
The family Sciomyzidae belongs to the typical flies (Brachycera) of the order Diptera. They are commonly called marsh flies, and in some cases snail-killing flies due to the food of their larvae.

Sandfly or sand fly is a colloquial name for any species or genus of flying, biting, blood-sucking dipteran (fly) encountered in sandy areas. In the United States, sandfly may refer to certain horse flies that are also known as "greenheads", or to members of the family Ceratopogonidae. The bites usually result in a small, intensely itchy bump or welt, the strength of which intensifies over a period of 5-7 days before dissipating. Moderate relief is achieved with varying success through the application of over the counter products such as Benadryl (ingested) or an analgesic cream such as After Bite. Outside the United States, sandfly may refer to members of the subfamily Phlebotominae within the Psychodidae. Biting midges (Ceratopogonidae) are sometimes called sandflies or no-see-ums. New Zealand sandflies are in the genus of sand fly Austrosimulium, a type of black fly.

A black fly or blackfly is any member of the family Simuliidae of the Culicomorpha infraorder. It is related to the Ceratopogonidae, Chironomidae, and Thaumaleidae. Over 2,200 species of black flies have been formally named, of which 15 are extinct. They are divided into two subfamilies: Parasimuliinae contains only one genus and four species; Simuliinae contains all the rest. Over 1,800 of the species belong to the genus Simulium.

The Nematocera are a suborder of elongated flies with thin, segmented antennae and mostly aquatic larvae. This group is paraphyletic and contains all flies except for species from suborder Brachycera, which includes more commonly known species such as the housefly or the common fruit fly. The equivalent clade to Nematocera is the whole Diptera, with Brachycera as a subclade. Families in Nematocera include mosquitoes, crane flies, gnats, black flies, and multiple families commonly known as midges. The Nematocera typically have fairly long, fine, finely-jointed antennae. In many species, such as most mosquitoes, the female antennae are more or less threadlike, but the males have spectacularly plumose antennae.

The Chamaemyiidae are a small family of acalyptrate flies with less than 200 species described worldwide. The larvae of these small flies are active and predatory and are often used for biological control of aphids, scale insects, and similar pests. Chamaemyiid fossils are poorly represented in amber deposits, but a few examples are known from the Eocene epoch onwards.

Leucocytozoon is a genus of parasitic alveolates belonging to the phylum Apicomplexa.
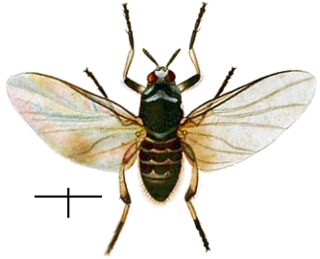
Simulium is a genus of black flies, which may transmit diseases such as onchocerciasis.

Culicoides is a genus of biting midges in the family Ceratopogonidae. There are over 1000 species in the genus, which is divided into many subgenera. Several species are known to be vectors of various diseases and parasites which can affect animals. The genus has a long fossil record, with earliest known fossils being from Burmese amber, around 99 million years old.
Ochlerotatus is a genus of mosquito. Until 2000, it was ranked as a subgenus of Aedes, but after Reinert's work, the clade was upgraded to the level of a genus. This change has resulted in the renaming of many subgenus species, and many aedini-related taxa are undergoing taxonomic revisions. Some authors are still using traditional taxonomic names in their publications.

The Simuliini is a tribe of black flies that contains over 2,000 species, with more than 1,800 in the genus Simulium. There are 19 living genera, and three genera only known from Cretaceous fossils.

The Helosciomyzidae are a small family of flies found exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere. With the exception of the South American genus Sciogriphoneura, helosciomyzids occur only in Australia and New Zealand.

Scaptia is a genus of horse-fly in the tribe Scionini.

Mabel Josephine (Jo) Mackerras was an Australian zoologist, entomologist and parasitologist. Her research and life's work contributed to entomology, veterinary medicine and medical science. Throughout her life she held a wide range of positions and duties that included Army medical officer, entomologist, medical scientist, and parasitologist. Mackerras was a major during WWII and served in the Army Malaria Research Unit. In an application for King's Birthday Honours her work earned the citation,: "few women can have made a greater contribution to the Allied war effort".
Novaustrosimulium is a subgenus of Austrosimulium, a genus made up of black flies. The flies in this subgenus are found exclusively in Australia.

A gnat is any of many species of tiny flying insects in the dipterid suborder Nematocera, especially those in the families Mycetophilidae, Anisopodidae and Sciaridae. Most often they fly in large numbers, called clouds. "Gnat" is a loose descriptive category rather than a phylogenetic or other technical term, so there is no scientific consensus on what constitutes a gnat. Some entomologists consider only non-biting flies to be gnats. Certain universities and institutes also distinguish eye gnats: the Smithsonian Institution describes them as "non-biting flies, no bigger than a few grains of salt, ... attracted to fluids secreted by your eyes".

Austrosimulium is a subgenus of Austrosimulium, a genus of Simuliidae. The flies in this subgenre are found mainly in New Zealand, with a few in Australia. They are the only Simuliidae found in New Zealand.

Austrosimulium ungulatum, known by the common name West Coast black fly or just sandfly, is a species of small fly of the family Simuliidae that is endemic to New Zealand. Females consume blood for nutrients to produce eggs and it is one of three species of Austrosimulium in New Zealand that often bite humans.

Tetanocerini is a tribe of flies in the family Sciomyzidae. There are more than 400 described species in the tribe.

Sciomyzinae is a subfamily of flies in the family Sciomyzidae.

Austrosimulium australense, known as the New Zealand black fly or more commonly sandfly, is a species of small fly of the family Simuliidae, endemic to New Zealand. Females consume blood for nutrients to produce eggs, and it is one of three species of Austrosimulium in New Zealand that often bite humans.


















