
The brown recluse is a recluse spider with necrotic venom. Similar to those of other recluse spiders, their bites sometimes require medical attention. The brown recluse is one of three spiders in North America with dangerous venom, the others being the black widow and the Chilean recluse.

Wolf spiders are members of the family Lycosidae, so named for their robust and agile hunting skills and excellent eyesight. They live mostly in solitude, hunt alone, and usually do not spin webs. Some are opportunistic hunters, pouncing upon prey as they find it or chasing it over short distances; others wait for passing prey in or near the mouth of a burrow.

Cheiracanthium inclusum, alternately known as the black-footed yellow sac spider or the American yellow sac spider, was formerly classified as a true sac spider, and then placed in the family Miturgidae, but now belongs to family Cheiracanthiidae. It is a rather small pale yellow species that is indigenous to the Americas. It is often found living in the foliage of forests and gardens but also can inhabit human homes. Despite common beliefs of necrosis, Cheiracanthium bites cause only localized swelling. C. inclusum is closely related to Cheiracanthium mildei, an introduced species native to Europe which is similar in appearance and natural history and can also be found in North American homes.

Huntsman spiders, members of the family Sparassidae, are known by this name because of their speed and mode of hunting. They are also called giant crab spiders because of their size and appearance. Larger species sometimes are referred to as wood spiders, because of their preference for woody places. In southern Africa the genus Palystes are known as rain spiders or lizard-eating spiders. Commonly, they are confused with baboon spiders from the Mygalomorphae infraorder, which are not closely related.

Latrodectus is a broadly distributed genus of spiders with several species that are commonly known as the true widows. This group is composed of those often loosely called black widow spiders, brown widow spiders, and similar spiders. However, the diversity of species is much greater. A member of the family Theridiidae, this genus contains 34 species, which include several North American "black widows". Besides these, North America also has the red widow Latrodectus bishopi and the brown widow Latrodectus geometricus, which, in addition to North America, has a much wider geographic distribution. Elsewhere, others include the European black widow, the Australian redback spider and the closely related New Zealand katipō, several different species in Southern Africa that can be called button spiders, and the South American black-widow spiders. Species vary widely in size. In most cases, the females are dark-coloured and can be readily identified by reddish markings on the central underside (ventral) abdomen, which are often hourglass-shaped.

The spider species Tegenaria domestica, commonly known as the barn funnel weaver in North America and the domestic house spider in Europe, is a member of the funnel-web family Agelenidae.

Heteropoda venatoria is a species of spider in the family Sparassidae, the huntsman spiders. It is native to the tropical regions of the world, and it is present in some subtropical areas as an introduced species. Its common names include giant crab spider, pantropical huntsman spider or cane spider.

The giant house spider has been treated as either one species, under the name Eratigena atrica, or as three species, E. atrica, E. duellica and E. saeva. As of April 2020, the three species view was accepted by the World Spider Catalog. They are among the largest spiders of Central and Northern Europe. They were previously placed in the genus Tegenaria. In 2013, they were moved to the new genus Eratigena as the single species Eratigena atrica. In 2018, the three separate species were restored. The bite of these species does not pose a threat to humans or pets, and they are generally reluctant to bite, preferring instead to hide or escape.

The woodlouse spider is a species of spider that preys primarily upon woodlice. Other common names refer to variations on the common name of its prey, including woodlouse hunter, sowbug hunter, sowbug killer, pillbug hunter and slater spider.

Cheiracanthium, commonly called yellow sac spiders, is a genus of araneomorph spiders in the family Cheiracanthiidae, and was first described by Carl Ludwig Koch in 1839. They are usually pale in colour, and have an abdomen that can range from yellow to beige. Both sexes range in size from 5 to 10 millimetres. They are unique among common house spiders because their tarsi do not point either outward, like members of Tegenaria, or inward, like members of Araneus, making them easier to identify.

Cheiracanthium punctorium, one of several species commonly known as the yellow sac spider, is a spider found from central Europe to Central Asia. They reach a length of about 15 mm, and their bite can penetrate human skin; the bite has been compared to a wasp sting, perhaps a bit more severe, although susceptible persons can have stronger reactions, like nausea. Females build an egg sac of about 4 cm in high grass. It opens below and is aggressively defended.

