
AD 14 (XIV) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Pompeius and Appuleius. The denomination AD 14 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

The 10s decade ran from January 1, AD 10, to December 31, AD 19.

AD 15 (XV) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Caesar and Flaccus. The denomination AD 15 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Carniola is a historical region that comprised parts of present-day Slovenia. Although as a whole it does not exist anymore, Slovenes living within the former borders of the region still tend to identify with its traditional parts Upper Carniola, Lower Carniola, and to a lesser degree with Inner Carniola. In 1991, 47% of the population of Slovenia lived within the borders of the former Duchy of Carniola.

Vipava is a town in western Slovenia. It is the largest settlement and the seat of the Municipality of Vipava. Vipava is located near the numerous sources of the Vipava River, in the upper Vipava Valley, 102 metres (335 ft) above sea level. Historically, it is part of the traditional region of Inner Carniola, but it is now generally regarded as part of the Slovenian Littoral.

Aquileia is an ancient Roman city in Italy, at the head of the Adriatic at the edge of the lagoons, about 10 kilometres (6 mi) from the sea, on the river Natiso, the course of which has changed somewhat since Roman times. Today, the city is small, but it was large and prominent in classical antiquity as one of the world's largest cities with a population of 100,000 in the 2nd century AD and is one of the main archaeological sites of northern Italy. In late antiquity the city was the first city in the Italian Peninsula to be sacked by Attila the Hun.

Ajdovščina is a town in the Vipava Valley, Slovenia. It is the administrative seat of the Municipality of Ajdovščina.

Legio XIII Gemina, in English the 13th Twin Legion was a legion of the Imperial Roman army. It was one of Julius Caesar's key units in Gaul and in the civil war, and was the legion with which he crossed the Rubicon in January, perhaps the 10th, 49 BC. The legion appears to have still been in existence in the 5th century AD. Its symbol was the lion.

Trojane is a settlement in the Municipality of Lukovica in central Slovenia. It lies in the northern part of the Sava Hills, on a hill near the border of two Slovene regions, Carniola and Styria. Until the freeway was finished in 2005, Trojane was on the main route from Ljubljana to Maribor.

Emona or Aemona was a Roman castrum, located in the area where the navigable Nauportus River came closest to Castle Hill, serving the trade between the city's settlers – colonists from the northern part of Roman Italy – and the rest of the empire. Emona was the region's easternmost city, although it was assumed formerly that it was part of the Pannonia or Illyricum, but archaeological findings from 2008 proved otherwise. From the late 4th to the late 6th century, Emona was the seat of a bishopric that had intensive contacts with the ecclesiastical circle of Milan, reflected in the architecture of the early Christian complex along Erjavec Street in present-day Ljubljana.

The Vipava Valley is a valley in the Slovenian Littoral, roughly between the village of Podnanos to the east and the border with Italy to the west. The main towns are Ajdovščina and Vipava.
The Via Annia was the Roman road in Venetia in north-eastern Italy. It run on the low plains of the lower River Po and of the lower Veneto and Friuli Venezia Giulia regions, an area which had many rivers and large marsh areas and bordered the coastal lagoons. It linked Atria to Aquileia, passing through Patavium. Then it got to the mainland coast of the Lagoon of Venice near today's Mestre and passed through Altinum. After this, it went through Iulia Concordia, which was further inland. It was paved only through the main towns. The rest was gravelled. It was six to eighteen metre wide. It played an important part in the Romanization of the region.
Nauportus(Navport, Navportus), was an ancient Roman town in Pannonia Superior on the road from Aquileia to Emona with a port at the Nauportus river, now the Ljubljanica River, Slovenia.
Drama is a village in the Municipality of Šentjernej in southeastern Slovenia. The area is part of the traditional region of Lower Carniola. It is now included in the Southeast Slovenia Statistical Region. It includes the hamlets of Dolenja Gomila, formerly an independent settlement, to the west and Otok to the northwest.

The Postojna Gate, less often the Postojna Gap, named after the local town of Postojna, is a major mountain pass of the Dinaric Alps. It lies in southwestern Slovenia, between the Hrušica Plateau to the north and the Javornik Hills to the south, at an elevation of 610 metres (2,000 ft). It formed due to tectonic subsidence and fluvial erosion by the Pivka River, which in the Pliocene flew superficially in this section. The terrain is significantly karstified. This relatively wide pass enables for the easiest passage from northearn Italy and northwestern Adriatic Sea to the Pannonian Plain, and had a very important strategic role in the past. Today, a rail line and the Slovenian A1 freeway traverse it.

Claustra Alpium Iuliarum was a defense system within the Roman Empire between Italia and Pannonia that protected Italy from possible invasions from the East. It secured the Postojna Gate, the land link between the eastern and western part of the empire, and thus the Claustra represented an inner border defense of the empire. Unlike a linear rampart, the Claustra consisted of a series of interconnected fortifications with its center at Castra ad Fluvium Frigidum ; other important fortresses were Ad Pirum on today's Hrušica Plateau and Tarsatica, now a part of the city of Rijeka. They had been governed from the town of Aquileia.

Castra ad Fluvium Frigidum, also simply Castra, referred to as mutatio Castra in Itinerarium Burdigalense, was a Late-Roman fortress (castrum) which constituted the centre of Claustra Alpium Iuliarum, an Ancient Roman defensive system of walls and towers stretching from the Gail Valley to the Učka mountain range. On its grounds, the Late Medieval market settlement of Ajdovščina developed.

Ljudmila Plesničar Gec was a Slovenian archaeologist who specialized in uncovering the Roman history of Ljubljana. Best known for her excavations at Emona, she received the Valvasor Prize in 1985, the Golden Order of Freedom of the Republic of Slovenia in 1997, and was honored in 2000 with the Lifetime Achievement Award from the Archaeological Society of Slovenia.
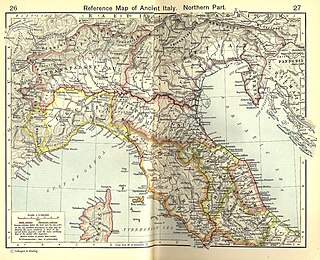
Venetia et Histria was an administrative subdivision in the northeast of Roman Italy. It was originally created by Augustus as the tenth regio in 7 AD alongside the nine other regiones. The region had been one of the last regions of Italy to be incorporated into the Roman Empire. It was later renamed by Diocletian the VIII provincia Venetia et Histria in the third century. Its capital was at Aquileia, and it stretched geographically from the Arsia River in the east in what is now Croatia to the Abdua in the current Italian region of Lombardy and from the Alps to the Adriatic Sea.

Roman Aquileia was founded in 181 BC by the Romans, in the territory of the ancient Carni:
In the same year [181 BC] the colony of Aquileia was deducted in the territory of the Gauls. 3 000 infantrymen received 50 iugera each, the centurions 100, the horsemen 140. The triumvirs who founded the colony were Publius Scipio Nasica, Gaius Flaminius, and Lucius Manlius Acidinus.

















