
In human anatomy, the arm refers to the upper limb in common usage, although academically the term specifically means the upper arm between the glenohumeral joint and the elbow joint. The distal part of the upper limb between the elbow and the radiocarpal joint is known as the forearm or "lower" arm, and the extremity beyond the wrist is the hand.

The left and right brachiocephalic veins are major veins in the upper chest, formed by the union of the ipsilateral internal jugular vein and subclavian vein behind the sternoclavicular joint. The left brachiocephalic vein is more than twice the length of the right brachiocephalic vein.

The suboccipital nerve is the dorsal primary ramus of the first cervical nerve (C1). It exits the spinal cord between the skull and the first cervical vertebra, the atlas.
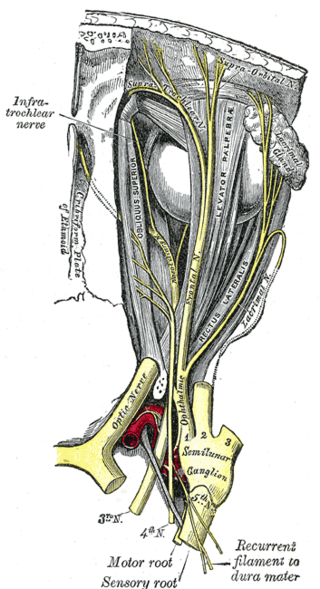
The supraorbital nerve is one of two terminal branches - the other being the supratrochlear nerve - of the frontal nerve (itself a branch of the ophthalmic nerve (CN V1)). It exits the orbit via the supraorbital foramen/notch before splitting into a medial branch and a lateral branch. It innervates the skin of the forehead, upper eyelid, and the root of the nose.

The deltoid muscle is the muscle forming the rounded contour of the human shoulder. It is also known as the 'common shoulder muscle', particularly in other animals such as the domestic cat. Anatomically, the deltoid muscle is made up of three distinct sets of muscle fibers, namely the
- anterior or clavicular part
- posterior or scapular part
- intermediate or acromial part

The musculocutaneous nerve is a mixed branch of the lateral cord of the brachial plexus derived from cervical spinal nerves C5-C7. It arises opposite the lower border of the pectoralis minor. It provides motor innervation to the muscles of the anterior compartment of the arm: the coracobrachialis, biceps brachii, and brachialis. It provides sensory innervation to the lateral forearm. It courses through the anterior part of the arm, terminating 2 cm above elbow; after passing the lateral edge of the tendon of biceps brachii it is becomes known as the lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm.
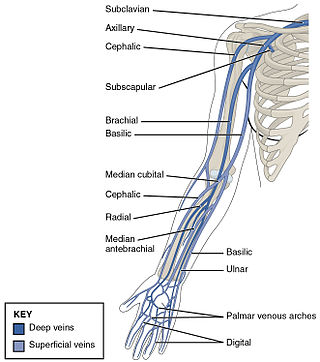
In human anatomy, the cephalic vein is a superficial vein in the arm. It is the longest vein of the upper limb. It starts at the anatomical snuffbox from the radial end of the dorsal venous network of hand, and ascends along the radial (lateral) side of the arm before emptying into the axillary vein. At the elbow, it communicates with the basilic vein via the median cubital vein.

The rhomboid muscles, often simply called the rhomboids, are rhombus-shaped muscles associated with the scapula. There are two rhomboid muscles on each side of the upper back:

The intercostal nerves are part of the somatic nervous system, and arise from the anterior rami of the thoracic spinal nerves from T1 to T11. The intercostal nerves are distributed chiefly to the thoracic pleura and abdominal peritoneum, and differ from the anterior rami of the other spinal nerves in that each pursues an independent course without plexus formation.

The medial pectoral nerve is (typically) a branch of the medial cord of the brachial plexus and is derived from spinal nerve roots C8-T1. It provides motor innervation to the pectoralis minor muscle, and the lower half of the pectoralis major muscle. It runs along the inferior border of the pectoralis minor muscle.

The subscapular artery, the largest branch of the axillary artery, arises from the third part of the axillary artery at the lower border of the subscapularis muscle, which it follows to the inferior angle of the scapula, where it anastomoses with the lateral thoracic and intercostal arteries, and with the descending branch of the dorsal scapular artery, and ends in the neighboring muscles.

The thyrocervical trunks are very small arteries of the neck arising from the subclavian arteries, lateral to the vertebral arteries. They divide into branches: the inferior thyroid artery, suprascapular artery, and the transverse cervical artery.

The anterior ethmoidal artery is a branch of the ophthalmic artery in the orbit. It exits the orbit through the anterior ethmoidal foramen alongside the anterior ethmoidal nerve. It contributes blood supply to the ethmoid sinuses, frontal sinuses, the dura mater, lateral nasal wall, and nasal septum. It issues a meningeal branch, and nasal branches.
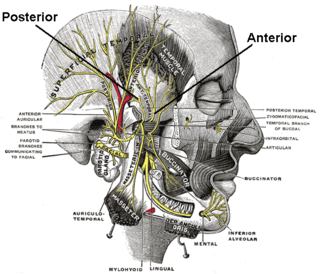
The deep temporal nerves are typically two nerves (one anterior and one posterior) which arise from the mandibular nerve (CN V3) and provide motor innervation to the temporalis muscle.

The lateral condyle is the lateral portion of the upper extremity of tibia.
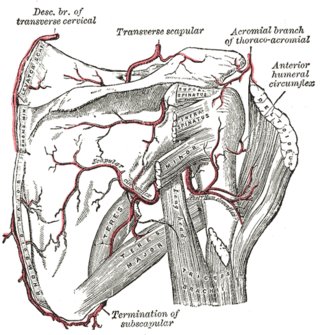
The anterior humeral circumflex artery is an artery in the arm. It is one of two circumflexing arteries that branch from the axillary artery, the other being the posterior humeral circumflex artery. The anterior humeral circumflex artery is considerably smaller than the posterior and arises nearly opposite to it, from the lateral side of the axillary artery.

The superior thoracic artery is a small artery located near the armpit. It usually originates from the axillary artery, but can instead originate from the thoracoacromial artery. It supplies the pectoralis minor and major muscles, and the chest wall.

The dorsal nasal artery is an artery of the face. It is one of the two terminal branches of the ophthalmic artery. It contributes arterial supply to the lacrimal sac, and outer surface of the nose.

The internal iliac vein begins near the upper part of the greater sciatic foramen, passes upward behind and slightly medial to the internal iliac artery and, at the brim of the pelvis, joins with the external iliac vein to form the common iliac vein.

The supratrochlear artery is one of the terminal branches of the ophthalmic artery. It arises within the orbit. It exits the orbit alongside the supratrochlear nerve. It contributes arterial supply to the skin, muscles and pericranium of the forehead.


















