The Sioux or Oceti Sakowin are groups of Native American tribes and First Nations peoples from the Great Plains of North America. The Sioux have two major linguistic divisions: the Dakota and Lakota peoples. Collectively, they are the Očhéthi Šakówiŋ, or "Seven Council Fires". The term "Sioux", an exonym from a French transcription ("Nadouessioux") of the Ojibwe term "Nadowessi", can refer to any ethnic group within the Great Sioux Nation or to any of the nation's many language dialects.
FlandreauFLAN-droo is a city in and county seat of Moody County, South Dakota, United States. The population was 2,372 at the 2020 census. It was named in honor of Charles Eugene Flandrau, a judge in the territory and state of Minnesota. He is credited with saving the community of New Ulm, Minnesota, from destruction during conflict with the Sioux tribe in 1862.
Nakota is the endonym used by those Native peoples of North America who usually go by the name of Assiniboine, in the United States, and of Stoney, in Canada.

Charles Alexander Eastman was an American physician, writer, and social reformer. He was the first Native American to be certified in Western medicine and was "one of the most prolific authors and speakers on Sioux ethnohistory and American Indian affairs" in the early 20th century.
The Mdewakanton or Mdewakantonwan are one of the sub-tribes of the Isanti (Santee) Dakota (Sioux). Their historic home is Mille Lacs Lake in central Minnesota. Together with the Wahpekute, they form the so-called Upper Council of the Dakota or Santee Sioux. Today their descendants are members of federally recognized tribes in Minnesota, South Dakota and Nebraska of the United States, and First Nations in Manitoba, Canada.

The Crow Creek Indian Reservation, home to Crow Creek Sioux Tribe is located in parts of Buffalo, Hughes, and Hyde counties on the east bank of the Missouri River in central South Dakota in the United States. It has a land area of 421.658 square miles (1,092.09 km2) and a 2000 census population of 2,225 persons. The major town and capital of the federally recognized Crow Creek Sioux Tribe is Fort Thompson.

Seth Eastman was an artist and West Point graduate who served in the US Army, first as a mapmaker and illustrator. He had two tours at Fort Snelling, Minnesota Territory; during the second, extended tour he was commanding officer of the fort. During these years, he painted many studies of Native American life. He was notable for the quality of his hundreds of illustrations for Henry Rowe Schoolcraft's six-volume study on the history of Indian tribes of the United States, commissioned by the US Congress.

Elaine Goodale Eastman (1863–1953) and Dora Read Goodale (1866–1953) were American poets and sisters from Massachusetts. They published their first poetry as children still living at home, and were included in Edmund Clarence Stedman's classic An American Anthology (1900).

The Santee Sioux Reservation of the Santee Sioux was established in 1863 in present-day Nebraska. The tribal seat of government is located in Niobrara, Nebraska, with reservation lands in Knox County.

The Dakota are a Native American tribe and First Nations band government in North America. They compose two of the three main subcultures of the Sioux people, and are typically divided into the Eastern Dakota and the Western Dakota.

The Debussy quadrangle (H-14) is one of fifteen quadrangles on Mercury. It runs from 270 to 360° longitude and from -20 to -70° latitude. Named after the Debussy crater, it was mapped in detail for the first time after MESSENGER entered orbit around Mercury in 2011. It had not been mapped prior to that point because it was one of the six quadrangles that was not illuminated when Mariner 10 made its flybys in 1974 and 1975. These six quadrangles continued to be known by their albedo feature names, with this one known as the Cyllene quadrangle.

The Episcopal Diocese of South Dakota is a diocese of the Episcopal Church with jurisdiction over the state of South Dakota.

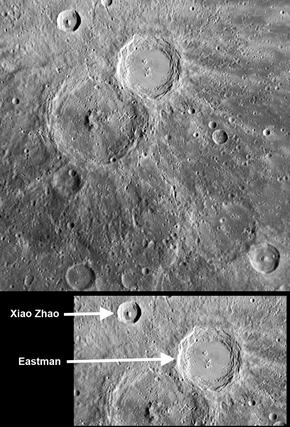
Xiao Zhao crater is small in comparison with many other craters on Mercury. However, Xiao Zhao's long bright rays make it a readily visible feature. The fresh, bright rays, which were created by material ejected outward during the impact event that formed the crater, indicate that Xiao Zhao is a relatively young crater on Mercury's surface.

The Flandreau Indian Reservation is an Indian reservation, belonging to the federally recognized Flandreau Santee Sioux Tribe of South Dakota. They are Santee Dakota people, part of the Sioux tribe of Native Americans. The reservation is located in Flandreau Township in central Moody County in eastern South Dakota, near the city of Flandreau.

Praxiteles is a crater on Mercury. It is one of 110 peak ring basins on Mercury.

Munkácsy, named after Mihály Munkácsy, is a crater on Mercury. Munkácsy originally had a double-ring basin structure, but most of the inner ring was buried when the basin was flooded with volcanic lava. Only a few remnants of the ring poke up through the lava, although low ridges in the lava seem to trace out much of the rest of the ring's circumference. Munkácsy is one of 110 peak ring basins on Mercury.

Izquierdo is a crater on Mercury. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in 2009, for the Mexican painter María Izquierdo. The floor of Izquierdo is smooth, the result of having been partially filled with volcanic lava. Circular outlines of the rims of “ghost craters” – smaller, older craters that have been largely buried by the lavas that infilled the basin – are visible in a few places on Izquierdo's floor. The remnants of a buried inner ring are also barely discernible in spots, and it is one of 110 peak ring basins on Mercury. There have been more recent impacts into the floor of Izquierdo, resulting in some small, sharply defined craters.

Copland is an impact crater on Mercury. Its floor is flooded with volcanic smooth plains material, which could be related to the activity that formed the nearby bright vent known as Nathair Facula.

Enheduanna is a crater on Mercury. It has a diameter of 105 kilometers. Its name was suggested by Gagan Toor from India in a naming contest which was eventually adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) on 2015. Enheduanna is named for the Sumerian poet Enheduanna. The craters Carolan, Kulthum, Karsh, and Rivera were also named as part of the contest.

Mary Henderson Eastman was an American historian and novelist who is noted for her works about Native American life. She was also an advocate of slavery in the United States. In response to Harriet Beecher Stowe's anti-slavery Uncle Tom's Cabin, Eastman defended Southern slaveholding society by writing Aunt Phillis's Cabin: or, Southern Life As It Is (1852), which earned her considerable fame. She was the wife of the American illustrator and army officer Seth Eastman.