Calpain small subunit 1, also known as CAPN4, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CAPNS1 gene. [5] [6] [7]
Calpain small subunit 1, also known as CAPN4, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CAPNS1 gene. [5] [6] [7]
Calpains are a ubiquitous, well-conserved family of calcium-dependent, cysteine proteases. Calpain families have been implicated in neurodegenerative processes, as their activation can be triggered by calcium influx and oxidative stress. Calpain I and II are heterodimeric with distinct large subunits associated with common small subunits, all of which are encoded by different genes. The small regulatory subunit consists of an N-terminal domain, containing about 30% glycine residues and a C-terminal Ca-binding domain. [8] Two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been identified for this gene. [7]
This gene encodes a small subunit common to both calpain I and II and is associated with myotonic dystrophy. [7]
Elevated expression of Capn4 has been found to be associated with progression of various cancers such as hepatocellular and renal carcinoma. [9]

A calpain is a protein belonging to the family of calcium-dependent, non-lysosomal cysteine proteases expressed ubiquitously in mammals and many other organisms. Calpains constitute the C2 family of protease clan CA in the MEROPS database. The calpain proteolytic system includes the calpain proteases, the small regulatory subunit CAPNS1, also known as CAPN4, and the endogenous calpain-specific inhibitor, calpastatin.
Calpain-2 is an intracellular heterodimeric calcium-activated cysteine protease. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Calpain-10 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CAPN10 gene.

Calpain-2 catalytic subunit is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CAPN2 gene.

Calpain-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CAPN3 gene.
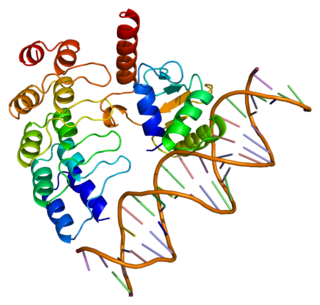
GA-binding protein alpha chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GABPA gene.

Calpain-1 catalytic subunit is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CAPN1 gene.
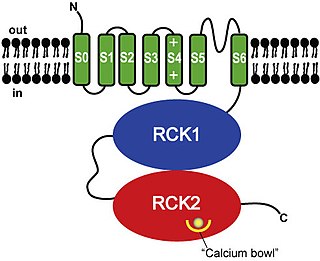
Calcium-activated potassium channel subunit alpha-1 also known as large conductance calcium-activated potassium channel, subfamily M, alpha member 1 (KCa1.1), or BK channel alpha subunit, is a voltage gated potassium channel encoded by the KCNMA1 gene and characterized by their large conductance of potassium ions (K+) through cell membranes.

Calpastatin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CAST gene.

Proteasome activator complex subunit 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PSME2 gene.
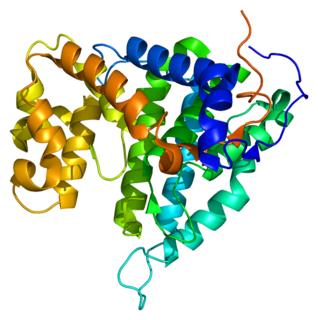
Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2A regulatory subunit B is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PPP2R4 gene.

Chloride channel accessory 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CLCA1 gene.
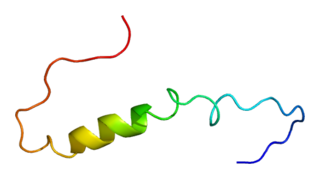
Calcium-activated potassium channel subunit beta-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCNMB2 gene.

Calpain-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CAPN5 gene.

Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activator 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CDK5R2 gene.

Calcium channel, voltage-dependent, T type, alpha 1H subunit, also known as CACNA1H, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the CACNA1H gene.
YY1-associated factor 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the YAF2 gene.

Calpain-9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CAPN9 gene.
Calpain-3 is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Calpain 6 is a protein in humans that is encoded by the CAPN6 gene.