The geothermal areas of Yellowstone include several geyser basins in Yellowstone National Park as well as other geothermal features such as hot springs, mud pots, and fumaroles. The number of thermal features in Yellowstone is estimated at 10,000. A study that was completed in 2011 found that a total of 1,283 geysers have erupted in Yellowstone, 465 of which are active during an average year. These are distributed among nine geyser basins, with a few geysers found in smaller thermal areas throughout the Park. The number of geysers in each geyser basin are as follows: Upper Geyser Basin (410), Midway Geyser Basin (59), Lower Geyser Basin (283), Norris Geyser Basin (193), West Thumb Geyser Basin (84), Gibbon Geyser Basin (24), Lone Star Geyser Basin (21), Shoshone Geyser Basin (107), Heart Lake Geyser Basin (69), other areas (33). Although famous large geysers like Old Faithful are part of the total, most of Yellowstone's geysers are small, erupting to only a foot or two. The hydrothermal system that supplies the geysers with hot water sits within an ancient active caldera. Many of the thermal features in Yellowstone build up sinter, geyserite, or travertine deposits around and within them.

Yellowstone Lake is the largest body of water in Yellowstone National Park. The lake is 7,732 feet (2,357 m) above sea level and covers 136 square miles (350 km2) with 110 miles (180 km) of shoreline. While the average depth of the lake is 139 ft (42 m), its greatest depth is at least 394 ft (120 m). Yellowstone Lake is the largest freshwater lake above 7,000 ft (2,100 m) in North America.

The Yellowstone Caldera is a volcanic caldera and supervolcano in Yellowstone National Park in the Western United States, sometimes referred to as the Yellowstone Supervolcano. The caldera and most of the park are located in the northwest corner of Wyoming. The major features of the caldera measure about 34 by 45 miles.

Castle Geyser is a cone geyser in the Upper Geyser Basin of Yellowstone National Park. It is noted for the particularly large geyserite sinter deposits, which form its cone. These deposits have been likened in appearance to a castle.

Artesia Geyser is a geyser in the Lower Geyser Basin of Yellowstone National Park in the United States. Artesia Geyser is located on the edge of Firehole Lake and is part of the Black Warrior Group which includes Young Hopeful Geyser, Gray Bulger Geyser, and Steady Geyser.

Bead Geyser is a fountain-type geyser in the Lower Geyser Basin of Yellowstone National Park in the United States.
Narcissus Geyser is a geyser in the Lower Geyser Basin of Yellowstone National Park in the United States. Narcissus Geyser is part of the Pink Cone Group. Other geysers in this group are Bead Geyser, Box Spring, Dilemma Geyser, Labial Geyser, Labial's Satellite Geyser, Pink Geyser, and Pink Cone Geyser.

Pink Cone Geyser is a cone-type geyser in the Lower Geyser Basin of Yellowstone National Park in the United States. It is part of the Pink Cone Group. Other geysers in this groups include Bead Geyser, Box Spring, Dilemma Geyser, Labial Geyser, Labial's Satellite Geyser, Narcissus Geyser, and Pink Geyser.

Pump Geyser is a cone geyser located in the Upper Geyser Basin of Yellowstone National Park. It is in the Geyser Hill Complex which includes Aurum Geyser, Beehive Geyser, Big Cub Geyser. Doublet Pool, Giantess Geyser and Lion Geyser, among others.

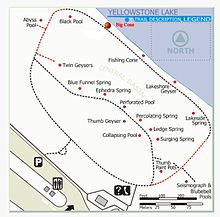
Fishing Cone is a geyser in the West Thumb Geyser Basin of Yellowstone National Park in the United States.

The Great Fountain Geyser is a fountain-type geyser located in the Firehole Lake area of Lower Geyser Basin of Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming. It is the only Lower Geyser Basin feature that the park makes predictions for.

Black Pool is a hot spring in the West Thumb Geyser Basin of Yellowstone National Park in the United States.

The Cook–Folsom–Peterson Expedition of 1869 was the first organized expedition to explore the region that became Yellowstone National Park. The privately financed expedition was carried out by David E. Folsom, Charles W. Cook and William Peterson of Diamond City, Montana, a gold camp in the Confederate Gulch area of the Big Belt Mountains east of Helena, Montana. The journals kept by Cook and Folsom, as well as their personal accounts to friends were of significant inspirational value to spur the organization of the Washburn-Langford-Doane Expedition which visited Yellowstone in 1870.

Isa Lake is located in Yellowstone National Park, in the U.S. state of Wyoming. The lake straddles the continental divide at Craig Pass and was first discovered in 1891 by Hiram M. Chittenden, who was exploring the best routes for a road to connect Old Faithful and West Thumb geyser basins. Chittenden named the lake after Miss Isabel Jelke, from Cincinnati, though it is not clear why.

The Grand Loop Road Historic District encompasses the primary road system in Yellowstone National Park. Much of the 140-mile (230 km) system was originally planned by Captain Hiram M. Chittenden of the US Army Corps of Engineers in the early days of the park, when it was under military administration. The Grand Loop Road provides access to the major features of the park, including the Upper, Midway and Lower geyser basins, Mammoth Hot Springs, Tower Fall, the Grand Canyon of the Yellowstone and Yellowstone Lake.

Lion Geyser is a cone-type geyser in the Upper Geyser Basin of Yellowstone National Park in the United States. It is located in the Geyser Hill complex.

The following articles relate to the history, geography, geology, flora, fauna, structures and recreation in Yellowstone National Park.

White Dome Geyser is a geyser located in the Lower Geyser Basin in Yellowstone National Park in the United States.

Lone Star Geyser is a cone type geyser located in the Lone Star Geyser Basin of Yellowstone National Park. The basin is a backcountry geyser basin located 3 miles (4.8 km) southeast of Old Faithful Geyser and the Upper Geyser Basin. The geyser is reached via an old service road open to hikers and biking with the trailhead near Kepler Cascades on the Grand Loop Road.