it is next to a major sea trade corridor and constitutes what remains of the once-vast Ottoman region of Rumelia. It is currently also of specific geostrategic importance because the sea corridor, which includes two narrow straits, provides access to the Mediterranean Sea from the Black Sea for the navies of five countries: Russia, Ukraine, Romania, Bulgaria, and Georgia. The region also serves as a future connector of existing Turkish, Bulgarian, and Greek high-speed rail networks.
Rezovo is a village and seaside resort in southeastern Bulgaria, part of Tsarevo Municipality, Burgas Province, in the coastal Strandzha geographical region.

The nature conservation site Poda was declared a protected area in 1989 by the Bulgarian Ministry of Water and Environment. It was the first protected area in Bulgaria that is completely managed and maintained by a non-governmental organization, the Bulgarian Society for the Protection of Birds (BSPB). BSPB prepares and implements activities adopted by the Council of Minister's Management Plan, but receives its funding completely from entrance fees, souvenirs sold, and donations. Through this arrangement, it aims to be a sustainable model for nature conservation, environmental education, and eco-tourism.

Greek colonisation refers to the expansion of Archaic Greeks, particularly during the 8th–6th centuries BC, across the Mediterranean Sea and the Black Sea.

Bolata is a small cove and Nature reserve located in the Northern Bulgarian Black Sea Coast.

Archaeological Museum is the oldest museum in Burgas, Bulgaria, preserving the cultural and historical heritage of some of the most ancient towns in the present Bulgarian territory - Sozopol (Apollonia), Nessebar (Messambria), Pomorie (Anhialo) and others.

Aquae Calidae, also known as Therma and Thermopolis in the Middle Ages, was an ancient town in Thrace located in the territory of today's Bulgarian port city of Burgas on the Black Sea. It was built around thermal baths using the hot springs and became one of the most important spa centres of ancient times.

Antheia was a town on the western coast of the Pontus Euxinus in ancient Thrace, a colony of the Milesians and Phocaeans. It later bore the Latin name Anthium, and was the precursor settlement to Apollonia Pontica. It was located on the Gulf of Burgas between the modern cities of Burgas and Sozopol in Bulgaria.

The Black Sea Biogeographic Region is a biogeographic region of land bordering the west and south of the Black Sea, as defined by the European Environment Agency.



















