
Gentianales is an order of flowering plant, included within the asterid clade of eudicots. It comprises more than 20,000 species in about 1,200 genera in 5 families. More than 80% of the species in this order belong to the family Rubiaceae.

The kola nut is the seed of certain species of plant of the genus Cola, placed formerly in the cocoa family Sterculiaceae and now usually subsumed in the mallow family Malvaceae. These cola species are trees native to the tropical rainforests of Africa. Their caffeine-containing seeds are about 5 centimetres (2.0 in) across and are used as flavoring ingredients in various carbonated soft drinks, from which the name cola originates.

Nyssaceae is a family of flowering trees sometimes included in the dogwood family (Cornaceae). Nyssaceae is composed of 37 known species in the following five genera:
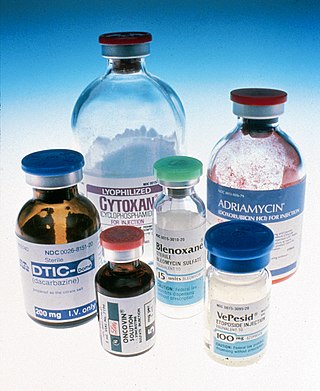
The era of cancer chemotherapy began in the 1940s with the first use of nitrogen mustards and folic acid antagonist drugs. The targeted therapy revolution has arrived, but many of the principles and limitations of chemotherapy discovered by the early researchers still apply.

Irinotecan, sold under the brand name Camptosar among others, is an anti-cancer medication used to treat colon cancer and small cell lung cancer. For colon cancer it is used either alone or with fluorouracil. For small cell lung cancer it is used with cisplatin. It is given intravenously.

Cruciferous vegetables are vegetables of the family Brassicaceae with many genera, species, and cultivars being raised for food production such as cauliflower, cabbage, kale, garden cress, bok choy, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, mustard plant and similar green leaf vegetables. The family takes its alternative name from the shape of their flowers, whose four petals resemble a cross.

Topotecan, sold under the brand name Hycamtin among others, is a chemotherapeutic agent medication that is a topoisomerase inhibitor. It is a synthetic, water-soluble analog of the natural chemical compound camptothecin. It is used in the form of its hydrochloride salt to treat ovarian cancer, lung cancer and other cancer types.
Topoisomerase inhibitors are chemical compounds that block the action of topoisomerases, which are broken into two broad subtypes: type I topoisomerases (TopI) and type II topoisomerases (TopII). Topoisomerase plays important roles in cellular reproduction and DNA organization, as they mediate the cleavage of single and double stranded DNA to relax supercoils, untangle catenanes, and condense chromosomes in eukaryotic cells. Topoisomerase inhibitors influence these essential cellular processes. Some topoisomerase inhibitors prevent topoisomerases from performing DNA strand breaks while others, deemed topoisomerase poisons, associate with topoisomerase-DNA complexes and prevent the re-ligation step of the topoisomerase mechanism. These topoisomerase-DNA-inhibitor complexes are cytotoxic agents, as the un-repaired single- and double stranded DNA breaks they cause can lead to apoptosis and cell death. Because of this ability to induce apoptosis, topoisomerase inhibitors have gained interest as therapeutics against infectious and cancerous cells.

Camptothecin (CPT) is a topoisomerase inhibitor. It was discovered in 1966 by M. E. Wall and M. C. Wani in systematic screening of natural products for anticancer drugs. It was isolated from the bark and stem of Camptotheca acuminata, a tree native to China used in traditional Chinese medicine. It has been used clinically more recently in China for the treatment of gastrointestinal tumors. CPT showed anticancer activity in preliminary clinical trials, especially against breast, ovarian, colon, lung, and stomach cancers. However, it has low solubility and adverse effects have been reported when used therapeutically, so synthetic and medicinal chemists have developed numerous syntheses of camptothecin and various derivatives to increase the benefits of the chemical, with good results. Four CPT analogues have been approved and are used in cancer chemotherapy today: topotecan, irinotecan, belotecan, and trastuzumab deruxtecan. Camptothecin has also been found in other plants including Chonemorpha fragrans.

DNA topoisomerase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TOP1 gene. It is a DNA topoisomerase, an enzyme that catalyzes the transient breaking and rejoining of a single strand of DNA.
CRLX101 is an experimental approach to cancer chemotherapy that is under investigation in human trials. It is an example of a nanomedicine.
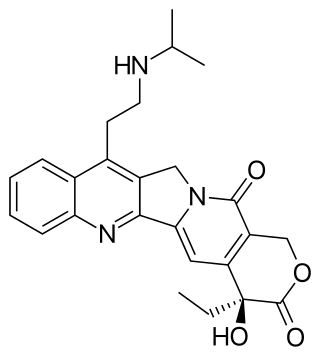
Belotecan is a drug used in chemotherapy. It is a semi-synthetic camptothecin analogue indicated for small-cell lung cancer and ovarian cancer, approved in South Korea under the trade name Camtobell, presented in 2 mg vials for injection. The drug has been marketed by Chong Kun Dang Pharmaceuticals since 2003.

Trifolin is a chemical compound. It is the kaempferol 3-galactoside. It can be found in Camptotheca acuminata, in Euphorbia condylocarpa or in Consolida oliveriana.

Hyperoside is a chemical compound. It is the 3-O-galactoside of quercetin.

Plant sources of anti-cancer agents are plants, the derivatives of which have been shown to be usable for the treatment or prevention of cancer in humans.

Ophiorrhiza is a genus of flowering plants in the coffee family (Rubiaceae). It contains 372 species native to the Indian subcontinent, Indochina, China, Japan, Malesia, Papuasia, Queensland, and the South Pacific. Species of the genus contain camptothecin, an alkaloid used to make chemotherapeutic agents. Many Ophiorrhiza species are endemic to certain areas of the Western Ghats.

Cleghornia is a genus of plants in the family Apocynaceae. It includes two species, which are native to Borneo, China, Laos, Malaysia, Sri Lanka, Thailand, and Vietnam.
This is a historical timeline of the development and progress of cancer treatments, which includes time of discovery, progress, and approval of the treatments.
Blastococcus endophyticus is a bacterium from the genus of Blastococcus which has been isolated from the leaves of the plant Camptotheca acuminata from Yunnan in China.

Mostuea is one of only three genera of flowering plants belonging to the small family Gelsemiaceae. Mostuea and Gelsemium were formerly placed in the family Loganiaceae, while Pteleocarpa was placed variously in the families Icacinaceae, Cardiopteridaceae, Boraginaceae, and others, before the description of the Gelsemiaceae was altered formally to accommodate it in 2014. Mostuea is native to Africa and South America. Anecdotal evidence suggests that the roots of certain Mostuea species are used as ritual aphrodisiacs and entheogens in West Tropical Africa.
















