
Westmorland County is a county in New Brunswick, a province of Canada. It is in the south-eastern part of the province. It contains the fast-growing commercial centre of Moncton and its northern and eastern suburbs. Also located in the county are the university town of Sackville and the local tourist destination of Shediac.

Sackville is a former town in southeastern New Brunswick, Canada. It held town status prior to 2023 and is now part of the town of Tantramar.
Route 2 is a major provincial highway in the Canadian province of New Brunswick, carrying the main route of the Trans-Canada Highway in the province. The highway connects with Autoroute 85 at the border with Quebec and Highway 104 at the border with Nova Scotia, as well as with traffic from Interstate 95 in the U.S. state of Maine via the short Route 95 connector. A core route in the National Highway System, Route 2 is a four-lane freeway in its entirety, and directly serves the cities of Edmundston, Fredericton, and Moncton.

The Tantramar Marshes, also known as the Tintamarre National Wildlife Area, is a tidal saltmarsh around the Bay of Fundy on the Isthmus of Chignecto. The area borders between Route 940, Route 16 and Route 2 near Sackville, New Brunswick. The government of Canada proposed the boundaries of the Tantramar Marshes in 1966 and was declared a National Wildlife Area in 1978.
The Isthmus of Chignecto is an isthmus bordering the Maritime provinces of New Brunswick and Nova Scotia that connects the Nova Scotia peninsula with North America.
Beaubassin was an important Acadian village and trading centre on the Isthmus of Chignecto in what is now Nova Scotia, Canada. The area was a significant place in the geopolitical struggle between the British and French empires. It was established in the 1670s on an upland close to an extensive area of saltwater marsh. Settlers reclaimed the land to engage in cattle ranching and trade.
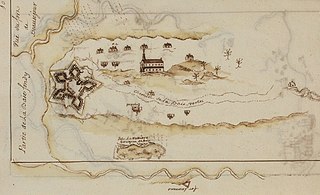
Fort Beauséjour, renamed Fort Cumberland in 1755, is a large, five-bastioned fort on the Isthmus of Chignecto in eastern Canada, a neck of land connecting the present-day province of New Brunswick with that of Nova Scotia. The site was strategically important in Acadia, a French colony that included primarily the Maritimes, the eastern part of Quebec, and northern Maine of the later United States. The fort was built by the French from 1751 to 1752. They surrendered it to the British in 1755 after their defeat in the Battle of Fort Beauséjour, during the Seven Years' War. The British renamed the structure as Fort Cumberland. The fort was strategically important throughout the Anglo-French rivalry of 1749–63, known as the French and Indian Wars by British colonists. Less than a generation later, it was the site of the 1776 Battle of Fort Cumberland, when the British forces repulsed sympathisers of the American Revolution.
Route 16 is a two-lane highway in the Canadian province of New Brunswick. The 52 km (32 mi) route begins at Route 2 in Tantramar and ends at the midpoint of the Confederation Bridge, where it becomes Prince Edward Island Route 1.

Lieutenant-General Robert Monckton was an officer of the British Army and colonial administrator in British North America. He had a distinguished military and political career, being second in command to General James Wolfe at the battle of Quebec and later being named the Governor of the Province of New York. Monckton is also remembered for his role in a number of other important events in the French and Indian War, most notably the capture of Fort Beauséjour in Acadia, and the island of Martinique in the West Indies, as well as for his role in the deportation of the Acadians from British controlled Nova Scotia and also from French-controlled Acadia. The city of Moncton, New Brunswick, and Fort Monckton in Port Elgin, New Brunswick, are named for him. A second more important Fort Monckton in Gosport, England, is also named for him. It remains an active military establishment, and currently houses the British Secret Intelligence Service (MI6) training section. Monckton sat in the British House of Commons between 1774 and 1782. Although never legally married, he raised and was survived by three sons and a daughter.

Fort Gaspareaux was a French fort at the head of Baie Verte near the mouth of the Gaspareaux River and just southeast of the modern community of Strait Shores, New Brunswick, Canada, on the Isthmus of Chignecto. It was built during Father Le Loutre's War and is now a National Historic Site of Canada overlooking the Northumberland Strait.
Port Elgin is a former Canadian village in Westmorland County, New Brunswick. It is located near the Nova Scotia border at the mouth of the Gaspereaux River where it empties into the Northumberland Strait's Baie Verte and is now part of the rural community of Strait Shores.
Fort Lawrence is a Canadian rural community located on the Isthmus of Chignecto in Cumberland County, Nova Scotia, which is named after Fort Lawrence.

There are two major national parks. The warmest salt water beaches north of Virginia can be found on the Northumberland Strait, at Parlee Beach in Shediac. New Brunswick's signature natural attraction are only a half hour's drive down the Petitcodiac river valley. The Confederation Bridge to Prince Edward Island is only an hour's drive east of Moncton.
Point de Bute is an unincorporated community in Westmorland County, New Brunswick, Canada.
Mount Whatley is a community in the Canadian province of New Brunswick, located in Westmorland County on New Brunswick Highway 16. Mount Whatley is situated upon the Aulac Ridge, a prominent rise running west–east across the Tantramar Marshes on the Isthmus of Chignecto,on the shore of the Missaguash River which forms the southern part of the inter-provincial boundary with Nova Scotia.The community is linked by a small bridge to Fort Lawrence Nova Scotia.

Sackville is a civil parish in Westmorland County, New Brunswick, Canada.

LaPlanche Street is the historic connector between Nova Scotia and New Brunswick, Canada. Located on the Isthmus of Chignecto, LaPlanche crosses the Tantramar Marshes between Amherst, NS and Sackville, NB. Historically, it hosted the key forts of peninsular Nova Scotia and continental Acadia and witnessed the Battle of Fort Beauséjour, the key battle between the two colonies during the Seven Years' War, and the Battle of Fort Cumberland of the American Revolutionary War.
This is a bibliography of notable works on New Brunswick, Canada.
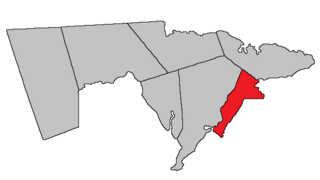
Westmorland is a civil parish in Westmorland County, New Brunswick, Canada.

Tantramar is a town in the Canadian province of New Brunswick. It was formed through the 2023 New Brunswick local governance reforms.












