
The Cryptobranchidae are a family of fully aquatic salamanders commonly known as the giant salamanders. They include some of the largest living amphibians. The family is native to China, Japan, and the eastern United States. They constitute one of two living families—the other being the Asiatic salamanders belonging to the family Hynobiidae—within the Cryptobranchoidea, one of two main divisions of living salamanders.
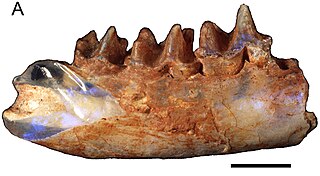
Steropodon is a genus of prehistoric platypus-like monotreme, or egg-laying mammal. It contains a single species, Steropodon galmani, that lived about 105 to 93.3 million years ago (mya) during the Cretaceous period, from early to middle Cenomanian. It is one of the oldest monotremes discovered, and is one of the oldest Australian mammal discoveries.

Necturus is a genus of aquatic salamanders in the family Proteidae. Species of the genus are native to the eastern United States and Canada. They are commonly known as waterdogs and mudpuppies. The common mudpuppy (N. maculosus) is probably the best-known species – as an amphibian with gill slits, it is often dissected in comparative anatomy classes. The common mudpuppy has the largest distribution of any fully aquatic salamander in North America.

Lissemys is a genus of softshell turtles in the subfamily Cyclanorbinae of the family Trionychidae. The genus is indigenous to southern Asia.

Keraterpeton is an extinct genus of lepospondyl amphibian, previously included within the monotypic Keraterpedontidae family, from the Carboniferous period of Europe and North America ; it is the oldest known member of the family Diplocaulidae.
Hyposaurus is a genus of extinct marine dyrosaurid crocodyliform. Fossils have been found in Paleocene aged rocks of the Iullemmeden Basin in West Africa, Campanian–Maastrichtian Shendi Formation of Sudan and Maastrichtian through Danian strata in New Jersey, Alabama and South Carolina. Isolated teeth comparable to Hyposaurus have also been found in Thanetian strata of Virginia. It was related to Dyrosaurus. The priority of the species H. rogersii has been debated, however there is no sound basis for the recognition of more than one species from North America. The other North American species are therefore considered nomina vanum.

Andrias is a genus of giant salamanders. It includes the largest salamanders in the world, with A. japonicus reaching a length of 1.44 metres, and A. sligoi reaching 1.80 metres. While extant species are only known from East Asia, several extinct species in the genus are known from late Oligocene and Neogene aged fossils collected in Europe and North America, indicating that the genus formerly had a much wider range.
Comonecturoides is an extinct genus of prehistoric caudate amphibians, possibly a salamander, from Reed's Quarry 9 of the Morrison Formation, near Como Bluff, Wyoming; the type species is C. marshi. It is considered a nomen dubium because the name is based on non-distinctive remains which cannot be classified in detail.
Eoscapherpeton is an extinct genus of giant salamander, known from the Late Cretaceous of Central Asia. Fossils have been found in the Cenomanian aged Khodzhakul Formation and Dzharakuduk Formation, Turonian aged Bissekty Formation and the Coniacian-Santonian aged Aitym Formation of Uzbekistan, the Santonian aged Yalovach Formation of Tajikistan, and the Santonian-lower Campanian aged Bostobe Formation and Campanian aged Darbasa Formation of Kazakhstan.
Iridotriton is an extinct genus of prehistoric salamander known from a fossil found in stratigraphic zone 6 of the late Jurassic Morrison Formation in the Dinosaur National Monument. One species has been described, Iridotriton hechti. It is likely a member of Cryptobranchoidea.
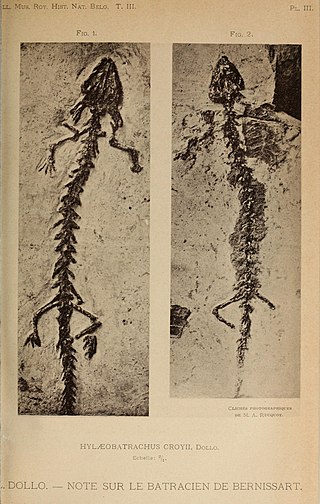
Hylaeobatrachus is an extinct genus of prehistoric salamander, known from the Early Cretaceous of Europe. The type species H. croyii is known from the Sainte-Barbe Clays Formation at the Iguanodon locality of Belgium, and was described by Louis Dollo. An unnamed Hylaeobatrachus-like taxon has also been reported from Las Hoyas, Spain. Both localities are of Barremian age. Hylaeobatrachus belongs to the crown group of modern salamanders, though its exact relationship with modern salamander groups is uncertain. It was neotenic, llike some modern salamanders.
Oligosemia is an extinct genus of prehistoric salamanders. Only one species is known, Oligosemia spinosa from Libros, Spain.
Metaceratodus is an extinct genus of prehistoric lungfish in the family Ceratodontidae, with an indeterminate specimen known from the Late Triassic (Norian)-aged Lissauer Breccia of Poland and more complete specimens known from the Late Cretaceous of Queensland, Australia and Argentina. The genus was named and described by Frederick Chapman in 1914.

Cyclanorbinae, also known commonly as the flapshell turtles, is a subfamily of softshell turtles in the family Trionychidae. The subfamily is native to Africa and Asia.

Chelonoidis is a genus of turtles in the tortoise family erected by Leopold Fitzinger in 1835. They are found in South America and the Galápagos Islands, and formerly had a wide distribution in the West Indies.

Zamites is a genus of sterile foliage known from the Mesozoic of North America, Europe, India and Antarctica through the Eocene of North America. It was erected as a form taxon for leaves that superficially resembled the extant cycad Zamia, however it is now believed to belong to a similar but phylogenetically different group, the cyacadeoids (Bennettitales). The fronds are linear or lanceolate in shape, and pinnately compound, with pinnae with parallel veins and smooth margins, and symmetrical and constricted at the base where they are attached obliquely to the upper surface of the rachis. It has been interpreted as a Bennettitalean plant in the family Williamsoniaceae. It is associated with the ovulate cone Williamsonia and male cone Weltrichia.

Batrachosauroididae is an extinct family of prehistoric salamanders with holarctic distribution. They were paedomorphic and presumably aquatic. They are possibly the sister taxon of Proteidae, an extant family of aquatic salamanders. They are definitively known from the Late Cretaceous to Miocene of North America and Europe. Remains from the earliest Cretaceous (Berriasian) Lulworth Formation of England have tenatively been attributed to this family.
Gigantohyrax was a genus of herbivorous hyrax-grouped mammals from the Pliocene Shungura Formation of Ethiopia. Fossils have also been found in Makapansgat of South Africa.

Florida hosts many types of fauna. From coral reefs of the Florida Keys to the cypress swamps of the Panhandle, the state's diverse habitats are home to a variety of wildlife. Florida is among the top five states in terms of endemic species. There are over 700 terrestrial animals, 200 freshwater fish species, 1,000 marine fish and thousands of terrestrial insects and other invertebrates that inhabit the state. Florida's peninsular geography spans from subtropical to tropical zones, which, combined with its distinctive geology and climate, contribute to habitat diversity and an array of species. The native wildlife that exists in the state are of temperate and tropical origin.

Boreostemma is an extinct genus of glyptodonts from northern South America. Fossils assigned to the genus were first described as belonging to Asterostemma from southern South America, but have been placed in the new genus Boreostemma by Carlini et al. in 2008. The type species is B. pliocena. Fossils of Boreostemma have been found in the Honda Group of Colombia, in Peru and Venezuela.












