
Celtis is a genus of about 60–70 species of deciduous trees, commonly known as hackberries or nettle trees, widespread in warm temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. The genus is part of the extended Cannabis family (Cannabaceae).
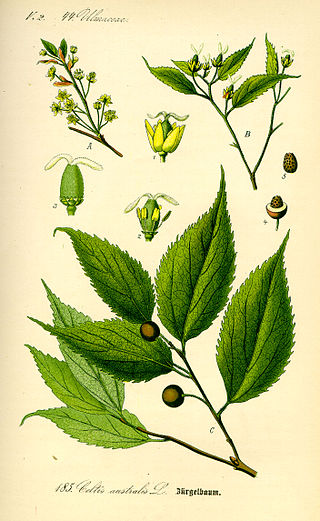
Celtis australis, the European nettle tree, Mediterranean hackberry, lote tree, or honeyberry, is a deciduous tree native to Southern Europe, North Africa, and Asia Minor. The tree was introduced to England in 1796.

The American snout or common snout butterfly is a member of the subfamily Libytheinae in the brush-footed butterfly family, Nymphalidae. This species is found in both North and South America. The larval host plants are Celtis species on which the eggs are laid singly. Massive migrations of this species often attract attention in the Texas and Mexican newspapers.

Celtis occidentalis, commonly known as the common hackberry, is a large deciduous tree native to North America. It is also known as the nettletree, sugarberry, beaverwood, northern hackberry, and American hackberry. It is a moderately long-lived hardwood with a light-colored wood, yellowish gray to light brown with yellow streaks.

Celtis laevigata is a medium-sized tree native to North America. Common names include sugarberry, southern hackberry, or in the southern U.S. sugar hackberry or just hackberry.

Celtis sinensis is a species of flowering plant in the hemp family, Cannabaceae, that is native to slopes in East Asia.

Celtis mildbraedii is a species of forest tree in the family Cannabaceae. It was previously assigned to the family Ulmaceae. These trees grow in limited areas of South Africa, Mozambique and Zimbabwe. They are also found in forested areas from West Africa to Sudan, DRC, Angola and Tanzania. Common names include natal white stinkwood, red-fruited white-stinkwood and natal elm. This species is more common in Tropical Africa than in Southern Africa.

Trema orientale is a species of flowering tree in the hemp family, Cannabaceae. It is known by many common names, including charcoal-tree, Indian charcoal-tree, pigeon wood, Oriental trema, and in Hawaii, where it has become naturalized, gunpowder tree, or nalita. It has a near universal distribution in tropical and warm temperate parts of the Old World, with a range extending from South Africa, through the Middle East, the Indian subcontinent and southern China to Southeast Asia and Australia.
Celtis zenkeri is a species of flowering plant native to sub-Saharan Africa.

Celtis timorensis, commonly known as stinkwood or stinking wood, is a species of flowering plant in the family Cannabaceae that grows in tropical Asia. The specific epithet comes from the name of the island of Timor, the locality of the type collection. The most notable characteristic of the tree is the strong excrement odour that it emits from the bark and sap, which pervades the surrounding forest. This is due to the presence of the malodorous organic compound skatole. In Thailand, it therefore known as kæ̂ng k̄hī̂ phrar̀wng or mị̂ chĕd tūd phrar̀wng which means 'wipe the bottom timber'. Thai legend has it that Phra Ruang wiped his buttocks with it. In Sri Lanka the heartwood of the tree is used as a traditional ayurvedic medicine against syphilis, chickenpox, and measles.
Celtis madagascariensis is a species of flowering plant endemic to Madagascar.

Trema lamarckianum, Lamarck's trema, West Indian nettle tree, or pain-in-the-back is a plant species in the genus Trema of the family Cannabaceae. It is a small evergreen shrub that is native of Florida and the West Indies. It has several common names such as pain-in-back, cabrilla and Lamarck trema. It is 6 m tall growing all year.

Celtis iguanaea, commonly known as the iguana hackberry is a deciduous tree in the genus Celtis.

Cynometra alexandri, the Uganda ironwood or muhimbi, is a species of legume that occurs in tropical lowland forests of central and east Africa. They grow gregariously in drier forest types and as a constituent of swamp forests. They reach some 120 feet (37 m) to 150 feet (46 m) in height, and larger trees often develop hollow boles and buttress roots.

Celtis ehrenbergiana, called the desert hackberry or spiny hackberry, is a plant species that has long been called C. pallida by many authors, including in the "Flora of North America" database. It is native to Arizona, Florida, New Mexico and Texas, and to Latin America as far south as central Argentina. It grows in dry locations such as deserts, brushlands, canyons, mesas and grasslands.

Celtis glabrata is a deciduous tree in the genus Celtis, native to parts of eastern Europe and western Asia. Its Turkish common name is dahum.

Celtis philippensis, is an Asian species of flowering plant in the family Cannabaceae. It is a tree which can grow up to 30 meters tall. It ranges from India and Sri Lanka to southern China and Taiwan, the Philippines, New Guinea and the Solomon Islands, and northern Australia.

Celtis biondii is a species of hackberry native to China, Taiwan, Korea, and Japan. It prefers to grow on limestone in the floristic assemblage that is thought to also include wild Ginkgo biloba. It is a deciduous tree growing 18 m (59 ft) tall.

Celtis caucasica, the Caucasian hackberry or Caucasian nettle tree, is a species of flowering plant in the family Cannabaceae. It is native to the Caucasus region, Central Asia, and on to the western Himalaya. Hardy to USDA zone 5b, it tolerates poor soils, drought, and nearby paving, and can be used as street tree. It is a nitrogen-fixer, in symbiosis with the mycorrhizal fungi Funneliformis mosseae and Rhizophagus intraradices.

Celtis gomphophylla is a species of flowering plant native to sub-Saharan Africa, Madagascar, and the Comoros.



















