
The scapula, also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus with the clavicle. Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the other. The name derives from the Classical Latin word for trowel or small shovel, which it was thought to resemble.

The deltoid muscle is the muscle forming the rounded contour of the human shoulder. It is also known as the 'common shoulder muscle', particularly in other animals such as the domestic cat. Anatomically, the deltoid muscle appears to be made up of three distinct sets of muscle fibers, namely the
- anterior or clavicular part
- posterior or scapular part
- intermediate or acromial part

The levator scapulae is a slender skeletal muscle situated at the back and side of the neck. It originates from the transverse processes of the four uppermost cervical vertebrae; it inserts onto the upper portion of the medial border of the scapula. It is innervated by the cervical nerves C3-C4, and frequently also by the dorsal scapular nerve. As the Latin name suggests, its main function is to lift the scapula.

In human anatomy, the rhomboid minor is a small skeletal muscle of the back that connects the scapula to the vertebrae of the spinal column. It arises from the nuchal ligament, and the 7th cervical and 1st thoracic vertebrae and intervening supraspinous ligaments; it inserts onto the medial border of the scapula. It is innervated by the dorsal scapular nerve.

The teres minor is a narrow, elongated muscle of the rotator cuff. The muscle originates from the lateral border and adjacent posterior surface of the corresponding right or left scapula and inserts at both the greater tubercle of the humerus and the posterior surface of the joint capsule.
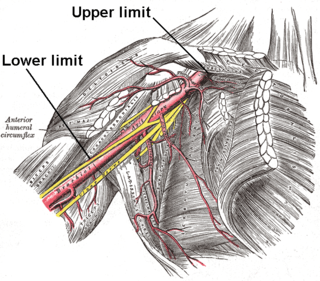
In human anatomy, the axillary artery is a large blood vessel that conveys oxygenated blood to the lateral aspect of the thorax, the axilla (armpit) and the upper limb. Its origin is at the lateral margin of the first rib, before which it is called the subclavian artery.

The shoulder joint is structurally classified as a synovial ball-and-socket joint and functionally as a diarthrosis and multiaxial joint. It involves an articulation between the glenoid fossa of the scapula and the head of the humerus. Due to the very loose joint capsule that gives a limited interface of the humerus and scapula, it is the most mobile joint of the human body.

The teres major muscle is a muscle of the upper limb. It attaches to the scapula and the humerus and is one of the seven scapulohumeral muscles. It is a thick but somewhat flattened muscle.

The subscapular artery, the largest branch of the axillary artery, arises from the third part of the axillary artery at the lower border of the subscapularis muscle, which it follows to the inferior angle of the scapula, where it anastomoses with the lateral thoracic and intercostal arteries, and with the descending branch of the dorsal scapular artery, and ends in the neighboring muscles.

The left colic artery is a branch of the inferior mesenteric artery distributed to the descending colon, and left part of the transverse colon. It ends by dividing into an ascending branch and a descending branch; the terminal branches of the two branches go on to form anastomoses with the middle colic artery, and a sigmoid artery (respectively).

The transverse cervical artery is an artery in the neck and a branch of the thyrocervical trunk, running at a higher level than the suprascapular artery.

The suprascapular artery is a branch of the thyrocervical trunk on the neck.

The supraspinous fossa of the posterior aspect of the scapula is smaller than the infraspinous fossa, concave, smooth, and broader at its vertebral than at its humeral end. Its medial two-thirds give origin to the Supraspinatus.

The scapular anastomosis is a system connecting certain subclavian artery and their corresponding axillary artery, forming a circulatory anastomosis around the scapula. It allows blood to flow past the joint in case of occlusion, damage, or pinching of the following scapular arteries:
In anatomy, arterial tree is used to refer to all arteries and/or the branching pattern of the arteries. This article regards the human arterial tree. Starting from the aorta:

The thoracodorsal artery is a branch of the subscapular artery. It travels inferiorly with the thoracodorsal nerve and supplies the latissimus dorsi.
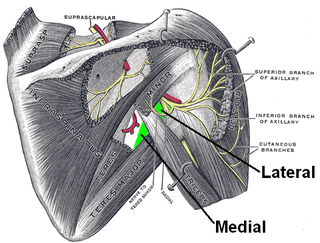
The quadrangular space, also known as the quadrilateral space (of Velpeau) and the foramen humerotricipitale, is one of the three spaces in the axillary space. The other two spaces are: triangular space and triangular interval.

The triangular space is one of the three spaces found at the axillary space. The other two spaces are the quadrangular space and the triangular interval.

The axillary spaces are anatomic spaces. through which axillary contents leave the axilla. They consist of the quadrangular space, triangular space, and triangular interval. It is bounded by teres major, teres minor, medial border of the humerus, and long head of triceps brachii.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:


















