
Clingfishes are fishes of the family Gobiesocidae, the only family in the order Gobiesociformes. These fairly small to very small fishes are widespread in tropical and temperate regions, mostly near the coast, but a few species live in deeper seas or fresh water. Most species shelter in shallow reefs or seagrass beds, clinging to rocks, algae and seagrass leaves with their sucking disc, a structure on their chest.

Kuiter's deepsea clingfish is a clingfish of the family Gobiesocidae, found only off southern Australia, at depths of between 90 and 110 metres.
Rudie Hermann Kuiter is an Australian underwater photographer, taxonomist, marine biologist and author of many identification guides to sea fishes. He has described new species of seahorses in the genus Hippocampus.

The King George whiting, also known as the spotted whiting or spotted sillago, is a coastal marine fish of the smelt-whitings family Sillaginidae. The King George whiting is endemic to Australia, inhabiting the south coast of the country from Jurien Bay, Western Australia to Botany Bay, New South Wales in the east. The King George whiting is the only member of the genus Sillaginodes and the largest member of the smelt-whiting family Sillaginidae, growing to a length of 80 cm and 4.8 kg in weight. The species is readily distinguishable from other Australian whitings by its unique pattern of spots, as well as its highly elongate shape. King George whiting are often found in bays and protected waterways over sand and seagrass beds, also venturing out onto deep continental shelf reefs during adulthood. The species is a benthic carnivore, consuming a variety of crustaceans, polychaete worms, molluscs and fish. The King George whiting forms the basis of one of southern Australia's most important commercial fisheries, reportedly worth over five million Australian dollars per year. The species is also heavily targeted by recreational anglers, who value the whiting for its sporting and eating qualities.

The southern school whiting ,also known as the silver whiting or trawl whiting, is a common species of coastal marine fish of the smelt-whiting family that inhabits the south and south-west coasts of Australia. Its distribution overlaps a number of other common sillaginids, with careful observation of anatomical features occasionally needed to distinguish between species. The southern school whiting is closely related to the eastern school whiting, Sillago flindersi, and initially were thought to be all one species. The species inhabits both shallow inshore sandy waters, as well as deeper offshore waters, with a transition of habitats occurring with increasing age. It is a predatory fish, taking a variety of crustaceans, polychaetes and bivalves as prey. It reaches sexual maturity at three years of age, and spawns multiple times between December and April. The southern school whiting is commonly caught by commercial and recreational fishermen, often while fishing for related species, especially the sought after King George whiting. The species is marketed fresh in southern Australia.

The sand whiting, also known as the summer whiting, yellowfin whiting or blue-nose whiting, is a common species of coastal marine fish of the family Sillaginidae, the smelt-whitings. It is a slender, slightly compressed fish that is very similar to other species of Sillago, with detailed spine, ray and lateral line scale counts needed to distinguish the species between its nearest relative Sillago analis. The sand whiting is distributed along the east coast of Australia from Cape York south to Tasmania, as well as Lord Howe Island and New Caledonia in the Pacific Ocean.
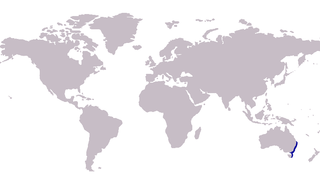
The eastern school whiting, also known as the redspot whiting, Bass Strait whiting, Flinders' sillago, silver whiting or spotted whiting, is a species of benthic marine fish of the smelt-whiting family Sillaginidae. The eastern school whiting is endemic to Australia, distributed along the east coast from southern Queensland down to Tasmania and South Australia, where it inhabits sandy substrates from shallow tidal flats to depths of 180 m on the continental shelf. Eastern school whiting prey on various crustaceans and polychaete worms, with the diet varying seasonally and throughout the range of the species. Eastern school whiting reproduce in the deeper waters twice a year, releasing up to 110,000 eggs during a season.
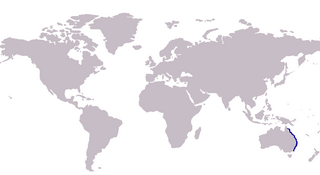
The trumpeter whiting, also known as the winter whiting or diver whiting, is a common species of coastal marine fish of the smelt-whiting family, Sillaginidae. The trumpeter whiting is endemic to Australia, inhabiting the eastern seaboard from southern New South Wales to northern Queensland. The species is found in bays, estuaries, coastal lakes and mangrove creeks on silty and muddy substrates in waters ranging from 0 to 30 m deep, occasionally inhabiting sandy and seagrass beds.

Chelmonops truncatus, the eastern talma or truncate coralfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a butterflyfish from the family Chaetodontidae. It is endemic to Australia.

Gymnothorax nudivomer, the starry moray or yellowmouth moray, is a species of marine fish in the family Muraenidae.

The whitemargin moray or the white-edged moray, Gymnothorax albimarginatus, is a species of marine fish in the family Muraenidae.

Chelmonops curiosus, truncate coralfish, truncate butterflyfish, western talma or squareback butterflyfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a butterflyfish from the family Chaetodontidae. It is endemic to Australia.

Thunnus tonggol is a species of tuna of tropical Indo-West Pacific waters.

Paraplesiops is a genus containing five largely allopatric species of fishes in the longfin, or roundhead, family Plesiopidae, commonly known as blue devils, bluedevils, or blue devilfish because of their colouration. The genus is most similar to the tropical genera Plesiops and Fraudella. It is restricted to subtropical and temperate rocky and coral reefs in Australian waters. Its species are mostly cryptic, occurring in submarine caves, crevices and under rocky ledges.

Cochleoceps is a genus of clingfishes endemic to the waters around Australia.

Kopua is a genus of clingfishes found in the Pacific Ocean.

Priacanthus hamrur, the lunar-tailed bigeye, goggle eye, or moontail bullseye, is a species of marine fishes belonging to the family Priacanthidae.

Scorpaenopsis diabolus, the false stonefish, false scorpionfish or the devil scorpionfish, is a species of venomous marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes. It has venomous spines and lives in the tropical Indian and Pacific Oceans as well as in the Red Sea. It is a bottom-dwelling predator that relies on its camouflage to catch passing prey.

Cochleoceps bicolor, the western cleaner clingfish, is a species of clingfish from the family Gobiesocidae which is endemic to southern Australia. This species has a ground colouration which varies from yellowish to reddish marked with regular transverse blue bands along its back and a bluish-grey caudal fin. This species occurs on rocky reefs and jetty or pier piles, where they establish cleaning stations, often over sponges and ascidians, but are known to use a wide variety of reef related sites as stations, perhaps the most important criterion being the prominent visibility of a site to passing parasite laden clients .A station may have from one to multiple Western Cleaner Clingfish, depending on the demand for services and other factors. Some divers have observed shared stations, where several other known temperate marine cleaner host species-notably juvenile moonlighter fish and rockpool shrimp - behave in cooperative fashion, possibly when client demand peaks, tide and season depending. They are thought to feed on parasites which they clean off larger fish. The distribution of this species extends from Lancelin, Western Australia to Port Phillip in Victoria. C. bicolor was described in 1991 by Barry Hutchins from a type locality of Flinders Island.
Thamnaconus hypargyreus, commonly known as the lesser-spotted leatherjacket, yellowspotted leatherjacket, or the yellow-fin filefish, is a fish native to the coastal waters of the South and East China Seas and northern Australian coast.


















