
The scapula, also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus with the clavicle. Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the other. The name derives from the Classical Latin word for trowel or small shovel, which it was thought to resemble.

The humerus is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a rounded head, a narrow neck, and two short processes. The body is cylindrical in its upper portion, and more prismatic below. The lower extremity consists of 2 epicondyles, 2 processes, and 3 fossae. As well as its true anatomical neck, the constriction below the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus is referred to as its surgical neck due to its tendency to fracture, thus often becoming the focus of surgeons.
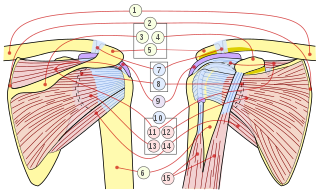
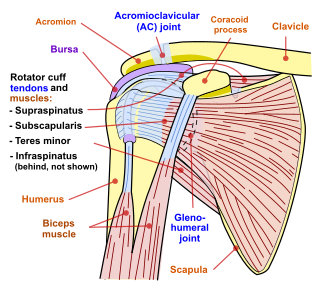
The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and their tendons that act to stabilize the human shoulder and allow for its extensive range of motion. Of the seven scapulohumeral muscles, four make up the rotator cuff. The four muscles are:
Shoulder problems including pain, are one of the more common reasons for physician visits for musculoskeletal symptoms. The shoulder is the most movable joint in the body. However, it is an unstable joint because of the range of motion allowed. This instability increases the likelihood of joint injury, often leading to a degenerative process in which tissues break down and no longer function well.

The human shoulder is made up of three bones: the clavicle (collarbone), the scapula, and the humerus as well as associated muscles, ligaments and tendons.

The deltoid muscle is the muscle forming the rounded contour of the human shoulder. It is also known as the 'common shoulder muscle', particularly in other animals such as the domestic cat. Anatomically, the deltoid muscle appears to be made up of three distinct sets of muscle fibers, namely the
- anterior or clavicular part
- posterior or scapular part
- intermediate or acromial part

Rotator cuff tendinopathy is a process of senescence. The pathophysiology is mucoid degeneration. Most people develop rotator cuff tendinopathy within their lifetime.

Adhesive capsulitis, also known as frozen shoulder, is a condition associated with shoulder pain and stiffness. It is a common shoulder ailment that is marked by pain and a loss of range of motion, particularly in external rotation. There is a loss of the ability to move the shoulder, both voluntarily and by others, in multiple directions. The shoulder itself, however, does not generally hurt significantly when touched. Muscle loss around the shoulder may also occur. Onset is gradual over weeks to months. Complications can include fracture of the humerus or biceps tendon rupture.

The acromioclavicular joint, or AC joint, is a joint at the top of the shoulder. It is the junction between the acromion and the clavicle. It is a plane synovial joint.

The supraspinatus is a relatively small muscle of the upper back that runs from the supraspinous fossa superior portion of the scapula to the greater tubercle of the humerus. It is one of the four rotator cuff muscles and also abducts the arm at the shoulder. The spine of the scapula separates the supraspinatus muscle from the infraspinatus muscle, which originates below the spine.

In human anatomy, the infraspinatus muscle is a thick triangular muscle, which occupies the chief part of the infraspinatous fossa. As one of the four muscles of the rotator cuff, the main function of the infraspinatus is to externally rotate the humerus and stabilize the shoulder joint.

The shoulder joint is structurally classified as a synovial ball-and-socket joint and functionally as a diarthrosis and multiaxial joint. It involves an articulation between the glenoid fossa of the scapula and the head of the humerus. Due to the very loose joint capsule that gives a limited interface of the humerus and scapula, it is the most mobile joint of the human body.

The subscapularis is a large triangular muscle which fills the subscapular fossa and inserts into the lesser tubercle of the humerus and the front of the capsule of the shoulder-joint.

The glenoid fossa of the scapula or the glenoid cavity is a bone part of the shoulder. The word glenoid is pronounced or and is from Greek: gléne, "socket", reflecting the shoulder joint's ball-and-socket form. It is a shallow, pyriform articular surface, which is located on the lateral angle of the scapula. It is directed laterally and forward and articulates with the head of the humerus; it is broader below than above and its vertical diameter is the longest.
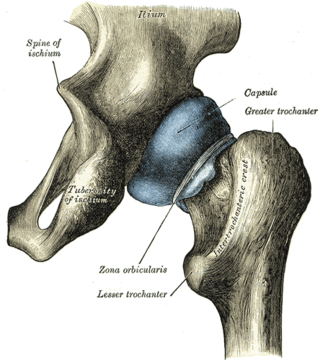
The zona orbicularis or annular ligament is a ligament on the neck of the femur formed by the circular fibers of the articular capsule of the hip joint. It is also known as the orbicular zone, ring ligament, and zonular band.

The coracoacromial ligament is a strong triangular ligament between the coracoid process and the acromion. It protects the head of the humerus. Its acromial attachment may be repositioned to the clavicle during reconstructive surgery of the acromioclavicular joint.

In human anatomy, the glenohumeral ligaments (GHL) are three ligaments on the anterior side of the glenohumeral joint. Reinforcing the anterior glenohumeral joint capsule, the superior, middle, and inferior glenohumeral ligaments play different roles in the stability of the head of the humerus depending on arm position and degree of rotation.
Shoulder surgery is a means of treating injured shoulders. Many surgeries have been developed to repair the muscles, connective tissue, or damaged joints that can arise from traumatic or overuse injuries to the shoulder.

Shoulder replacement is a surgical procedure in which all or part of the glenohumeral joint is replaced by a prosthetic implant. Such joint replacement surgery generally is conducted to relieve arthritis pain or fix severe physical joint damage.

The elbow is the region between the upper arm and the forearm that surrounds the elbow joint. The elbow includes prominent landmarks such as the olecranon, the cubital fossa, and the lateral and the medial epicondyles of the humerus. The elbow joint is a hinge joint between the arm and the forearm; more specifically between the humerus in the upper arm and the radius and ulna in the forearm which allows the forearm and hand to be moved towards and away from the body. The term elbow is specifically used for humans and other primates, and in other vertebrates it is not used. In those cases, forelimb plus joint is used.

















