
Mercury is the first planet from the Sun and the smallest in the Solar System. In English, it is named after the ancient Roman god Mercurius (Mercury), god of commerce and communication, and the messenger of the gods. Mercury is classified as a terrestrial planet, with roughly the same surface gravity as Mars. The surface of Mercury is heavily cratered, as a result of countless impact events that have accumulated over billions of years. Its largest crater, Caloris Planitia, has a diameter of 1,550 km (960 mi), which is about one-third the diameter of the planet. Similarly to the Earth's Moon, Mercury's surface displays an expansive rupes system generated from thrust faults and bright ray systems formed by impact event remnants.

Caloris Planitia is a plain within a large impact basin on Mercury, informally named Caloris, about 1,550 km (960 mi) in diameter. It is one of the largest impact basins in the Solar System. "Calor" is Latin for "heat" and the basin is so-named because the Sun is almost directly overhead every second time Mercury passes perihelion. The crater, discovered in 1974, is surrounded by the Caloris Montes, a ring of mountains approximately 2 km (1.2 mi) tall.

Kuiper is a moderate-size crater with a central peak cluster located at 11.35°S 31.23°W on Mercury. It is 62 kilometers in diameter and was named after Dutch-American astronomer Gerard Kuiper in 1976. It is one of only 2 Mercurian craters which are named not after artists, and one of very few cases when the same name is used for 3 craters. Gerard Kuiper, being a leader of American planetary science, died shortly before the first images of Mercurian surface were made.

The Eminescu quadrangle (H-9) is one of fifteen quadrangles on Mercury. It runs from 216 to 288° longitude and from -25 to 25° latitude. Named after the Eminescu crater, it was mapped in detail for the first time after MESSENGER entered orbit around Mercury in 2011. It had not been mapped prior to that point because it was one of the six quadrangles that was not illuminated when Mariner 10 made its flybys in 1974 and 1975. These six quadrangles continued to be known by their albedo feature names, with this one known as the Solitudo Criophori quadrangle.

The Michelangelo quadrangle is in the southern hemisphere of the planet Mercury, where the imaged part is heavily cratered terrain that has been strongly influenced by the presence of multiring basins. At least four such basins, now nearly obliterated, have largely controlled the distribution of plains materials and structural trends in the map area. Many craters, interpreted to be of impact origin, display a spectrum of modification styles and degradation states. The interaction between basins, craters, and plains in this quadrangle provides important clues to geologic processes that have formed the morphology of the mercurian surface.

Boethius is a crater on the planet Mercury. It was named after Anicius Manlius Severinus Boethius, the Roman philosopher, by the IAU in 1976. The crater was first imaged by Mariner 10 in 1974.

Shakespeare is a 370 km diameter impact basin in the Shakespeare quadrangle of Mercury, which is named after this crater. It is located at 48.1°N, 152.3°W and is named after playwright William Shakespeare. The crater was first imaged by Mariner 10 in 1974.

Sholem Aleichem is a crater on Mercury, named after the Yiddish writer Sholem Aleichem. The inter-crater plain deposits have been deformed by linear ridges.
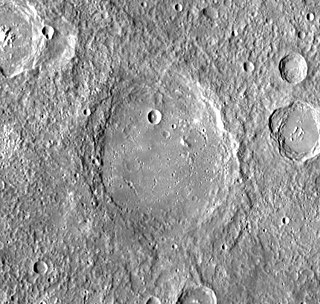
Sullivan is a crater on Mercury. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in 1976, and is named for the American architect Louis Sullivan. The crater was first imaged by Mariner 10 in 1974.

Vyāsa is a crater on Mercury. It was named by the IAU in 1979, after the Indian poet Vyasa. It is Tolstojan in age.

Homer is a crater on Mercury. It is one of 110 peak ring basins on Mercury. It is Tolstojan in age.
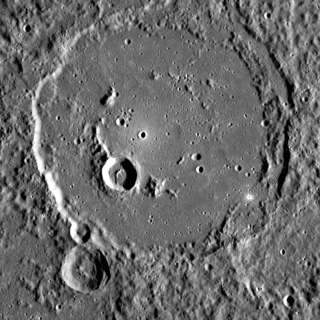
Polygnotus is a crater on Mercury, named by the IAU in 1976, after ancient Greek painter Polygnotus. The crater was first imaged by Mariner 10 in 1974.

Qi Baishi is a crater on Mercury. The crater was named after famed Chinese painter Qi Baishi. The crater has an asymmetric pattern of ejecta rays, which formed by an object traveling to the east or to the west and impacting Mercury's surface at a very low incidence angle. However, Qi Baishi crater is still roughly circular, which is in contrast to the elongated shape of neighboring Hovnatanian crater.

Futabatei is a crater on Mercury. It has a diameter of 57 kilometers. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union in 1976. Futabatei is named for the Japanese novelist Futabatei Shimei, who lived from 1864 to 1909. The crater was first imaged by Mariner 10 in 1974.

Machaut is a crater on Mercury. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union in 1976. Machaut is named for the French composer and poet Guillaume de Machaut, who lived from 1300 to 1377. The crater was first imaged by Mariner 10 in 1974.
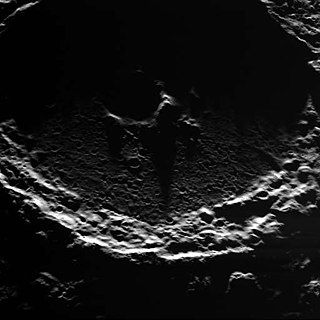
Prokofiev is a crater near the north pole of the planet Mercury, named after the Russian composer Sergei Prokofiev. Data from the MESSENGER spacecraft indicates that it contains water ice and organic compounds. Although other craters in Mercury's north polar region are also believed to contain ice, Prokofiev is the largest of them, with probable surface ice along the southern crater floor that is in perpetual darkness.

Holst is a crater on Mercury. Its name was adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) on April 24, 2012.

Carolan is a crater on Mercury. Its name was suggested by an Irishman, Fergal Donnelly, and two Americans, Joseph Brusseau and Deane Morrison, in a naming contest which was eventually adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) on 2015. Carolan is named for the Irish composer and performer Turlough O'Carolan, who lived from 1670 to 1738 C.E. The craters Kulthum, Enheduanna, Karsh, and Rivera were also named as part of the contest.
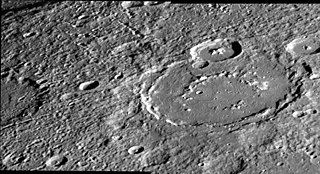
Larrocha is an impact crater on Mercury. It has a diameter of 196 km (122 mi), and it is one of 110 peak ring basins on Mercury. It is located in the Victoria quadrangle at 43.29°N 69.83°W.




