Peucetia viridans, the green lynx spider, is a bright-green lynx spider usually found on green plants. It is the largest North American species in the family Oxyopidae. This spider is common in the southern U.S., Mexico, Central America, and in many West Indies islands, especially Jamaica. Lynx spiders are hunters specialized for living on plants. This species does not use a web to capture its prey. It pounces on its prey in a cat-like manner, which is the reason for the name lynx. It is active during the day.
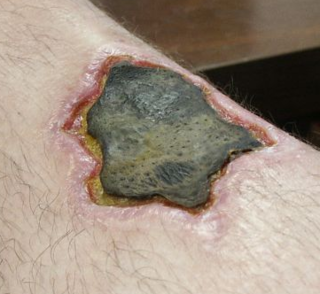
Loxoscelism is a condition occasionally produced by the bite of the recluse spiders. The area becomes dusky and a shallow open sore forms as the skin around the bite dies (necrosis). It is the only proven type of necrotic arachnidism in humans. While there is no known therapy effective for loxoscelism, there has been research on antibiotics, surgical timing, hyperbaric oxygen, potential antivenoms and vaccines. Because of the number of diseases that may mimic loxoscelism, it is frequently misdiagnosed by physicians.

Spodoptera littoralis, also referred to as the African cotton leafworm or Egyptian cotton leafworm or Mediterranean brocade, is a species of moth in the family Noctuidae. S. littoralis is found widely in Africa, Mediterranean Europe and Middle Eastern countries. It is a highly polyphagous organism that is a pest of many cultivated plants and crops. As a result, this species was assigned the label of A2 quarantine pest by the EPPO and was cautioned as a highly invasive species in the United States. The devastating impacts caused by these pests have led to the development of both biological and chemical control methods. This moth is often confused with Spodoptera litura.

Tarantulas comprise a group of large and often hairy spiders of the family Theraphosidae. As of December 2023, 1,100 species have been identified, with 166 genera. The term "tarantula" is usually used to describe members of the family Theraphosidae, although many other members of the same infraorder (Mygalomorphae) are commonly referred to as "tarantulas" or "false tarantulas". Some of the more common species have become popular in the exotic pet trade. Many New World species kept as pets have setae known as urticating hairs that can cause irritation to the skin, and in extreme cases, cause damage to the eyes.

The common rain spider, formerly P. natalius, is a species of huntsman spider native to Southern Africa. It is the most common and widespread species in the genus Palystes. In South Africa its distribution ranges from KwaZulu-Natal province in the east, then westwards to the provinces of Mpumalanga, Limpopo, Gauteng and North West in the north, and Eastern Cape and Western Cape in the south. It has a body length of 15–36 mm and a leg span of up to 110mm. The species was first described by Ludwig Carl Christian Koch in 1875.

Palystes is a genus of huntsman spiders, commonly called rain spiders or lizard-eating spiders, occurring in Africa, India, Australia, and the Pacific. The most common and widespread species is P. superciliosus, found in South Africa, home to 12 species in the genus. The name Palystes is derived from either the Latin palaestes or the Greek palaistes, meaning "wrestler". The genus was first described by Ludwig Carl Christian Koch in 1875.

Tigrosa helluo, commonly known as the Wetland Giant Wolf Spider, is a species of spider belonging to the family Lycosidae, also known as wolf spiders. T. helluo was formerly known as Hogna helluo before differences between dorsal color patterns, habitat preferences, body structures, etc. were discovered. The species is native to the United States, Canada, and Mexico. It can be found across the eastern half of the United States, primarily in the Northeast and New England, and as far west as Nebraska and Kansas. T. helluo can be found in diverse habitats including woods, marshes, fields, and riparian areas. Typically, members of this species prefer to live in wetter areas as opposed to dry environments. Males tend to live for around a year and females will live for close to two years.
Schizocosa stridulans is a sibling species of S. ocreata and S. rovneri and is part of the wolf spider family. The name of the genus comes from the epigynum structure being lycosid and having a split T excavation. This spider is well-known for its specific leg ornamentation and courtship rituals and that is how it has been differentiated from its related species. The S. stridulans take systematic steps during its courtship ritual, which involves two independent signals. More specifically, female spiders will leave silk and pheromones to communicate that they are ready to mate.


















