
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the collection of symptoms and signs associated with nerve compression of the median nerve at the carpal tunnel. Most CTS is related to idiopathic compression of the median nerve as it travels through the wrist at the carpal tunnel. Idiopathic means that there is no other disease process contributing to pressure on the nerve. As with most structural issues, it occurs in both hands, and the strongest risk factor is genetics.

The carpal bones are the eight small bones that make up the wrist (carpus) that connects the hand to the forearm. The term "carpus" and "carpal" is derived from the Latin carpus and the Greek καρπός (karpós), meaning "wrist". In human anatomy, the main role of the carpal bones is to articulate with the radial and ulnar heads to form a highly mobile condyloid joint, to provide attachments for thenar and hypothenar muscles, and to form part of the rigid carpal tunnel which allows the median nerve and tendons of the anterior forearm muscles to be transmitted to the hand and fingers.

In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; (2) the wrist joint or radiocarpal joint, the joint between the radius and the carpus and; (3) the anatomical region surrounding the carpus including the distal parts of the bones of the forearm and the proximal parts of the metacarpus or five metacarpal bones and the series of joints between these bones, thus referred to as wrist joints. This region also includes the carpal tunnel, the anatomical snuff box, bracelet lines, the flexor retinaculum, and the extensor retinaculum.

The trapezoid bone is a carpal bone in tetrapods, including humans. It is the smallest bone in the distal row of carpal bones that give structure to the palm of the hand. It may be known by its wedge-shaped form, the broad end of the wedge constituting the dorsal, the narrow end the palmar surface; and by its having four articular facets touching each other, and separated by sharp edges. It is homologous with the "second distal carpal" of reptiles and amphibians.
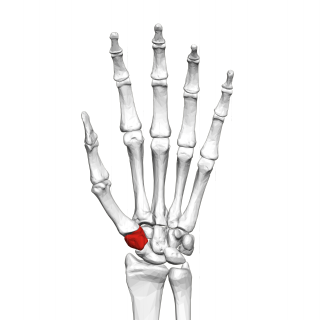
The trapezium bone is a carpal bone in the hand. It forms the radial border of the carpal tunnel.

In human anatomy, the metacarpal bones or metacarpus, also known as the "palm bones", are the appendicular bones that form the intermediate part of the hand between the phalanges (fingers) and the carpal bones, which articulate with the forearm. The metacarpal bones are homologous to the metatarsal bones in the foot.

The scaphoid bone is one of the carpal bones of the wrist. It is situated between the hand and forearm on the thumb side of the wrist. It forms the radial border of the carpal tunnel. The scaphoid bone is the largest bone of the proximal row of wrist bones, its long axis being from above downward, lateralward, and forward. It is approximately the size and shape of a medium cashew nut.

The capitate bone is a bone in the human wrist found in the center of the carpal bone region, located at the distal end of the radius and ulna bones. It articulates with the third metacarpal bone and forms the third carpometacarpal joint. The capitate bone is the largest of the carpal bones in the human hand. It presents, above, a rounded portion or head, which is received into the concavity formed by the scaphoid and lunate bones; a constricted portion or neck; and below this, the body. The bone is also found in many other mammals, and is homologous with the "third distal carpal" of reptiles and amphibians.

The hamate bone, or unciform bone, Latin os hamatum and occasionally abbreviated as just hamatum, is a bone in the human wrist readily distinguishable by its wedge shape and a hook-like process ("hamulus") projecting from its palmar surface.

The lunate bone is a carpal bone in the human hand. It is distinguished by its deep concavity and crescentic outline. It is situated in the center of the proximal row carpal bones, which lie between the ulna and radius and the hand. The lunate carpal bone is situated between the lateral scaphoid bone and medial triquetral bone.

The pisiform bone, also spelled pisiforme, is a small knobbly, sesamoid bone that is found in the wrist. It forms the ulnar border of the carpal tunnel.

The triquetral bone is located in the wrist on the medial side of the proximal row of the carpus between the lunate and pisiform bones. It is on the ulnar side of the hand, but does not directly articulate with the ulna. Instead, it is connected to and articulates with the ulna through the Triangular fibrocartilage disc and ligament, which forms part of the ulnocarpal joint capsule. It connects with the pisiform, hamate, and lunate bones. It is the 2nd most commonly fractured carpal bone.

The flexor retinaculum is a fibrous band on the palmar side of the hand near the wrist. It arches over the carpal bones of the hands, covering them and forming the carpal tunnel.

The intercarpal joints can be subdivided into three sets of joints : Those of the proximal row of carpal bones, those of the distal row of carpal bones, and those of the two rows with each other.

The palmar intercarpal ligaments are fibrous bands that extend transversely across the palmar surfaces of the carpal bones, connecting adjacent carpals. These are the ligaments that define the structure of the ligamentous palmar arch.

In the human body, the carpal tunnel or carpal canal is a flattened body cavity on the flexor (palmar/volar) side of the wrist, bounded by the carpal bones and flexor retinaculum. It forms the passageway that transmits the median nerve and the tendons of the extrinsic flexor muscles of the hand from the forearm to the hand. There are described cases of the anatomical variant median artery occurrence.

The dorsal intercarpal ligament consists of a series of fibrous bands that extend transversely across the dorsal surfaces of the carpal bones, connecting them to each other.
The interosseous intercarpal ligaments are short fibrous bands that connect the adjacent surfaces of the various carpal bones.

A hand is a prehensile, multi-fingered appendage located at the end of the forearm or forelimb of primates such as humans, chimpanzees, monkeys, and lemurs. A few other vertebrates such as the koala are often described as having "hands" instead of paws on their front limbs. The raccoon is usually described as having "hands" though opposable thumbs are lacking.

















