


There were many areas annexed by Nazi Germany both immediately before and throughout the course of World War II. Territories that were part of Germany before the annexations were known as the "Altreich" (Old Reich). [1]



There were many areas annexed by Nazi Germany both immediately before and throughout the course of World War II. Territories that were part of Germany before the annexations were known as the "Altreich" (Old Reich). [1]


The respective dates of annexation should be viewed with caution, as various sources offer differing statements.
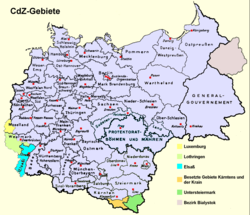
Fully annexed territories also include those that were subordinate to a head of the civil administration (CdZ). These territories were de facto, but in some cases never formally, incorporated into the Reich. One example is Luxembourg, which was de facto incorporated in August 1940. However, this did not formally occur until August 1942.
The Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia and the General Government were considered Reich territory, but were administered separately and were therefore semi-autonomous territories.
The Operational zones on the other hand, were never considered Reich territory.
According to the Treaty of Versailles, the Territory of the Saar Basin was split from Germany for at least 15 years. In 1935, the Saarland rejoined Germany in a lawful way after a plebiscite.
The territories listed below are those that were fully annexed into Germany proper.
The territories listed below are those that were partially incorporated into the Greater German Reich.
| Date of establishment | Preceded by | Succeeded by |
|---|---|---|
| 16 Mar 1939 [22] |
| Date of establishment | Preceded by | Succeeded by |
|---|---|---|
| 26 Oct 1939 [23] [24] | ||
| 1 Aug 1941 [25] | ||
| Date of establishment | Preceded by | Succeeded by |
|---|---|---|
| 10 Sep 1943 [26] | ||
In the coming Nazi New Order, other lands were considered for annexation sooner or later. Territorially speaking, this encompassed the already-enlarged German Reich itself (consisting of pre-1938 Germany proper, Austria, Bohemia, Moravia, Czech Silesia, Alsace-Lorraine, Eupen-Malmedy, Memel, Lower Styria, Upper Carniola, Southern Carinthia, Danzig, and Poland), the Netherlands, the Flemish part of Belgium, Luxembourg, Denmark, Norway, Sweden, Iceland, Liechtenstein, and at least the German-speaking parts of Switzerland. [27] The goal was to unite all or as many as possible ethnic Germans and Germanic peoples, including non-Germanic speaking ones considered "Aryans", in a Greater Germanic Reich.
In Norway, construction of the city of Nordstern began during the German occupation of Norway. It was intended to be adminstred directly from Germany. [28]
The eastern Reichskommissariats in the vast stretches of Ukraine and Russia were also intended for future integration into that Reich, with plans for them stretching to the Volga or even beyond the Urals, where the potential westernmost reaches of Imperial Japanese influence would have existed, following an Axis victory in World War II. They were deemed of vital interest for the survival of the German nation, as it was a core tenet of Nazism that Germany needed "living space" ( Lebensraum ), creating a "pull towards the East" ( Drang nach Osten ) where that could be found and colonized.
North-East Italy was also eventually to be annexed, including both the Operational Zone of the Adriatic Littoral and the Operational Zone of the Alpine Foothills, but also the Venice region. [29] [30] Goebbels went as far as to suggest taking control of Lombardy as well:
Whatever was once an Austrian possession we must get back into our own hands. The Italians by their infidelity and treachery have lost any claim to a national state of the modern type. — Joseph Goebbels, September 1943 [31]
The annexation of the entire North Italy was also suggested in the long run. [32]