
The Devonian is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era during the Phanerozoic eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian period at 419.2 million years ago (Ma), to the beginning of the succeeding Carboniferous period at 358.9 Ma. It is named after Devon, South West England, where rocks from this period were first studied.
The Mississippian is a subperiod in the geologic timescale or a subsystem of the geologic record. It is the earlier of two subperiods of the Carboniferous period lasting from roughly 358.9 to 323.2 million years ago. As with most other geochronologic units, the rock beds that define the Mississippian are well identified, but the exact start and end dates are uncertain by a few million years. The Mississippian is so named because rocks with this age are exposed in the Mississippi Valley.

The Silurian is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at 443.8 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, 419.2 Mya. The Silurian is the shortest period of the Paleozoic Era. As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the exact dates are uncertain by a few million years. The base of the Silurian is set at a series of major Ordovician–Silurian extinction events when up to 60% of marine genera were wiped out.

The Old Red Sandstone is an assemblage of rocks in the North Atlantic region largely of Devonian age. It extends in the east across Great Britain, Ireland and Norway, and in the west along the eastern seaboard of North America. It also extends northwards into Greenland and Svalbard. These areas were a part of the ancient continent of Euramerica/Laurussia. In Britain it is a lithostratigraphic unit to which stratigraphers accord supergroup status and which is of considerable importance to early paleontology. For convenience the short version of the term, ORS is often used in literature on the subject. The term was coined to distinguish the sequence from the younger New Red Sandstone which also occurs widely throughout Britain.

Goniatids, informally goniatites, are ammonoid cephalopods that form the order Goniatitida, derived from the more primitive Agoniatitida during the Middle Devonian some 390 million years ago. Goniatites (goniatitids) survived the Late Devonian extinction to flourish during the Carboniferous and Permian only to become extinct at the end of the Permian some 139 million years later.
The Great Devonian Controversy began in 1834 when Roderick Murchison disagreed with Henry De la Beche as to the dating of certain petrified plants found in coals in the Greywacke stratum in North Devon, England. De La Beche was claiming that since Carboniferous fossils were found deep in the Greywacke stratum, which itself was older than the Carboniferous period, this method of dating rocks was not valid. Murchison, in contrast, claimed that De La Beche had not placed the fossils correctly, as they were occurring quite near the top of the stratum as opposed to deep within it. De La Beche soon agreed with Murchison's argument as to the placing of fossils but maintained that since a layer of Old Red Sandstone, present in other formations, was missing between the layer of older rock and this new formation, there was still insufficient evidence to suggest the formation was not part of the older Silurian strata.

Start Point is a promontory in the South Hams district in Devon, England, grid reference SX832370. Close to the most southerly point in the county, it marks the southern limit of Start Bay, which extends northwards to the estuary of the River Dart.

The Caledonian orogeny was a mountain-building cycle recorded in the northern parts of the British Isles, the Scandinavian Caledonides, Svalbard, eastern Greenland and parts of north-central Europe. The Caledonian orogeny encompasses events that occurred from the Ordovician to Early Devonian, roughly 490–390 million years ago (Ma). It was caused by the closure of the Iapetus Ocean when the Laurentia and Baltica continents and the Avalonia microcontinent collided.

The Sidlaws are a range of hills in the counties of Perthshire and Angus in Scotland that extend for 30 miles (45 km) from Kinnoull Hill, near Perth, northeast to Forfar. A continuation of the Ochils, they separate Strathmore to the north from the Carse of Gowrie on the shore of the Tay.
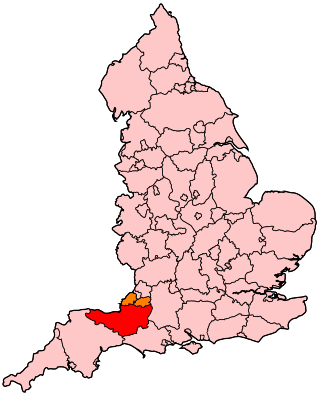
Somerset is a rural county in the southwest of England, covering 4,171 square kilometres (1,610 sq mi). It is bounded on the north-west by the Bristol Channel, on the north by Bristol and Gloucestershire, on the north-east by Wiltshire, on the south-east by Dorset, and on the south west and west by Devon. It has broad central plains with several ranges of low hills. The landscape divides into four main geological sections from the Silurian through the Devonian and Carboniferous to the Permian which influence the landscape, together with water-related features.
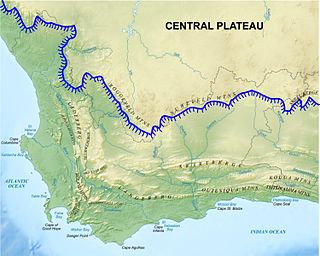
The Cape Fold Belt is a fold and thrust belt of late Paleozoic age, which affected the sequence of sedimentary rock layers of the Cape Supergroup in the southwestern corner of South Africa. It was originally continuous with the Ventana Mountains near Bahía Blanca in Argentina, the Pensacola Mountains, the Ellsworth Mountains and the Hunter-Bowen orogeny in eastern Australia. The rocks involved are generally sandstones and shales, with the shales persisting in the valley floors while the erosion resistant sandstones form the parallel ranges, the Cape Fold Mountains, which reach a maximum height of 2325 m at Seweweekspoortpiek.

