
Pseudanthus is a genus of plants under the family Picrodendraceae. The genus is endemic to Australia described as a genus in 1827.

Robert Wight MD FRS FLS was a Scottish surgeon in the East India Company, whose professional career was spent entirely in southern India, where his greatest achievements were in botany – as an economic botanist and leading taxonomist in south India. He contributed to the introduction of American cotton. As a taxonomist he described 110 new genera and 1267 new species of flowering plants. He employed Indian botanical artists to illustrate many plants collected by himself and Indian collectors he trained. Some of these illustrations were published by William Hooker in Britain, but from 1838 he published a series of illustrated works in Madras including the uncoloured, six-volume Icones Plantarum Indiae Orientalis (1838–53) and two hand-coloured, two-volume works, the Illustrations of Indian Botany (1838–50) and Spicilegium Neilgherrense (1845–51). By the time he retired from India in 1853 he had published 2464 illustrations of Indian plants. The standard author abbreviation Wight is used to indicate this person as the author when citing a botanical name.

Dillenia is a genus of flowering evergreen or semi-evergreen trees and shrubs in the family Dilleniaceae, native to tropical and subtropical regions of southern Asia, Australasia, and the Indian Ocean islands.

Actinodaphne is an Asian genus of flowering plants in the laurel family (Lauraceae). It contains approximately 125 species of dioecious evergreen trees and shrubs.
Dischidia is a genus of plants in the “dog-bane” family Apocynaceae, collectively known as the “milkweeds”. They are epiphytes, native to tropical areas of China, India as well as Bhutan’s southern borders, wherever minimal frost occurs. Additionally, they are known from most areas of Indo-China, including forested areas of Myanmar, Thailand, Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos, and some parts of Malaysia and Singapore.

Anodendron is a genus of plant in the family Apocynaceae first described as a genus in 1844. It is native to most of tropical Asia: China, the Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia, New Guinea, and some islands of the western Pacific.
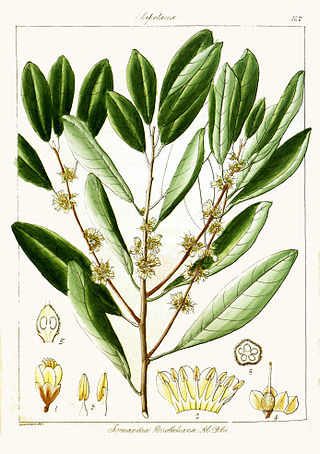
Isonandra is a genus of plants in the family Sapotaceae found in tropical Asia, described as a genus in 1840.

Lasianthus is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. They are tropical subshrubs, shrubs, or rarely, small trees. They inhabit the understory of primary forests.

Madhuca is a genus of plants in the family Sapotaceae first described as a genus in 1791.

Willughbeia is a genus of plant in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1820. It is native to Southeast Asia with a few species in the Indian Subcontinent. Several species have edible fruits enjoyed in many countries. Many species are vines with sticky latex.

Parsonsia is a genus of woody vines in the family Apocynaceae. Species occur throughout Indomalaya, Australasia and Melanesia.

Salacia is a genus of plants in the family Celastraceae. They are woody climbers naturally found in tropical regions.

Ampelocissus is a genus of Vitaceae having 90 or more species found variously in tropical Africa, Asia, Central America, and Oceania. The type species, A. latifolia, was originally treated under its basionym, Vitis latifolia, and was collected from the Indian subcontinent.
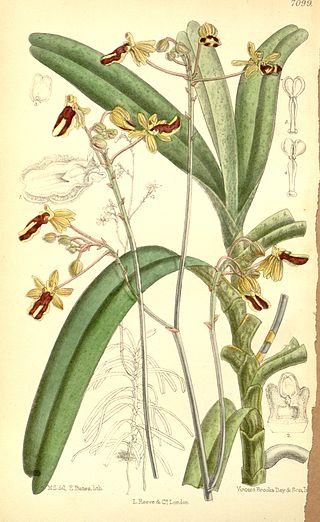
Cottonia is a monotypic genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae: the only known species is Cottonia peduncularis. It is native to India and Sri Lanka. The genus was erected by Robert Wight and named after Major Frederick Cotton, an amateur botanist who served in the Madras Engineer Group and collected the species from Tellichery. A coloured illustration of the plant had been sent to Wight by Thomas C. Jerdon.

Mussaenda is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. They are native to the African and Asian tropics and subtropics. Several species are cultivated as ornamental plants.
Sida mysorensis, common name in India Mysore fanpetals, is a plant species native to South and Southeast Asia. It has been reported from the wild in Indonesia, Vietnam, Laos, Cambodia, Thailand, India, Pakistan and southern China, and is cultivated elsewhere. It grows in grassy slopes, on roadsides, and in forest boundaries.
Sindechites is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1888. It is native to southern China, Laos, and Thailand.

Atalantia is a genus of flowering plants in the citrus family, the Rutaceae.

Dorstenia indica is a small plant species in the family Moraceae native to Southern India and Sri Lanka. It was first described by Robert Wight in 1853.

Hippocratea is a genus of flowering plants in the family Celastraceae, usually lianas, native to tropical and subtropical North America, South America and Africa.
















