
Shivaji I was an Indian ruler and a member of the Bhonsle Maratha clan. Shivaji carved out his own independent kingdom from the declining Adilshahi sultanate of Bijapur which formed the genesis of the Maratha Empire. In 1674, he was formally crowned the Chhatrapati of his realm at Raigad Fort.

Sambhaji, also known as Shambhuraje was the second Chhatrapati of the Maratha Empire, ruling from 1681 to 1689. He was the eldest son of Shivaji, the founder of the Maratha Empire. Sambhaji's rule was largely shaped by the ongoing wars between the Maratha Empire and the Mughal Empire, as well as other neighbouring powers such as the Abyssinians of Janjira, Wadiyars of Mysore and the Portuguese Empire in Goa. After Sambhaji's death, his brother Rajaram I succeeded him as the next Chhatrapati and continued the Mughal–Maratha Wars.

Panhala is a city and a Hill station Municipal Council 18 km northwest of Kolhapur, in Kolhapur district in the Indian state of Maharashtra. Panhala is the smallest city in Maharashtra and being a Municipal Council the city is developing rapidly. The city sprawls in the Panhala fort commands a panoramic view of the valley below. The main historical attraction here is the Panhala fort. There are many places of interest, each with its share of haunting anecdotes.

Baji Prabhu Deshpande was general of the Maratha Army. He is well known for his role in the Battle of Pavan Khind at Ghod Khind, where he sacrificed his life to protect Shivaji from incoming Mughal forces].

Miraj is a city part of the Sangli metropolitan region in Sangli district, Maharashtra. Founded in the early 10th century. It was an important jagir of the Adil Shahi court of Bijapur.

Netoji Palkar (1620–1681) was a Sardar Senapati or Sarnaubat (Commander-in-Chief) under Chhatrapati Shivaji, founder of the Maratha empire.

Shahaji Bhosale was a 17th century Indian military leader who served the Ahmadnagar Sultanate, the Bijapur Sultanate, and the Mughal Empire at various points in his career. As a member of the Bhonsle clan, Shahaji inherited the Pune and Supe jagirs (fiefs) from his father Maloji, who previously served the Ahmadnagar Sultanate. During the Mughal invasion of the Deccan, Shahaji joined the Mughal forces and served under Emperor Shah Jahan for a short period. After being deprived of his jagirs, he defected to the Bijapur Sultanate in 1632 and regained control over Pune and Supe. In 1638, he received the jagir of Bangalore after Bijapur's invasion of Kempe Gowda III's territories. Afterwards, he became the chief general of Bijapur and oversaw its expansion.

Afzal Khan was a general who served the Adil Shahi dynasty of Bijapur Sultanate in India. He played an important role in the southern expansion of the Bijapur Sultanate by subjugating the Nayaka chiefs who had taken control of the former Vijayanagara territory.

Balaji Vishwanath Bhat (1662–1720) was the first of a series of hereditary Peshwas hailing from the Bhat family who gained effective control of the Maratha Empire and the Mughal vassals of the Marathas during the early 18th century. Balaji Vishwanath assisted a young Maratha king Shahu to consolidate his grip on a kingdom that had been racked by civil war and persistently intruded on by the Mughals under Aurangzeb. He was called the Second Founder of the Maratha State. He secured a grant from the Mughal court that confirmed Shahu as the legitimate Mughal vassal, at the expense of his rival Sambhaji. Later, his son Bajirao I became the Peshwa.

Rajaram Bhonsle I was the third Chhatrapati of Maratha Empire, who ruled from 1689 to his death in 1700. He was the second son of the Shivaji, the founder of the empire and younger half-brother of Sambhaji, who he succeeded. His eleven-year reign was marked with a constant struggle against the Mughals. He was succeeded by his infant son Shivaji II under the regentship of his dowager Maharani Tarabai.
Rajapur is a city and a municipal council in Ratnagiri district in the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is 385 km away from Mumbai.

