
Zola is a crater on Mercury. The crater was named after the French novelist and playwright Émile Zola by the IAU in 1979.
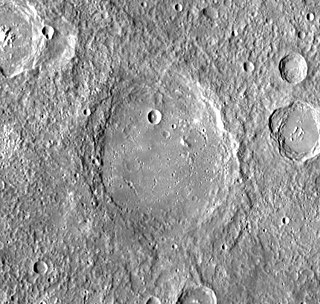
Sullivan is a crater on Mercury. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in 1976, and is named for the American architect Louis Sullivan. The crater was first imaged by Mariner 10 in 1974.

Vyāsa is a crater on Mercury. It was named by the IAU in 1979, after the Indian poet Vyasa. It is Tolstojan in age.

Raphael is a crater on Mercury. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in 1976, and is named for the Italian painter Raphael. It is Tolstojan in age. The crater was first imaged by Mariner 10 in 1974.

Homer is a crater on Mercury. It is one of 110 peak ring basins on Mercury. It is Tolstojan in age.

Verdi is an impact crater on the planet Mercury. It was named after Italian Romantic composer Giuseppe Verdi (1813–1901) in 1979, as recognized by the International Astronomical Union. The crater's extensive ejecta blanket and secondary crater field are superposed on plains materials and older craters.
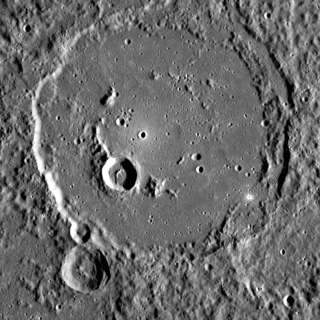
Polygnotus is a crater on Mercury, named by the IAU in 1976, after ancient Greek painter Polygnotus. The crater was first imaged by Mariner 10 in 1974.

Ahmad Baba is a crater on Mercury. It has a diameter of 127 kilometers. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in 1979.

Futabatei is a crater on Mercury. It has a diameter of 57 kilometers. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union in 1976. Futabatei is named for the Japanese novelist Futabatei Shimei, who lived from 1864 to 1909. The crater was first imaged by Mariner 10 in 1974.

Gogol is a crater on Mercury. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in 1985. Gogol is named for the Russian playwright Nikolai Gogol, who lived from 1809 to 1852.

Janáček is a crater on Mercury. It has a diameter of 47 kilometers. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in 1985. Janáček is named for the Czech composer Leoš Janáček, who lived from 1854 to 1928. The MESSENGER Mercury orbiter crashed near the crater on 30 April 2015.

Machaut is a crater on Mercury. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union in 1976. Machaut is named for the French composer and poet Guillaume de Machaut, who lived from 1300 to 1377. The crater was first imaged by Mariner 10 in 1974.

Mark Twain is a crater on Mercury. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in 1976. Mark Twain is named for the American author Mark Twain, who lived from 1835 to 1910.

Martial is a crater on Mercury. It has a diameter of 51 kilometers. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union in 1979. Martial is named for the ancient Roman poet Martial, who lived from 40 to 103. The crater was first imaged by Mariner 10 in 1974.

Mussorgskij is a crater on Mercury. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in 1979. Mussorgskij is named for the Russian composer Modest Mussorgsky, who lived from 1839 to 1881. The crater was first imaged by Mariner 10 in 1974.

Neumann is a crater on Mercury. It has a diameter of 120 kilometers. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in 1976. Neumann is named for the German architect Johann Balthasar Neumann, who lived from 1687 to 1753.

Phidias is a crater on Mercury. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in 1976. Phidias is named for the Greek artist Phidias, who lived from 490 to 430 BCE. The crater was first imaged by Mariner 10 in 1974.

Wagner is an impact crater in the south polar region of the planet Mercury. It was named after the German composer Richard Wagner (1813–1883) in 1976, as recognized by the International Astronomical Union. It is located in the Bach quadrangle, between Bach and Chopin.

Flaiano is a crater on Mercury. It has a diameter of 43 kilometres. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) on March 15, 2013. Flaiano is named for the Italian writer Ennio Flaiano. The crater was first imaged by Mariner 10 in 1974.





















