Pectoralis minor muscle is a thin, triangular muscle, situated at the upper part of the chest, beneath the pectoralis major in the human body. It arises from ribs III-V; it inserts onto the coracoid process of the scapula. It is innervated by the medial pectoral nerve. Its function is to stabilise the scapula by holding it fast in position against the chest wall.

The internal pudendal artery is one of the three pudendal arteries. It branches off the internal iliac artery, and provides blood to the external genitalia.
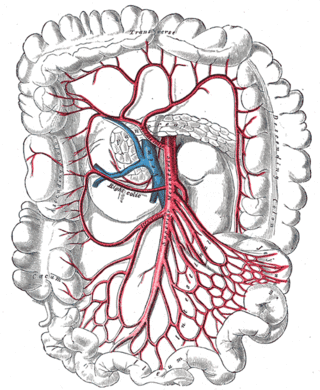
In human anatomy, the superior mesenteric artery (SMA) is an artery which arises from the anterior surface of the abdominal aorta, just inferior to the origin of the celiac trunk, and supplies blood to the intestine from the lower part of the duodenum through two-thirds of the transverse colon, as well as the pancreas.
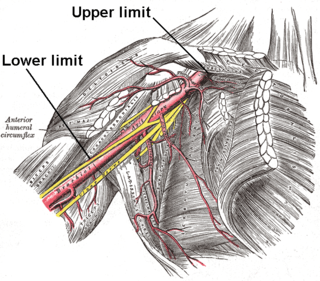
In human anatomy, the axillary artery is a large blood vessel that conveys oxygenated blood to the lateral aspect of the thorax, the axilla (armpit) and the upper limb. Its origin is at the lateral margin of the first rib, before which it is called the subclavian artery.

In anatomy, the gastroduodenal artery is a small blood vessel in the abdomen. It supplies blood directly to the pylorus and proximal part of the duodenum. It also indirectly supplies the pancreatic head.

In human anatomy, the left gastric artery arises from the celiac artery and runs along the superior portion of the lesser curvature of the stomach before anastomosing with the right gastric artery. It also issues esophageal branches that supply lower esophagus and ascend through the esophageal hiatus to form anastomoses with the esophageal branches of thoracic part of aorta.

The thoracoacromial artery is a short trunk that arises from the second part of the axillary artery, its origin being generally overlapped by the upper edge of the pectoralis minor.

The thoracodorsal nerve is a nerve present in humans and other animals, also known as the middle subscapular nerve or the long subscapular nerve. It supplies the latissimus dorsi muscle.

The inferior rectal artery is an artery that supplies blood to the lower third of the anal canal below the pectinate line.
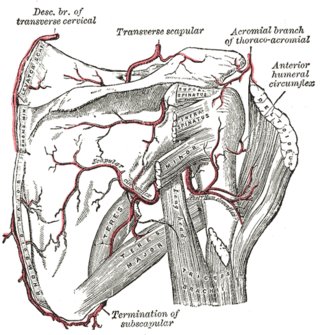
The circumflex scapular artery is a branch of the subscapular artery and part of the scapular anastomoses.

The left gastroepiploic artery, the largest branch of the splenic artery, runs from left to right about a finger's breadth or more from the greater curvature of the stomach, between the layers of the greater omentum, and anastomoses with the right gastroepiploic.

The left colic artery is a branch of the inferior mesenteric artery distributed to the descending colon, and left part of the transverse colon. It ends by dividing into an ascending branch and a descending branch; the terminal branches of the two branches go on to form anastomoses with the middle colic artery, and a sigmoid artery (respectively).

The ileocolic artery is the lowest branch arising from the concavity of the superior mesenteric artery. It supplies the cecum, ileum, and appendix.
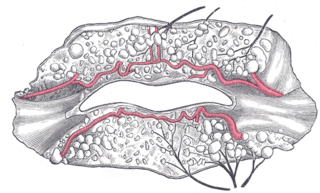
The superior labial artery is larger and more egregious than the inferior labial artery.
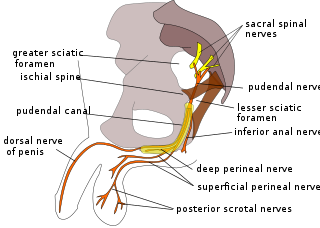
The perineal nerve is a nerve of the pelvis. It arises from the pudendal nerve in the pudendal canal. It gives superficial branches to the skin, and a deep branch to muscles. It supplies the skin and muscles of the perineum. Its latency is tested with electrodes.

The circumflex branch of left coronary artery is a branch of the left coronary artery. It winds around the left side of the heart along the atrioventricular groove. It supplies the posterolateral portion of the left ventricle.

The clavipectoral fascia is a strong fascia situated under cover of the clavicular portion of the pectoralis major.

The dorsal artery of the penis is a bilaterally paired terminal branch of the internal pudendal artery which passes upon the dorsum of the penis to the base of the glans penis, where it unites with its contralateral partner and supply the glans and foreskin.

The intercostal arteries are a group of arteries passing within an intercostal space. There are 9 anterior and 11 posterior intercostal arteries on each side of the body. The anterior intercostal arteries are branches of the internal thoracic artery and its terminal branch – the musculophrenic artery. The posterior intercostal arteries are branches of the supreme intercostal artery and thoracic aorta.

The inferior cervical ganglion is one of the three cervical sympathetic ganglia. It is situated between the base of the transverse process of the last cervical vertebra and the neck of the first rib, on the medial side of the costocervical artery.