The Albanian National Awakening, commonly known as the Albanian Renaissance or Albanian Revival, is a period throughout the 19th and 20th century of a cultural, political, and social movement in the Albanian history where the Albanian people gathered strength to establish an independent cultural and political life, as well as the country of Albania.

Preveza is a city in the region of Epirus, northwestern Greece, located on the northern peninsula of the mouth of the Ambracian Gulf. It is the capital of the regional unit of Preveza, which is the southern part of the region of Epirus. The Aktio-Preveza Immersed Tunnel –the first, and so far only, undersea tunnel in Greece– was completed in 2002. The 1,570 m (5,150 ft) long immersed tunnel connects Preveza in the north, to Aktio of western Acarnania to the south. The ruins of the ancient city of Nicopolis lie 7 kilometres north of Preveza.

The League of Prizren, officially the League for the Defense of the Rights of the Albanian Nation, was an Albanian political organization that was officially founded on June 10, 1878 in the old town of Prizren in the Kosovo Vilayet of the Ottoman Empire. It was suppressed in April 1881.
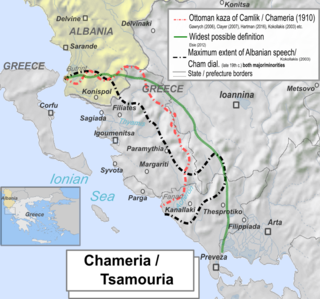
Chameria is a term used today mostly by Albanians to refer to parts of the coastal region of Epirus in southern Albania and Greece, traditionally associated with the Albanian ethnic subgroup of the Chams. For a brief period (1909-1912), three kazas were combined by the Ottomans into an administrative district called Çamlak sancak. During the interwar period, the toponym was in common use and the official name of the area above the Acheron river in all Greek state documents. Today it is obsolete in Greek, surviving in some old folk songs. Most of what is called Chameria is divided between parts of the Greek regional units of Thesprotia, Preveza, and Ioannina ; and the municipality of Konispol at the southernmost extremity of Albania. Apart from geographic and ethnographic usages, in contemporary times within Albania the toponym has also acquired irredentist connotations.

The Parliament of Albania or Kuvendi is the unicameral representative body of the citizens of the Republic of Albania; it is Albania's legislature. The Parliament is composed of no less than 140 members elected to a four-year term on the basis of direct, universal, periodic and equal suffrage by secret ballot. The Parliament is presided over by the Speaker, who is assisted by at least one deputy speaker. The electoral system is based on party-list proportional representation. There are 12 multi-seat constituencies, corresponding to the country's counties.

Abdyl Dume bey Frashëri was an Ottoman Albanian civil servant, politician during the First Constitutional Era of the Ottoman Empire, and one of the first Albanian political ideologues of the Albanian National Awakening. During his lifetime Frashëri endeavoured to instill among Albanians patriotism and a strong identity while promoting a reform program based on Albanian language education and literature.

Haxhi Zekë Byberi mostly known as Haxhi Zeka was an Albanian nationalist leader, a member of the League of Prizren, while in 1899 he was part of the establishment and leadership of the League of Peja, another organization seeking protection of Albanians territories from Balkan states. Zeka was assassinated by a Serbian agent in 1902.

The Albanian Declaration of Independence was the declaration of independence of Albania from the Ottoman Empire. Independent Albania was proclaimed in Vlorë on 28 November 1912. Six days later the Assembly of Vlorë formed the first Government of Albania which was led by Ismail Qenali and the Council of Elders (Pleqnia).
Veli Gërra was a leading member of the Albanian independence movement and one of the delegates of Albanian Declaration of Independence, representing the region of Chameria.
Jakup Veseli was a leading figure in the Albanian independence movement one of the delegates of Albanian Declaration of Independence, representing the region of Chameria.

Abidin Pasha Dino or Abedin bey Dino, also Abedin Pasha was an Albanian patriot, politician, ideologue and diplomat. As a rilindas involved in the Albanian National Awakening, he was one of the founders of the League of Prizren and its chief representative for Epirus (1878). Dino was one of the main promoters in the need for the creation of the Autonomous Albanian Vilayet under the Ottoman suzerainty.

