The geology of Mercury is the scientific study of the surface, crust, and interior of the planet Mercury. It emphasizes the composition, structure, history, and physical processes that shape the planet. It is analogous to the field of terrestrial geology. In planetary science, the term geology is used in its broadest sense to mean the study of the solid parts of planets and moons. The term incorporates aspects of geophysics, geochemistry, mineralogy, geodesy, and cartography.

Lermontov is an impact crater on the planet Mercury. The crater is named after Mikhail Yuryevich Lermontov, a 19th-century Russian poet. The name was approved by the International Astronomical Union in 1976.

The Shakespeare quadrangle is a region of Mercury running from 90 to 180° longitude and 20 to 70° latitude. It is also called Caduceata.

The Elysium quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Elysium quadrangle is also referred to as MC-15.

The Phoenicis Lacus quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Phoenicis Lacus quadrangle is also referred to as MC-17. Parts of Daedalia Planum, Sinai Planum, and Solis Planum are found in this quadrangle. Phoenicis Lacus is named after the phoenix which according to myth burns itself up every 500 years and then is reborn.

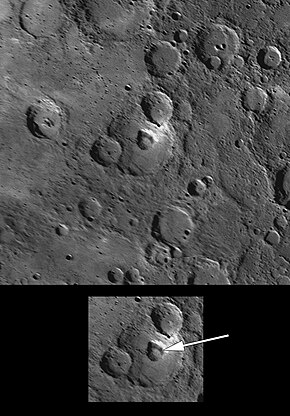
Praxiteles is a crater on Mercury. It is one of 110 peak ring basins on Mercury.

Navoi is a crater on Mercury. It contains uncommon reddish material that indicates a different rock composition from its surroundings. Navoi also appears to have an irregularly shaped depression in its center. Such depressions have been seen elsewhere on Mercury, including within Praxiteles crater, and may indicate past volcanic activity.

Raditladi is a large impact crater on Mercury with a diameter of 263 km. Inside its peak ring there is a system of concentric extensional troughs (graben), which are rare surface features on Mercury. The floor of Raditladi is partially covered by relatively light smooth plains, which are thought to be a product of the effusive volcanism. The troughs may also have resulted from volcanic processes under the floor of Raditladi. The basin is relatively young, probably younger than one billion years, with only a few small impact craters on its floor and with well-preserved basin walls and peak-ring structure. It is one of 110 peak ring basins on Mercury.

Beckett is a pit-floored crater on Mercury, which was discovered in January 2008 during the first flyby of the planet by the MESSENGER spacecraft. The crater was named in November 2008 by the IAU.

Glinka is a pit-floored crater on Mercury, which was discovered in 1974 by Mariner 10 spacecraft. It was named by the IAU in 2008, after Russian composer Mikhail Glinka.

Scarlatti is a pit-floored crater on Mercury, which was discovered in 1974 by the Mariner 10 spacecraft. It has a prominent peak ring, and it is one of 110 peak ring basins on Mercury. The crater floor is covered by the smooth plains material. The crater displays an arcuate collapse feature along the northeastern peak ring. The size of the pit, which was first noticed in MESSENGER images obtained in January 2008, is 38 × 12 km. Such a feature may have resulted from collapse of a magma chamber underlying the central peak ring complex of the crater. The collapse feature is an analog of Earth's volcanic calderas. Scarlatti is thought to have the same age as the Caloris basin.

To Ngoc Van is a pit-floored crater on Mercury, named after the Vietnamese artist Tô Ngọc Vân. It was discovered in January 2008 during the first flyby of the planet by MESSENGER spacecraft. Its floor displays an irregularly shaped collapse feature, which is called a central pit. The size of the pit is 21 × 10 km. Such a feature may have resulted from collapse of a magma chamber underlying the central part of the crater. The collapse feature is an analog of Earth's volcanic calderas.

Picasso is a crater on Mercury. It has drawn scientific attention because of the large, arc-shaped pit crater located on the eastern side of its floor. Similar pits have been discovered on the floors of several other Mercury craters, such as Beckett, Glinka, and Gibran. These pits are postulated to have formed when subsurface magma subsided or drained, causing the surface to collapse into the resulting void. If this interpretation is correct, pit-floor craters such as Picasso provide evidence of shallow magmatic activity in Mercury's history.
Mars may contain ores that would be very useful to potential colonists. The abundance of volcanic features together with widespread cratering are strong evidence for a variety of ores. While nothing may be found on Mars that would justify the high cost of transport to Earth, the more ores that future colonists can obtain from Mars, the easier it would be to build colonies there.

Geddes is a crater on Mercury. It has a diameter of 84 kilometers. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in 2010. Geddes is named for the Irish stained glass artist Wilhelmina Geddes, who lived from 1887 to 1955.

Hauptmann is a crater on Mercury. It has a diameter of 118 kilometers. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in 1985. Hauptmann is named for the German playwright Gerhart Hauptmann, who lived from 1862 to 1946.

A crater is a landform consisting of a hole or depression on a planetary surface, usually caused either by an object hitting the surface, or by geological activity on the planet. A crater has classically been described as: "a bowl-shaped pit that is formed by a volcano, an explosion, or a meteorite impact". On Earth, craters are "generally the result of volcanic eruptions", while "meteorite impact craters are common on the Moon, but are rare on Earth".

Enheduanna is a crater on Mercury. It has a diameter of 105 kilometers. Its name was suggested by Gagan Toor from India in a naming contest which was eventually adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) on 2015. Enheduanna is named for the Sumerian poet Enheduanna. The craters Carolan, Kulthum, Karsh, and Rivera were also named as part of the contest.

Pahinui is a crater on Mercury. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union in 2016, after the Hawaiian musician, Charles Phillip Kahahawai "Gabby" Pahinui.

Grainger is a crater on Mercury. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in 2012, after the Australian-born composer George Percy Aldridge Grainger.