
The Gnaphalieae are a tribe of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae. It is most closely related to the tribes Anthemideae, Astereae, and Calenduleae.

Commersonia is a genus of twenty-five species of flowering plants in the family Malvaceae. Plants in this genus are shrubs or trees, occurring from Indochina to Australia and have stems, leaves and flowers covered with star-like hairs. The leaves are simple, often with irregularly-toothed edges, the flowers bisexual with five sepals, five petals and five stamens and the fruit a capsule with five valves. The genus underwent a revision in 2011 and some species were separated from Commersonia, others were added from Rulingia.

Ozothamnus is a genus of plants found in Australia, New Zealand and New Caledonia.

Banksia cynaroides is a species of shrub that is endemic to Western Australia. It has crowded, linear, pinnatifid leaves, white and dull golden yellow flowers and few follicles in each head.

Keraudrenia is a genus of flowering plants native to Australia, New Guinea and Madagascar.

Comesperma is a genus of shrubs, herbs and lianas in the family Polygalaceae. The genus is endemic to Australia. It was defined by the French botanist Jacques Labillardière in his 1806 work Novae Hollandiae Plantarum Specimen. The genus name is derived from the Ancient Greek words come ("hair") and sperma ("seed"), and relates to the seeds bearing tufts of hair. The genus is distributed over southern Australia, particularly in the southwest of Western Australia, where 19 species are found. 24 species have been described.
Chthonocephalus tomentellus is an annual herb in the family Asteraceae. It is endemic to Western Australia, occurring in saline depressions. Yellow flowers are produced between August and November in its native range. The species was first formally described as Lachnothalamus tomentellus by botanist Ferdinand von Mueller in 1863 in Fragmenta Phytographiae Australiae from a type specimen collected near the mouth of the Murchison River.

Platytheca is a genus of small shrubs in the family Elaeocarpaceae from the south-west of Western Australia. The genus was formally described by Joachim Steetz, his description published in Plantae Preissianae in 1845.
Hyalosperma is a genus of Australian flowering plants in the family Asteraceae.

Calotis is a genus of herbs or small shrubs in the daisy family Asteraceae. Most of the species are native to Australia, while two occur in Asia.

Podotheca is a genus of flowering plants in the pussy's-toes tribe (Gnaphalieae) within the Asteraceae. All species are endemic to Western Australia, except for Podotheca angustifolia which occurs across the south of Australia.

Rulingia is a genus of flowering plants native to Australia and Madagascar. In 2011, all species were transferred to Commersonia with the exception of Rulingia cuneata, R. loxophylla, R.luteiflora and R. procumbens which have been transferred to the new genus Androcalva.
Millotia is a genus of small annual herbs in the pussy's-toes tribe within the sunflower family.

Angianthus is a genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae, which was first described by Wendland in 1810. The type species is Angianthus tomentosus.

Asteridea is a genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae. Evidence suggests that the genus, Asteridea, is monophyletic.

Waitzia acuminata, commonly known as orange immortelle, is an annual herb in the family Asteraceae. It is native to Australia. Plants grow to between 0.1 and 0.6 metres in height and have leaves that are long and narrow. These are between 2 and 10 cm long and 2 to 5 mm in width. The yellow, orange or white flowers appear between July and January.
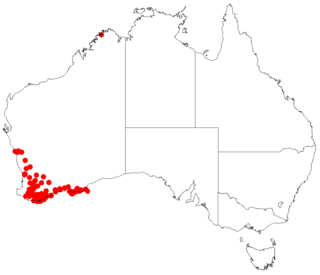
Asteridea nivea is a herb in the Asteraceae family, which is endemic to Western Australia. It was first described in 1845 by Joachim Steetz as Chrysodiscus niveus. In 1980, G. Kroner assigned it to the genus, Asteridea, giving it the name Asteridea nivea. It is a perennial herb, sometimes erect, sometimes low-spreading which grows on sandy soils often over granite, laterite, or limestone to heights from 10 cm to 60 cm, in rock crevices, on ridges and coastal cliffs. Its white to white-pink flowers may seen from April to May or August to September in Beard's South-West Province, that is, the IBRA regions of Avon Wheatbelt, Esperance Plains, Geraldton Sandplains, Jarrah Forest, Mallee, and Warren.

Argentipallium niveum is a species of flowering plant within the genus, Argentipallium, in the daisy family (Asteraceae). It is endemic to Western Australia.

Pterochaeta is a monotypic plant genus in the Asteraceae family, endemic to Western Australia. It was first described in 1845 by Joachim Steetz and its only species is Pterochaeta paniculata.

Olearia paucidentata is a plant in the Asteraceae family. It was first described as Eurybia paucidentata in 1845 by Joachim Steetz. In 1867, George Bentham assigned it to the genus Olearia in his Flora Australiensis.
















