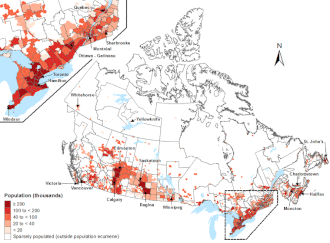
Eastern Canada | |
|---|---|
Region | |
 Eastern Canada (red) within the rest of Canada (tan) | |
| Country | Canada |
| Composition |
|
| Principal cities | |
| Area | |
• Total | 2,783,400 km2 (1,074,700 sq mi) |
| Population (2021) | |
• Total | 29,730,600 |
| • Density | 10.681/km2 (27.665/sq mi) |
Eastern Canada (French : Est du Canada, also known as the Eastern provinces, Canadian East or the East) is generally considered to be the region of Canada south of Hudson Bay/Hudson Strait and east of Manitoba, consisting of the following provinces (from east to west): Newfoundland and Labrador, Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, New Brunswick, Quebec and Ontario.
Contents
Eastern Canada overlaps into other geographic regions; Ontario and Quebec, Canada's two largest provinces, define Central Canada, while the other provinces in Eastern Canada constitute Atlantic Canada. New Brunswick, Nova Scotia and Prince Edward Island are also known as the Maritime provinces. [1]