The Battle of Pavan Khind ; was a rearguard last stand that took place on 13 July 1660, at a mountain pass in the vicinity of fort Vishalgad, near the city of Kolhapur by the Maratha general Baji Prabhu Deshpande and Shambhu Singh Jadhav against Siddi Masud of the Bijapur Sultanate. The engagement ended with the destruction of the Maratha forces, and a tactical victory for the Bijapur Sultanate that failed to achieve a strategic victory.
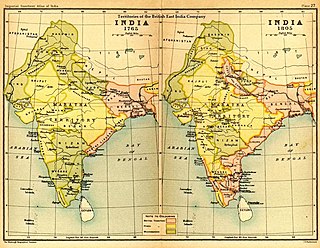
The Maratha Conquests were a series of conquests in the Indian subcontinent which led to the building of the Maratha Empire. These conquests were started by Shivaji in 1659, from the victory at the Battle of Pratapgad against Bijapur. The expansion of the empire was limited and interrupted by the Mughal conquests of south India by Mughal emperor Aurangzeb. Marathas were forced to defend their territories against the overwhelmingly strong Mughal army in the 27 years long Deccan wars. They were able to defend their territories and gain an upper hand over Mughals in the sustained conflict.
Rangnath Narayan Orpe, historically mentioned as ‘Rango Narayan’, was a warrior and administrative officer on Fort Vishalgad, under the regime of Shivaji, founder of the Maratha Empire and his son Sambhaji in the 17th century India. He is mainly known for defeating the Bijapur army in the battle of Vishalgad in July, 1660.

Panhala fort, is located in Panhala, 20 kilometres northwest of Kolhapur in Maharashtra, India. It is strategically located looking over a pass in the Sahyadri mountain range which was a major trade route from Bijapur in the interior of Maharashtra to the coastal areas. Due to its strategic location, it was the centre of several skirmishes in the Deccan involving the Marathas, the Mughals and the British East India Company, the most notable being the Battle of Pavan Khind. Here, the queen regent of Kolhapur, Tarabai Ranisaheb, spent her formative years. Several parts of the fort and the structures within are still intact. It is also called as the 'Fort of Snakes' as it is zigzagged in shape.
Rustam-i-Zaman was the title of a Bijapuri general who commanded Adil Shah's 10,000 strong army, in the Battle of Kolhapur against Shivaji's forces. He also was the son of Ranadulla Khan, an experienced and senior general of Bijapur and the chief mentor and guardian of Shahaji.

Dhondia Wagh was a military soldier and adventurer in 18th century India. He started his career in the service of Hyder Ali, the ruler of Mysore. During the Third Anglo-Mysore War, he deserted Ali's successor Tipu Sultan, and subsequently raided territories on the Maratha-Mysore border. After the Marathas forced him to retreat, he sought refuge from Tipu and converted to Islam, changing his name to Malik Jahan Khan. After Tipu's death in the Fourth Anglo-Mysore War, he raised a force comprising soldiers from the former Mysore Army, and took control of northern part of the Mysore Kingdom. He styled himself as Ubhaya-Lokadheeshwara. The British East India Company as well as the Maratha Peshwa sent armies to check his rising power. He was ultimately defeated and killed by a British force led by Arthur Wellesley.

Veer Shivaji is an Indian historical drama series that aired on Colors TV. The show focuses on the life of Shivaji, the 17th century founder of the Maratha Empire. It premiered on 2 September 2011 and was produced by Contiloe Telefilms, who had earlier created the historical drama Jhansi Ki Rani on Zee TV. Due to the instant success and popularity and with TRP of more than 2.60, the show timing were extended to five days a week from 3 October 2011.

The Maratha Navy was the naval wing of the armed forces of the Maratha Empire, which existed from around mid-17th century to mid-18th century in the Indian subcontinent.

Pawankhind ; is a 2022 Indian Marathi-language historical action drama film directed by Digpal Lanjekar and produced under the banner of Almonds Creations in association with AA Films. The film based on the life of Maratha warrior, Baji Prabhu Deshpande, stars Chinmay Mandlekar, Mrinal Kulkarni, Ajay Purkar, Sameer Dharmadhikari, along with Ankit Mohan, Prajakta Mali and Kshitee Jog in supporting roles.

