The Vilayet of Janina, Yanya or Ioannina was a first-level administrative division (vilayet) of the Ottoman Empire, established in 1867. In the late 19th century, it reportedly had an area of 18,320 square kilometres (7,070 sq mi). It was created by merging the Pashalik of Yanina and the Pashalik of Berat with the sanjaks of Janina, Berat, Ergiri, Preveze, Tırhala and Kesriye. Kesriye was later demoted to kaza and bounded to Monastir Vilayet and Tırhala was given to Greece in 1881.

The Congress of Dibër was a congress held by members of Albanian committee in Debar from July 23 to July 29, 1909. The congress was chaired by Vehbi Dibra, Grand Mufti of the Sanjak of Dibra and was sponsored by the government of the Young Turks. It was held on the first anniversary of the Young Turk Revolution and was a countermeasure on the Latin script based Albanian alphabet which came out of the Congress of Manastir.
Ahmet Koronica was an Albanian military commander and regional leader of the League of Prizren.

The Attack against Mehmed Ali Pasha, known in Albanian historiography as the Action of Gjakova, was undertaken from 3–6 September 1878 by the Gjakova Committee of the League of Prizren in the estate of Abdullah Pasha Dreni near Gjakova. During the battle Mehmed Ali Pasha, the Ottoman marshal who was to overview the cession of the predominantly Albanian Plav and Gusinje region to the Principality of Montenegro, Abdullah Pasha Dreni, a notable official of the region and former member of the league, many Ottoman soldiers, and volunteers of the Gjakova Committee were killed.

The Sanjak of Preveza, also once known as the Liva of Preveza, was a sanjak of the Ottoman Empire named for its capital at Preveza in southern Epirus, now part of northwestern Greece. The sanjak existed from its formation in 1863 until its conquest in the First Balkan War and reorganization in 1915 as the Preveza Prefecture of the Kingdom of Greece.

Mihal Turtulli Bey, also known as Michail Tourtoulis or Dr. Turtulli, was an Albanian oculist, politician, member of the High Council of State, and representative of Albania at the Paris Peace Conference of 1919.
The Second Congress of Manastir was an Albanian congress held on 2–3 April 1910 in Manastir, back then Ottoman Empire, today's Bitola in the Republic of North Macedonia. It dealt with the challenges that the Albanian language and schools faced at the time within the context of the empire, and the platform to overcome them.

Menduh Zavalani (1889–1914) was an Albanian revolutionary and political leader active during the last years of the Albanian National Awakening. He formed his own revolutionary band and was one of the leaders that liberated Përmet and the environs from the Ottoman Empire. Menduh was an appointed delegate from his hometown Korça to the Albanian National Congress that proclaimed the Independence of Albania. In the intellectual level Menduh was noted for the translation of Friedrich Schiller's drama Wilhelm Tell into Albanian. He was assassinated at a very young age near Pogradec by a local collaborationist band.
The Convention of Mat was organized on 7 November 1594 by Albanian leaders fighting against the Ottoman Empire. Mat was chosen as the place of the meeting due to its role in Albanian revolts of the 16th century. The aim was a better organization of the revolts to achieve independence from the Ottoman Empire. The convention decided that help should be sought from the Pope, and for negotiations were chosen Tom Plezha, Mark Gjini and Nikollë Mekajshi. However, the Pope refused to give help, claiming that it was not the right time to fight the Ottoman Empire. Another decision of Albanian leaders was to not let the Republic of Venice know about their plans as the latter did not want to open a new conflict with the Ottomans. The news came out and Venetians managed to divide the organizers of the convention between themselves. In the following two years, Albanian leaders continued their work to get help from Christian powers, taking heart from geopolitical circumstances. In 1596, 10,000 men marched towards Vlora in hope of receiving arms from Spain but the arms sent were confiscated by Venetians. The events damaged the relations between Albanian leaders and Christian powers but did not weaken the efforts for independence.













