A dorsal fin is a fin located on the back of most marine and freshwater vertebrates within various taxa of the animal kingdom. Many species of animals possessing dorsal fins are not particularly closely related to each other, though through convergent evolution they have independently evolved external superficial fish-like body plans adapted to their marine environments, including most numerously fish, but also mammals such as cetaceans, and even extinct ancient marine reptiles such as various known species of ichthyosaurs. Most species have only one dorsal fin, but some have two or three.

In human anatomy, the metacarpal bones or metacarpus, also known as the "palm bones", are the appendicular bones that form the intermediate part of the hand between the phalanges (fingers) and the carpal bones, which articulate with the forearm. The metacarpal bones are homologous to the metatarsal bones in the foot.

Afferent nerve fibers are axons of sensory neurons that carry sensory information from sensory receptors to the central nervous system. Many afferent projections arrive at a particular brain region.

The spinothalamic tract is a part of the anterolateral system or the ventrolateral system, a sensory pathway to the thalamus. From the ventral posterolateral nucleus in the thalamus, sensory information is relayed upward to the somatosensory cortex of the postcentral gyrus.

A carapace is a dorsal (upper) section of the exoskeleton or shell in a number of animal groups, including arthropods, such as crustaceans and arachnids, as well as vertebrates, such as turtles and tortoises. In turtles and tortoises, the underside is called the plastron.

The dorsal column–medial lemniscus pathway (DCML) is a sensory pathway of the central nervous system that conveys sensations of fine touch, vibration, two-point discrimination, and proprioception from the skin and joints. It transmits information from the body to the primary somatosensory cortex in the postcentral gyrus of the parietal lobe of the brain. The pathway receives information from sensory receptors throughout the body, and carries this in nerve tracts in the white matter of the dorsal column of the spinal cord to the medulla, where it is continued in the medial lemniscus, on to the thalamus and relayed from there through the internal capsule and transmitted to the somatosensory cortex. The name dorsal-column medial lemniscus comes from the two structures that carry the sensory information: the dorsal columns of the spinal cord, and the medial lemniscus in the brainstem.

The torso or trunk is an anatomical term for the central part, or the core, of the body of many animals, from which the head, neck, limbs, tail and other appendages extend. The tetrapod torso — including that of a human — is usually divided into the thoracic segment, the abdominal segment, and the pelvic and perineal segments.

The lateral lemniscus is a tract of axons in the brainstem that carries information about sound from the cochlear nucleus to various brainstem nuclei and ultimately the contralateral inferior colliculus of the midbrain. Three distinct, primarily inhibitory, cellular groups are located interspersed within these fibers, and are thus named the nuclei of the lateral lemniscus.

A dorsal root ganglion is a cluster of neurons in a dorsal root of a spinal nerve. The cell bodies of sensory neurons known as first-order neurons are located in the dorsal root ganglia.

The spinocerebellar tract is a nerve tract originating in the spinal cord and terminating in the same side (ipsilateral) of the cerebellum.

The dorsal root of spinal nerve is one of two "roots" which emerge from the spinal cord. It emerges directly from the spinal cord, and travels to the dorsal root ganglion. Nerve fibres with the ventral root then combine to form a spinal nerve. The dorsal root transmits sensory information, forming the afferent sensory root of a spinal nerve.

In human anatomy, the dorsal interossei (DI) are four muscles in the back of the hand that act to abduct (spread) the index, middle, and ring fingers away from hand's midline and assist in flexion at the metacarpophalangeal joints and extension at the interphalangeal joints of the index, middle and ring fingers.

The dorsal ramus of spinal nerve, posterior ramus of spinal nerve, or posterior primary division is the posterior division of a spinal nerve. The dorsal rami provide motor innervation to the deep muscles of the back, and sensory innervation to the skin of the posterior portion of the head, neck and back.

In human male anatomy, the dorsal veins of the penis are blood vessels that drain the shaft, the skin and the glans of the human penis. They are typically located in the midline on the dorsal aspect of the penis and they comprise the superficial dorsal veinof the penis, that lies in the subcutaneous tissue of the shaft, and the deep dorsal veinof the penis, that lies beneath the deep fascia.

In snakes, the dorsal scales are the longitudinal series of plates that encircle the body, but do not include the ventral scales.
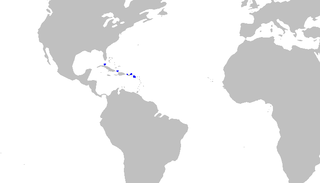
Springer's sawtail catshark is a species of catshark, belonging to the family Scyliorhinidae, found in waters 457–699 m (1,499–2,293 ft) deep off the islands of the Antilles, from Cuba to the Leewards. A small, slim-bodied species reaching a length of 48 cm (19 in), the Springer's sawtail catshark can be identified by its color pattern of horizontal dark stripes in front of the first dorsal fin, and dark dorsal saddles behind. It is additionally characterized by the presence of saw-toothed crests, made of enlarged dermal denticles along both the dorsal and the ventral edges of the caudal fin. The Springer's sawtail catshark is oviparous.

The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal cord is hollow and contains a structure called the central canal, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The spinal cord is also covered by meninges and enclosed by the neural arches. Together, the brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system.

Overosaurus is an extinct genus of sauropod dinosaurs, containing only a single species, Overosaurus paradasorum. This species lived approximately 86 to 84 million years ago during the latter part of the Cretaceous Period in what is now Patagonia. Overosaurus paradasorum was relatively small compared to other sauropods from Patagonia, like the saltasaurids and other aeolosaurines, estimated as approximately 10 m (33 ft). It was a ground-dwelling herbivore.

Yongjinglong is an extinct genus of titanosauriform sauropod dinosaur known from the Early Cretaceous of Lanzhou-Minhe Basin of Gansu Province, China. It contains a single species, Yongjinglong datangi.

Vectiraptor is a genus of dromaeosaurid dinosaur from the Barremian aged Wessex Formation of the United Kingdom. The type and only species is Vectiraptor greeni, known from associated dorsal vertebrae and a partial sacrum.