The brachioradialis is a muscle of the forearm that flexes the forearm at the elbow. It is also capable of both pronation and supination, depending on the position of the forearm. It is attached to the distal styloid process of the radius by way of the brachioradialis tendon, and to the lateral supracondylar ridge of the humerus.

The thenar eminence is the mound formed at the base of the thumb on the palm of the hand by the intrinsic group of muscles of the thumb. The skin overlying this region is the area stimulated when trying to elicit a palmomental reflex. The word thenar comes from Ancient Greek θέναρ (thenar) 'palm of the hand'.

The external carotid artery is a major artery of the head and neck. It arises from the common carotid artery when it splits into the external and internal carotid artery. The external carotid artery supplies blood to the face, brain and neck.

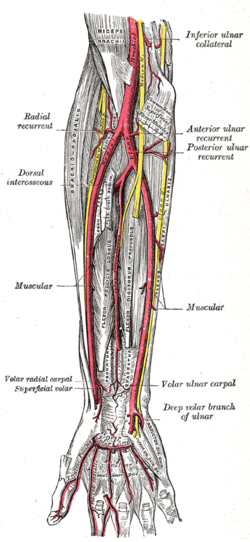
The ulnar artery is the main blood vessel, with oxygenated blood, of the medial aspects of the forearm. It arises from the brachial artery and terminates in the superficial palmar arch, which joins with the superficial branch of the radial artery. It is palpable on the anterior and medial aspect of the wrist.

The posterior interosseous artery is an artery of the forearm. It is a branch of the common interosseous artery, which is a branch of the ulnar artery.

The radial recurrent artery arises from the radial artery immediately below the elbow.

The common interosseous artery, about 1 cm. in length, arises immediately below the tuberosity of the radius from the ulnar artery.

The inferior thyroid artery is an artery in the neck. It arises from the thyrocervical trunk and passes upward, in front of the vertebral artery and longus colli muscle. It then turns medially behind the carotid sheath and its contents, and also behind the sympathetic trunk, the middle cervical ganglion resting upon the vessel.

The anterior interosseous artery is an artery in the forearm. It is a branch of the common interosseous artery.

The inferior ulnar collateral artery is an artery in the arm. It arises about 5 cm. above the elbow from the brachial artery.

The superior ulnar collateral artery, of small size, arises from the brachial artery a little below the middle of the arm; it frequently springs from the upper part of the a. profunda brachii.

The deep artery of arm is a large artery of the arm which arises from the brachial artery. It descends in the arm before ending by anastomosing with the radial recurrent artery.
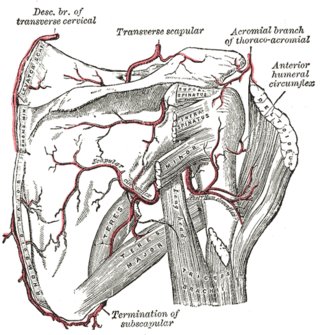
The anterior humeral circumflex artery is an artery in the arm. It is one of two circumflexing arteries that branch from the axillary artery, the other being the posterior humeral circumflex artery. The anterior humeral circumflex artery is considerably smaller than the posterior and arises nearly opposite to it, from the lateral side of the axillary artery.

The medial epicondyle of the humerus is an epicondyle of the humerus bone of the upper arm in humans. It is larger and more prominent than the lateral epicondyle and is directed slightly more posteriorly in the anatomical position. In birds, where the arm is somewhat rotated compared to other tetrapods, it is called the ventral epicondyle of the humerus. In comparative anatomy, the more neutral term entepicondyle is used.

The anterior ulnar recurrent artery is an artery in the forearm. It is one of two recurrent arteries that arises from the ulnar artery, the other being the posterior ulnar recurrent artery.

The carotid triangle is a portion of the anterior triangle of the neck.

The inferior carotid triangle, is bounded, in front, by the median line of the neck from the hyoid bone to the sternum; behind, by the anterior margin of the sternocleidomastoid; above, by the superior belly of the omohyoid.

The intercostal arteries are a group of arteries passing within an intercostal space. There are 9 anterior and 11 posterior intercostal arteries on each side of the body. The anterior intercostal arteries are branches of the internal thoracic artery and its terminal branch - the musculophrenic artery. The posterior intercostal arteries are branches of the supreme intercostal artery and thoracic aorta.

The fascial compartments of arm refers to the specific anatomical term of the compartments within the upper segment of the upper limb of the body. The upper limb is divided into two segments, the arm and the forearm. Each of these segments is further divided into two compartments which are formed by deep fascia – tough connective tissue septa (walls). Each compartment encloses specific muscles and nerves.
The coronoid process of the ulna is a triangular process projecting forward from the anterior proximal portion of the ulna.