The geology of Wales is complex and varied; its study has been of considerable historical significance in the development of geology as a science. All geological periods from the Cryogenian to the Jurassic are represented at outcrop, whilst younger sedimentary rocks occur beneath the seas immediately off the Welsh coast. The effects of two mountain-building episodes have left their mark in the faulting and folding of much of the Palaeozoic rock sequence. Superficial deposits and landforms created during the present Quaternary period by water and ice are also plentiful and contribute to a remarkably diverse landscape of mountains, hills and coastal plains.
New Jersey is a very geologically and geographically diverse region in the United States' Middle Atlantic region, offering variety from the Appalachian Mountains and the Highlands in the state's northwest, to the Atlantic Coastal Plain region that encompasses both the Pine Barrens and the Jersey Shore. The state's geological features have impacted the course of settlement, development, commerce and industry over the past four centuries.

Table Mountain Sandstone (TMS) is a group of rock formations within the Cape Supergroup sequence of rocks. Although the term "Table Mountain Sandstone" is still widely used in common parlance, the term TMS is no longer formally recognized; the correct name is the "Peninsula Formation Sandstone", which is part of the Table Mountain Group. The designation "Table Mountain Sandstone" will, however, in deference to the title, continue to be used in the rest of this article. The name is derived from the famous landmark in Cape Town, Table Mountain.
The Orcadian Basin is a sedimentary basin of Devonian age that formed mainly as a result of extensional tectonics in northeastern Scotland after the end of the Caledonian orogeny. During part of its history, the basin was filled by a lake now known as Lake Orcadie. In that lacustrine environment, a sequence of finely bedded sedimentary rocks was deposited, containing well-preserved fish fossils, with alternating layers of mudstone and coarse siltstone to very fine sandstone. These flagstones split easily along the bedding and have been used as building material for thousands of years. The deposits of the Orcadian Basin form part of the Old Red Sandstone (ORS). The lithostratigraphic terms lower, middle and upper ORS, however, do not necessarily match exactly with sediments of lower, middle and upper Devonian age, as the base of the ORS is now known to be in the Silurian and the top in the Carboniferous.

Gondwana was a large landmass, sometimes referred to as a supercontinent. It was formed by the accretion of several cratons, beginning c. 800 to 650Ma with the East African Orogeny, the collision of India and Madagascar with East Africa, and culminating in c. 600 to 530 Ma with the overlapping Brasiliano and Kuunga orogenies, the collision of South America with Africa, and the addition of Australia and Antarctica, respectively. Eventually, Gondwana became the largest piece of continental crust of the Palaeozoic Era, covering an area of some 100,000,000 km2 (39,000,000 sq mi), about one-fifth of the Earth's surface. It fused with Euramerica during the Carboniferous to form Pangea. It began to separate from northern Pangea (Laurasia) during the Triassic, and started to fragment during the Early Jurassic. The final stages of break-up, involving the separation of Antarctica from South America and Australia, occurred during the Paleogene (from around 66 to 23 million years ago. Gondwana was not considered a supercontinent by the earliest definition, since the landmasses of Baltica, Laurentia, and Siberia were separated from it. To differentiate it from the Indian region of the same name, it is also commonly called Gondwanaland.

The geology of the Orkney islands in northern Scotland is dominated by the Devonian Old Red Sandstone (ORS). In the southwestern part of Mainland, this sequence can be seen to rest unconformably on a Moinian type metamorphic basement.

Gondwanascorpio emzantsiensis is an extinct Gondwanan scorpion that lived 360 million years ago in the Devonian. Its fossil remains, clearly showing pincer and sting, were discovered in rocks of the Witteberg Group near Grahamstown in South Africa. At present, this scorpion is the oldest known land-dwelling animal from Gondwana, which in Devonian times was separated from Laurasia by a deep ocean. At the time, the fossil site was only 15° from the South Pole, but rather than arctic-like tundra, the region was probably wooded, providing ample insect life for food. Previously, only two scorpion species were known from the late Devonian – Hubeiscorpio gracilitarsus from China and Petaloscorpio bureaui from Canada. The species was described by Robert Gess of Wits University in the journal African Invertebrates. The specific epithet derives from umZantsi, the isiXhosa word for "south", sometimes used for South Africa.

Patagonia comprises the southernmost region of South America, portions of which lie on either side of the Argentina-Chile border. It has traditionally been described as the region south of the Rio Colorado, although the physiographic border has more recently been moved southward to the Huincul fault. The region's geologic border to the north is composed of the Rio de la Plata craton and several accreted terranes comprising the La Pampa province. The underlying basement rocks of the Patagonian region can be subdivided into two large massifs: the North Patagonian Massif and the Deseado Massif. These massifs are surrounded by sedimentary basins formed in the Mesozoic that underwent subsequent deformation during the Andean orogeny. Patagonia is known for its vast earthquakes and the damage they cause.
The geology of Belgium encompasses rocks, minerals and tectonic events stretching back more than 500 million years. Belgium covers an area of about 30,507 square kilometers and was instrumental in the development of geology. The extensive outcrops in Belgium became the standard reference points in stratigraphy as early as the mid-19th century. Some of them are internationally recognized features related to the Carboniferous and the Devonian periods. These rocks were folded by two orogeny mountain building events --the Hercynian orogeny, and Caledonian Orogeny. Paleozoic basement rocks cover much of the country and are overlain by Mesozoic and Cenozoic sediments.














