
The New Zealand urchin clingfish is a clingfish. It is found around New Zealand wherever sea urchins are present. Its length is between 2 and 3 cm.

Clingfishes are fishes of the family Gobiesocidae, the only family in the order Gobiesociformes. These fairly small to very small fishes are widespread in tropical and temperate regions, mostly near the coast, but a few species in deeper seas or fresh water. Most species shelter in shallow reefs or seagrass beds, clinging to rocks, algae and seagrass leaves with their sucking disc, a structure on their chest.

The Slender clingfish(Gastrocyathus gracilis) is a clingfish of the family Gobiesocidae, the only species in the genus Gastrocyathus. This species grows to a length of 4.5 centimetres (1.8 in) TL. Endemic to New Zealand, this species is apparently only found in beds of strap-fronded algae. Harpacticoid copepods comprise the main component of their diet.

Kuiter's deepsea clingfish is a clingfish of the family Gobiesocidae, found only off southern Australia, at depths of between 90 and 110 metres.

Apletodon is a genus of marine fish in the family Gobiesocidae (clingfishes). The genus was first named by John Carmon Briggs in 1955.

Arcos is a genus of clingfishes.

Aspasmogaster is a genus of clingfishes native to the Indian and Pacific Oceans.
Derilissus is a genus of clingfishes belonging to the family Gobiesocinae found in the western Atlantic Ocean. This family of fish is identified by their appearance as small fish with sucking discs which allow them to attach themselves to various surfaces. Derilissus differs from other genera due to its attached gill membranes.

Diplecogaster is a genus of fish in the family Gobiesocidae found in Black Sea, Mediterranean Sea and Atlantic Ocean.

Discotrema is a genus of clingfishes found on reefs in the Indo-Pacific where they live on crinoids. These tiny fish have distinctive pattern consisting of long white or yellow lines along their body.

Kopua is a genus of clingfishes found in the Pacific Ocean.
Pherallodiscus is a genus of clingfishes native to the central eastern Pacific Ocean along the coast of Mexico. Based on genetic studies the genus should be merged into Gobiesox.

The Posidonia clingfish is a species of clingfish native to the Australia coast. This species grows to a length of 2 centimetres (0.79 in) SL. Pale green to pale blue with fine spots forming dark reticulations on back and sides, larger blue spots often on back, and a pinkish to brown line from snout to gill cover. The posidonia clingfish is endemic to southern Australia where its range extends from Corner Inlet in Victoria west as far as Rottnest Island in Western Australia. It occurs down to a depth of 10 metres (33 ft) where it is found on macroalgae and within seagrass beds, its favoured substrate to adhere to is the leaves of the sea grass Posidonia australis. This species is the only known member of its genus and was described by John C. Briggs in 1993 with a type locality of Fiddler's Bay which is 16 kilometres south of Tamby Bay in South Australia. Briggs gave the species the specific name hutchinsi in honour of the ichthyologist Barry Hutchins of the Western Australia Museum in Perth, Western Australia.
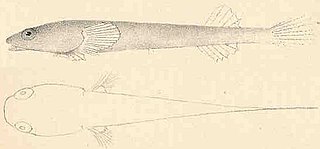
Rimicola is a genus of clingfishes found along the coasts of the eastern Pacific Ocean.

Trachelochismus is a genus of clingfishes endemic to the shores of New Zealand, with currently three recognized species:

Cochleoceps orientalis, common name eastern cleaner-clingfish, is a species of clingfish that is endemic to the marine waters around southeastern Australia.

Diplecogaster bimaculata, the two-spotted clingfish, is a species of fish in the family Gobiesocidae found in Black Sea, Mediterranean Sea and Atlantic Ocean where it is found on rocks and among seagrass or shell beds.

Cochleoceps bicolor, the western cleaner clingfish, is a species of clingfish from the family Gobiesocidae which is endemic to southern Australia. This species has a ground colouration which varies from yellowish to reddish marked with regular transverse blue bands along its back and a bluish-grey caudal fin. This species occurs on rocky reefs and jetty or pier piles, where they establish cleaning stations, often over sponges and ascidians, but are known to use a wide variety of reef related sites as stations, perhaps the most important criterion being the prominent visibility of a site to passing parasite laden clients .A station may have from one to multiple Western Cleaner Clingfish, depending on the demand for services and other factors. Some divers have observed shared stations, where several other known temperate marine cleaner host species-notably juvenile moonlighter fish and rockpool shrimp - behave in cooperative fashion, possibly when client demand peaks, tide and season depending. They are thought to feed on parasites which they clean off larger fish. The distribution of this species extends from Lancelin, Western Australia to Port Phillip in Victoria. C. bicolor was described in 1991 by Barry Hutchins from a type locality of Flinders Island.
Diplecogaster tonstricula, commonly known as the Eastern Atlantic cleaner clingfish, is a species of clingfish from the family Gobiesocidae, which is found in the tropical eastern North Atlantic Ocean. It has been observed cleaning larger species of fish.
Kopua japonica, the Japanese ceepwater clingfish, is a clingfish of the family Gobiesocidae, found in the Northwest Pacific, the East China Sea and Japan. This species reaches a length of 3.0 cm (1.2 in).













