
The Auriculariales are an order of fungi in the class Agaricomycetes. Species within the order were formerly referred to the "heterobasidiomycetes" or "jelly fungi", since many have gelatinous basidiocarps that produce spores on septate basidia. Around 200 species are known worldwide, placed in six or more families, though the status of these families is currently uncertain. All species in the Auriculariales are believed to be saprotrophic, most growing on dead wood. Fruit bodies of several Auricularia species are cultivated for food on a commercial scale, especially in China.

Tremella is a genus of fungi in the family Tremellaceae. All Tremella species are parasites of other fungi and most produce anamorphic yeast states. Basidiocarps, when produced, are gelatinous and are colloquially classed among the "jelly fungi". Over 100 species of Tremella are currently recognized worldwide. One species, Tremella fuciformis, is commercially cultivated for food.
Rhymbocarpus is a genus of lichenicolous (lichen-dwelling) fungi in the family Cordieritidaceae. It has 10 species. The genus was circumscribed by German mycologist Friedrich Wilhelm Zopf in 1896, with Rhymbocarpus punctiformis assigned as the type species.

The Agaricostilbomycetes are a class of fungi in the subdivision Pucciniomycotina of the Basidiomycota. The class consists of a single order, six families, and 15 genera. Its type genus, Agaricostilbum was originally placed in Ascomycota, and later, Agaricomycotina, before being placed in Pucinniomycotina.
The Cystobasidiomycetes are a class of fungi in the subdivision Pucciniomycotina of the Basidiomycota. Most species are known from their yeast states; hyphal states, when present, produce auricularioid basidia and are frequently parasites of other fungi. The class contains five orders as well as two families and one genus (Queiroziella) of uncertain disposition. An additional order, Cyphobasidiales, has been proposed to accommodate several lichenicolous species, but its separation from the Erythrobasidiales has not been demonstrated.
Basidiopycnis is a fungal genus in the family Hoehnelomycetaceae. The genus is monotypic, containing the single species Basidiopycnis hyalina. The species forms minute pycnidial basidiocarps in bark beetle tunnels. Teleomorphs produce auricularioid basidia, whilst anamorphs produce asexual conidia. Basidiopycnis hyalina was described from Germany and is also known from Italy and Switzerland. Anamorphic fruit bodies collected in Canada were given the name Basidiopycnides albertensis, but are currently considered conspecific with the European species.
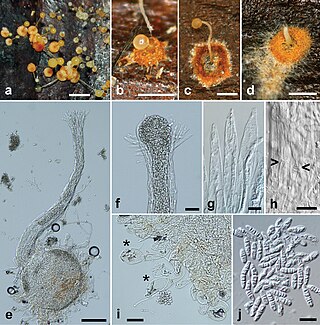
The Heterogastridiales are an order of fungi in the class Microbotryomycetes. The order contains a single family, the Heterogastridiaceae, which currently contains five genera. Some species in the order are currently known only from their yeast states. Those producing hyphal states have auricularioid basidia and are parasitic on other fungi. Basidiocarps, when present, are minute and variously stilboid (pin-shaped), pustular, or pycnidioid (flask-shaped). Molecular research, based on cladistic analysis of DNA sequences, has shown that the order is a monophyletic (natural) group, though the type and only species of Krieglsteinera has not yet been sequenced and may belong elsewhere.

Robert Joseph Bandoni was a mycologist who specialized on the taxonomy and morphology of the heterobasidiomycetes.
The Agaricostilbales are an order of fungi in the class Agaricostilbomycetes. The order consists of six families and 15 genera.
Briancoppinsia is a fungal genus in the family Arthoniaceae. It is monotypic, containing the single species Briancoppinsia cytospora, a lichenicolous fungus that parasitises parmelioid lichens, as well as Cladonia, Lepra, and Lecanora conizaeoides, among others. The species was first described scientifically by Léon Vouaux in 1914 as Phyllosticta cytospora. The genus was circumscribed in 2012 by Paul Diederich, Damien Ertz, James Lawrey, and Pieter van den Boom. The genus was named for Brian John Coppins, who is, according to the authors, an "eminent British lichenologist and expert of lichenicolous fungi".

Colacogloea is a genus of fungi belonging to the class Microbotryomycetes. Most species in the genus are known only from their yeast states. Where known, basidiocarps have auricularioid basidia and occur as parasites on or in the fruit bodies of other fungi.
Stilbum is a genus of fungi in the family Chionosphaeraceae. Though many species were formerly referred to the genus, it is effectively monotypic since the type species, Stilbum vulgare, currently has no close relative. Stilbum vulgare forms groups of minute, gelatinous, synnema-like basidiocarps up to 0.5 mm tall with a distinct stem and inflated, fertile head. Microscopically, it produces auricularioid basidia and basidiospores that germinate by budding off yeast cells. The species has been collected on rotting wood and old agaric fruit bodies and may be a parasite of other fungi. It was originally described from Europe, but is also known from Asia, North America, and Australia.
Crittendenia is a genus of lichenicolous (lichen-dwelling) fungi in the monogeneric family Crittendeniaceae. The genus was circumscribed in 2021 to contain two species, C. lichenicola, and the type, C. coppinsii; these species were previously classified in the genus Chionosphaera. An additional 16 species were added to the genus the following year. The genus name honours British lichenologist Peter Crittenden.
The Melaniellaceae are a family of fungi in the division Basidiomycota and order of Doassansiales. The family contains 1 genera and 2 species. They have a distribution in south and south-east Asia.

Reichlingia is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Arthoniaceae. It has seven species. The genus was originally circumscribed by Paul Diederich and Christoph Scheidegger in 1996, with Reichlingia leopoldii as the type, and at that time, only species. The fungus was at first thought to be a lichenicolous (lichen-dwelling) fungus, but is now considered a lichenised hyphomycete.
The Pachnocybe are a genus of fungi, within the monotypic family of PachnocybaceaeOberw. & R.Bauer, 1989, and within the monotypic order of Pachnocybales, within the class Pucciniomycetes. They are parasitic on plants or saprobic on rotten wood.

The Eocronartiaceae are a family of fungi in the class Pucciniomycetes. Species in the family have auricularioid basidia and are typically plant parasites on ferns and mosses.
Platygloea is a genus of fungi belonging to the class Pucciniomycetes. Basidiocarps of the type species are disc-shaped, gelatinous, and occur on dead wood, probably as a saprotroph. Microscopically, all species of Platygloea sensu lato have auricularioid basidia. Currently the genus contains a heterogeneous mix of auricularioid fungi not yet accommodated in other genera.
Tremella coffeicolor is a species of fungus in the family Tremellaceae. It produces brown, lobed to foliaceous, gelatinous basidiocarps and is parasitic on other fungi on dead branches of broad-leaved trees. It was originally described from Bermuda, where it was collected as part of the Challenger expedition.

Syzygospora is a genus of fungi in the family Filobasidiaceae. Circumscribed by the American mycologist George Willard Martin in 1937, the genus is characterized by its gelatinous fruiting bodies that often form galls on host organisms. Syzygospora species possess distinctive features such as thin-walled hyphae with clamp connections, haustorial branches, and a hymenium containing probasidia that develop into elongated, club-shaped basidia. The genus has undergone taxonomic revisions, including the synonymization of Christiansenia and the transfer of some lichenicolous (lichen-dwelling) species to the newly established genus Zyzygomyces. As of 2024, the genus comprises 13 accepted species.








