Cometabolism is defined as the simultaneous degradation of two compounds, in which the degradation of the second compound depends on the presence of the first compound. This is in contrast to simultaneous catabolism, where each substrate is catabolized concomitantly by different enzymes. Cometabolism occurs when an enzyme produced by an organism to catalyze the degradation of its growth-substrate to derive energy and carbon from it is also capable of degrading additional compounds. The fortuitous degradation of these additional compounds does not support the growth of the bacteria, and some of these compounds can even be toxic in certain concentrations to the bacteria.
N-Acetylglutamate synthase (NAGS) is an enzyme that catalyses the production of N-acetylglutamate (NAG) from glutamate and acetyl-CoA.
In enzymology, a succinylglutamate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.1.71) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glycine dehydrogenase (cyanide-forming) (EC 1.4.99.5) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an ornithine racemase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
In enzymology, an acetate CoA-transferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a succinyl-CoA:(R)-benzylsuccinate CoA-transferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an arginine deiminase (EC 3.5.3.6) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-succinylarginine dihydrolase (EC 3.5.3.23) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a succinylglutamate desuccinylase (EC 3.5.1.96) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 3-oxoadipyl-CoA thiolase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an acetylornithine transaminase (EC 2.6.1.11) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an arginine-pyruvate transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a succinylornithine transaminase (EC 2.6.1.81) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
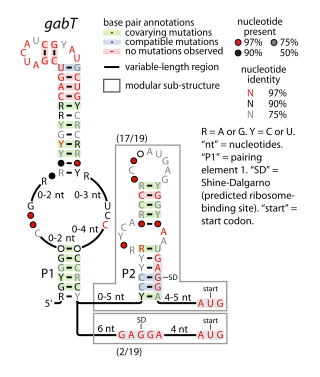
The gabT RNA motif is the name of a conserved RNA structure identified by bioinformatics whose function is unknown. The gabT motif has been detected exclusively in bacteria within the genus Pseudomonas, and is found only upstream of gabT genes, and downstream to gabD genes.

The rsmX gene is part of the Rsm/Csr family of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). Members of the Rsm/Csr family are present in a diverse range of bacteria, including Escherichia coli, Erwinia, Salmonella, Vibrio and Pseudomonas. These ncRNAs act by sequestering translational repressor proteins, called RsmA, activating expression of downstream genes that would normally be blocked by the repressors. Sequestering of target proteins is dependent upon exposed GGA motifs in the stem loops of the ncRNAs. Typically, the activated genes are involved in secondary metabolism, biofilm formation and motility.
In molecular biology, members of the ArgJ protein family are bifunctional protein that catalyses the first and fifth steps in arginine biosynthesis. The structure has been determined for glutamate N-acetyltransferase 2, an ArgJ-like protein from Streptomyces clavuligerus.
In molecular biology, the arginine repressor (ArgR) is a repressor of prokaryotic arginine deiminase pathways.

Rhamnolipids are a class of glycolipid produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, amongst other organisms, frequently cited as bacterial surfactants. They have a glycosyl head group, in this case a rhamnose moiety, and a 3-(hydroxyalkanoyloxy)alkanoic acid (HAA) fatty acid tail, such as 3-hydroxydecanoic acid.
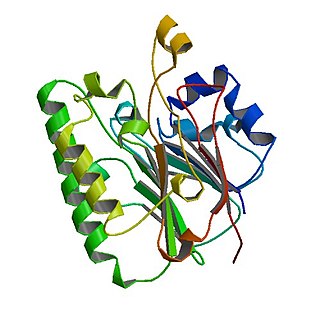
The Catabolite repression control (Crc) protein participates in suppressing expression of several genes involved in utilization of carbon sources in Pseudomonas bacteria. Presence of organic acids triggers activation of Crc and in conjunction with the Hfq protein genes that metabolize a given carbon source are downregulated until another more favorable carbon source is depleted. Crc-mediated regulation impact processes such as biofilm formation, virulence and antibiotic susceptibility.








