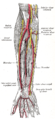
The brachioradialis is a muscle of the forearm that flexes the forearm at the elbow. It is also capable of both pronation and supination, depending on the position of the forearm. It is attached to the distal styloid process of the radius by way of the brachioradialis tendon, and to the lateral supracondylar ridge of the humerus.

The radial nerve is a nerve in the human body that supplies the posterior portion of the upper limb. It innervates the medial and lateral heads of the triceps brachii muscle of the arm, as well as all 12 muscles in the posterior osteofascial compartment of the forearm and the associated joints and overlying skin.

The median nerve is a nerve in humans and other animals in the upper limb. It is one of the five main nerves originating from the brachial plexus.
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is most often used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in anatomy, technically, means only the region of the upper arm, whereas the lower "arm" is called the forearm. It is homologous to the region of the leg that lies between the knee and the ankle joints, the crus.

In human anatomy, the radial artery is the main artery of the lateral aspect of the forearm.

The inferior ulnar collateral artery is a artery in the arm. It arises about 5 cm. above the elbow from the brachial artery.

The superior ulnar collateral artery, of small size, arises from the brachial artery a little below the middle of the arm; it frequently springs from the upper part of the a. profunda brachii.

The deep artery of arm is a large vessel which arises from the lateral and posterior part of the brachial artery, just below the lower border of the teres major.

The princeps pollicis artery, or principal artery of the thumb, arises from the radial artery just as it turns medially towards the deep part of the hand; it descends between the first dorsal interosseous muscle and the oblique head of the adductor pollicis, along the medial side of the first metacarpal bone to the base of the proximal phalanx, where it lies beneath the tendon of the flexor pollicis longus muscle and divides into two branches.

The dorsal carpal arch is an anatomical term for the combination (anastomosis) of dorsal carpal branch of the radial artery and the dorsal carpal branch of the ulnar artery near the back of the wrist.

The posterior ulnar recurrent artery is an artery in the forearm. It is one of two recurrent arteries that arises from the ulnar artery, the other being the anterior ulnar recurrent artery. The posterior ulnar recurrent artery being much larger than the anterior and also arises somewhat lower than it.

The anterior ulnar recurrent artery is an artery in the forearm. It is one of two recurrent arteries that arises from the ulnar artery, the other being the posterior ulnar recurrent artery.
In anatomy, arterial tree is used to refer to all arteries and/or the branching pattern of the arteries. This article regards the human arterial tree. Starting from the aorta:

The anterior interosseous nerve is a branch of the median nerve that supplies the deep muscles on the anterior of the forearm, except the ulnar (medial) half of the flexor digitorum profundus.
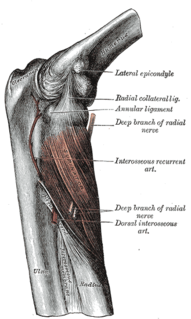
The interosseous membrane of the forearm is a fibrous sheet that connects the interosseous margins of the radius and the ulna. It is the main part of the radio-ulnar syndesmosis, a fibrous joint between the two bones.

The fascial compartments of arm refers to the specific anatomical term of the compartments within the upper segment of the upper limb(the arm) of the body. The upper limb is divided into two segments, the arm and the forearm. Each of these segments is further divided into two compartments which are formed by deep fascia – tough connective tissue septa (walls). Each compartment encloses specific muscles and nerves.
Recurrent artery may refer to
The public domain consists of all the creative works to which no exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly waived, or may be inapplicable.

Gray's Anatomy is an English language textbook of human anatomy originally written by Henry Gray and illustrated by Henry Vandyke Carter. Earlier editions were called Anatomy: Descriptive and Surgical, Anatomy of the Human Body and Gray's Anatomy: Descriptive and Applied, but the book's name is commonly shortened to, and later editions are titled, Gray's Anatomy. The book is widely regarded as an extremely influential work on the subject, and has continued to be revised and republished from its initial publication in 1858 to the present day. The latest edition of the book, the 41st, was published in September 2015.